+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of basal beta-arrestin2 | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GPCR / Arrestin / SIGNALING PROTEIN / SIGNALING PROTEIN-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtype 2A serotonin receptor binding / platelet activating factor receptor binding / postsynaptic signal transduction / negative regulation of opioid receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of opioid receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, dopaminergic / alpha-1A adrenergic receptor binding / follicle-stimulating hormone receptor binding / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / G alpha (s) signalling events ...type 2A serotonin receptor binding / platelet activating factor receptor binding / postsynaptic signal transduction / negative regulation of opioid receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of opioid receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, dopaminergic / alpha-1A adrenergic receptor binding / follicle-stimulating hormone receptor binding / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / G alpha (s) signalling events / alpha-1B adrenergic receptor binding / follicle-stimulating hormone signaling pathway / angiotensin receptor binding / protein kinase B binding / positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell differentiation / WNT5A-dependent internalization of FZD4 / MAP2K and MAPK activation / Ub-specific processing proteases / negative regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / negative regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / negative regulation of interleukin-12 production / regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of calcium ion transport / arrestin family protein binding / G protein-coupled receptor internalization / type 1 angiotensin receptor binding / positive regulation of epithelial cell apoptotic process / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / mitogen-activated protein kinase binding / response to morphine / adult walking behavior / negative regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process / negative regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria / positive regulation of receptor internalization / negative regulation of smooth muscle cell apoptotic process / detection of temperature stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain / negative regulation of interleukin-6 production / endocytic vesicle / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process / D1 dopamine receptor binding / negative regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / clathrin-coated pit / positive regulation of glial cell proliferation / 14-3-3 protein binding / negative regulation of protein ubiquitination / transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / cell chemotaxis / G protein-coupled receptor binding / regulation of protein phosphorylation / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / receptor internalization / circadian rhythm / endocytosis / positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / protein transport / positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / cytoplasmic vesicle / basolateral plasma membrane / postsynaptic membrane / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process / transcription by RNA polymerase II / molecular adaptor activity / dendritic spine / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / postsynaptic density / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / endosome / protein ubiquitination / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / protein domain specific binding / signaling receptor binding / glutamatergic synapse / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / protein-containing complex binding / positive regulation of gene expression / enzyme binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Maharana J / Sarma P / Yadav MK / Chami M / Banerjee R / Shukla AK | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  India, 4 items India, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2024 Journal: Science / Year: 2024Title: Molecular insights into atypical modes of β-arrestin interaction with seven transmembrane receptors. Authors: Jagannath Maharana / Fumiya K Sano / Parishmita Sarma / Manish K Yadav / Longhan Duan / Tomasz M Stepniewski / Madhu Chaturvedi / Ashutosh Ranjan / Vinay Singh / Sayantan Saha / Gargi ...Authors: Jagannath Maharana / Fumiya K Sano / Parishmita Sarma / Manish K Yadav / Longhan Duan / Tomasz M Stepniewski / Madhu Chaturvedi / Ashutosh Ranjan / Vinay Singh / Sayantan Saha / Gargi Mahajan / Mohamed Chami / Wataru Shihoya / Jana Selent / Ka Young Chung / Ramanuj Banerjee / Osamu Nureki / Arun K Shukla /      Abstract: β-arrestins (βarrs) are multifunctional proteins involved in signaling and regulation of seven transmembrane receptors (7TMRs), and their interaction is driven primarily by agonist-induced receptor ...β-arrestins (βarrs) are multifunctional proteins involved in signaling and regulation of seven transmembrane receptors (7TMRs), and their interaction is driven primarily by agonist-induced receptor activation and phosphorylation. Here, we present seven cryo-electron microscopy structures of βarrs either in the basal state, activated by the muscarinic receptor subtype 2 (M2R) through its third intracellular loop, or activated by the βarr-biased decoy D6 receptor (D6R). Combined with biochemical, cellular, and biophysical experiments, these structural snapshots allow the visualization of atypical engagement of βarrs with 7TMRs and also reveal a structural transition in the carboxyl terminus of βarr2 from a β strand to an α helix upon activation by D6R. Our study provides previously unanticipated molecular insights into the structural and functional diversity encoded in 7TMR-βarr complexes with direct implications for exploring novel therapeutic avenues. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_36110.map.gz emd_36110.map.gz | 59.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-36110-v30.xml emd-36110-v30.xml emd-36110.xml emd-36110.xml | 19.3 KB 19.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_36110_fsc.xml emd_36110_fsc.xml | 8.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_36110.png emd_36110.png | 49.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-36110.cif.gz emd-36110.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_36110_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36110_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36110_half_map_2.map.gz emd_36110_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.4 MB 59.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36110 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36110 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36110 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36110 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_36110_validation.pdf.gz emd_36110_validation.pdf.gz | 724.4 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_36110_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_36110_full_validation.pdf.gz | 724 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_36110_validation.xml.gz emd_36110_validation.xml.gz | 16 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_36110_validation.cif.gz emd_36110_validation.cif.gz | 20.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36110 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36110 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36110 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36110 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8j9kMC  8go9C  8j8rC  8j8vC  8j8zC  8j97C  8ja3C  8jafC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_36110.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_36110.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.2347 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
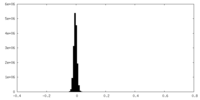
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_36110_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
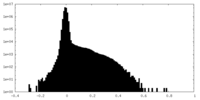
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_36110_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : beta-arrestin2 in complex with Fab6
| Entire | Name: beta-arrestin2 in complex with Fab6 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: beta-arrestin2 in complex with Fab6
| Supramolecule | Name: beta-arrestin2 in complex with Fab6 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: beta-arrestin2
| Supramolecule | Name: beta-arrestin2 / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Fab6
| Supramolecule | Name: Fab6 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Beta-arrestin-2
| Macromolecule | Name: Beta-arrestin-2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.490906 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GTRVFKKSSP NCKLTVYLGK RDFVDHLDKV DPVDGVVLVD PDYLKDRKVF VTLTCAFRYG REDLDVLGLS FRKDLFIATY QAFPPMPNP PRPPTRLQDR LLKKLGQHAH PFFFTIPQNL PCSVTLQPGP EDTGKACGVD FEIRAFCAKS IEEKSHKRNS V RLIIRKVQ ...String: GTRVFKKSSP NCKLTVYLGK RDFVDHLDKV DPVDGVVLVD PDYLKDRKVF VTLTCAFRYG REDLDVLGLS FRKDLFIATY QAFPPMPNP PRPPTRLQDR LLKKLGQHAH PFFFTIPQNL PCSVTLQPGP EDTGKACGVD FEIRAFCAKS IEEKSHKRNS V RLIIRKVQ FAPETPGPQP SAETTRHFLM SDRRSLHLEA SLDKELYYHG EPLNVNVHVT NNSAKTVKKI RVSVRQYADI CL FSTAQYK CPVAQLEQDD QVSPSSTFCK VYTITPLLSD NREKRGLALD GQLKHEDTNL ASSTIVKEGA NKEVLGILVS YRV KVKLVV SRGGDVSVEL PFVLMHPKPH DHITLPRPQS APREIDIPVD TNLIEFDTNY ATDDDIVFED FARLRLK UniProtKB: Beta-arrestin-2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Fab6 light chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab6 light chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.356607 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: DIQMTQSPSS LSASVGDRVT ITCRASQSVS SAVAWYQQKP GKAPKLLIYS ASSLYSGVPS RFSGSRSGTD FTLTISSLQP EDFATYYCQ QSKYDGLITF GQGTKVA |
-Macromolecule #3: Fab6 heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab6 heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.636962 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SEVQLVESGG GLVQPGGSLR LSCAASGFNF SSSYIHWVRQ APGKGLEWVA SISSYYGYTS YADSVKGRFT ISADTSKNTA YLQMNSLRA EDTAVYYCAR QGYYYNSYMQ GALDYWGQGT LVTVSS |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 55.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)