+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of beta-arrestin1 in complex with D6Rpp | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GPCR / Arrestin / SIGNALING PROTEIN / SYGNALING PROTEIN-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationV2 vasopressin receptor binding / alpha-1A adrenergic receptor binding / follicle-stimulating hormone receptor binding / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / sensory perception of touch / G alpha (s) signalling events / regulation of inositol trisphosphate biosynthetic process / follicle-stimulating hormone signaling pathway / protein phosphorylated amino acid binding / alpha-1B adrenergic receptor binding ...V2 vasopressin receptor binding / alpha-1A adrenergic receptor binding / follicle-stimulating hormone receptor binding / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / sensory perception of touch / G alpha (s) signalling events / regulation of inositol trisphosphate biosynthetic process / follicle-stimulating hormone signaling pathway / protein phosphorylated amino acid binding / alpha-1B adrenergic receptor binding / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / angiotensin receptor binding / AP-2 adaptor complex binding / Ub-specific processing proteases / chemokine receptor activity / MAP2K and MAPK activation / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / clathrin adaptor activity / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / negative regulation of interleukin-8 production / C-C chemokine receptor activity / regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / C-C chemokine binding / G protein-coupled receptor internalization / cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process / arrestin family protein binding / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding / Chemokine receptors bind chemokines / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / scavenger receptor activity / response to morphine / clathrin binding / stress fiber assembly / positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / pseudopodium / negative regulation of interleukin-6 production / positive regulation of receptor internalization / negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway / phototransduction / positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / clathrin-coated pit / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / negative regulation of protein ubiquitination / GTPase activator activity / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / cell chemotaxis / actin filament / phosphoprotein binding / calcium-mediated signaling / G protein-coupled receptor binding / recycling endosome / negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / endocytosis / protein transport / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / cytoplasmic vesicle / nuclear membrane / regulation of apoptotic process / basolateral plasma membrane / molecular adaptor activity / dendritic spine / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process / transmembrane transporter binding / postsynaptic membrane / transcription coactivator activity / early endosome / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / protein ubiquitination / endosome / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / postsynaptic density / intracellular signal transduction / immune response / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / inflammatory response / response to xenobiotic stimulus / signaling receptor binding / external side of plasma membrane / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of apoptotic process / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / chromatin / glutamatergic synapse / enzyme binding / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / nucleoplasm / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |    Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
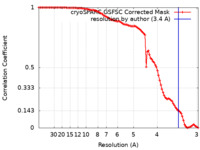
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Maharana J / Sarma P / Yadav MK / Chami M / Banerjee R / Shukla AK | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  India, 4 items India, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2024 Journal: Science / Year: 2024Title: Molecular insights into atypical modes of β-arrestin interaction with seven transmembrane receptors. Authors: Jagannath Maharana / Fumiya K Sano / Parishmita Sarma / Manish K Yadav / Longhan Duan / Tomasz M Stepniewski / Madhu Chaturvedi / Ashutosh Ranjan / Vinay Singh / Sayantan Saha / Gargi ...Authors: Jagannath Maharana / Fumiya K Sano / Parishmita Sarma / Manish K Yadav / Longhan Duan / Tomasz M Stepniewski / Madhu Chaturvedi / Ashutosh Ranjan / Vinay Singh / Sayantan Saha / Gargi Mahajan / Mohamed Chami / Wataru Shihoya / Jana Selent / Ka Young Chung / Ramanuj Banerjee / Osamu Nureki / Arun K Shukla /      Abstract: β-arrestins (βarrs) are multifunctional proteins involved in signaling and regulation of seven transmembrane receptors (7TMRs), and their interaction is driven primarily by agonist-induced receptor ...β-arrestins (βarrs) are multifunctional proteins involved in signaling and regulation of seven transmembrane receptors (7TMRs), and their interaction is driven primarily by agonist-induced receptor activation and phosphorylation. Here, we present seven cryo-electron microscopy structures of βarrs either in the basal state, activated by the muscarinic receptor subtype 2 (M2R) through its third intracellular loop, or activated by the βarr-biased decoy D6 receptor (D6R). Combined with biochemical, cellular, and biophysical experiments, these structural snapshots allow the visualization of atypical engagement of βarrs with 7TMRs and also reveal a structural transition in the carboxyl terminus of βarr2 from a β strand to an α helix upon activation by D6R. Our study provides previously unanticipated molecular insights into the structural and functional diversity encoded in 7TMR-βarr complexes with direct implications for exploring novel therapeutic avenues. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_36082.map.gz emd_36082.map.gz | 83.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-36082-v30.xml emd-36082-v30.xml emd-36082.xml emd-36082.xml | 22.7 KB 22.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_36082_fsc.xml emd_36082_fsc.xml | 9.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_36082.png emd_36082.png | 65.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-36082.cif.gz emd-36082.cif.gz | 7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_36082_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36082_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36082_half_map_2.map.gz emd_36082_half_map_2.map.gz | 84.5 MB 84.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36082 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36082 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36082 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36082 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_36082_validation.pdf.gz emd_36082_validation.pdf.gz | 780.3 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_36082_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_36082_full_validation.pdf.gz | 779.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_36082_validation.xml.gz emd_36082_validation.xml.gz | 17.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_36082_validation.cif.gz emd_36082_validation.cif.gz | 22.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36082 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36082 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36082 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36082 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 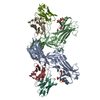 8j8zMC  8go9C  8j8rC  8j8vC  8j97C  8j9kC  8ja3C 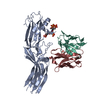 8jafC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_36082.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_36082.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.4633 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
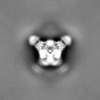
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_36082_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
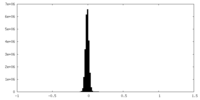
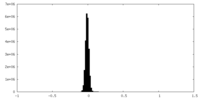
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_36082_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
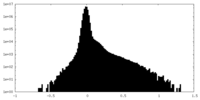
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : beta-arrestin1 in complex with D6Rpp
| Entire | Name: beta-arrestin1 in complex with D6Rpp |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: beta-arrestin1 in complex with D6Rpp
| Supramolecule | Name: beta-arrestin1 in complex with D6Rpp / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: beta-arrestin-1
| Supramolecule | Name: beta-arrestin-1 / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Fab30 Heavy Chain
| Supramolecule | Name: Fab30 Heavy Chain / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #4: Fab30 Light Chain
| Supramolecule | Name: Fab30 Light Chain / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #5: Phosphopeptide derived from the C-terminal tail of ACKR2 (D6R) re...
| Supramolecule | Name: Phosphopeptide derived from the C-terminal tail of ACKR2 (D6R) receptor type: complex / ID: 5 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Synthetically produced: Yes Homo sapiens (human) / Synthetically produced: Yes |
-Macromolecule #1: Beta-arrestin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Beta-arrestin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 47.088508 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGDKGTRVFK KASPNGKLTV YLGKRDFVDH IDLVDPVDGV VLVDPEYLKE RRVYVTLTCA FRYGREDLDV LGLTFRKDLF VANVQSFPP APEDKKPLTR LQERLIKKLG EHAYPFTFEI PPNLPCSVTL QPGPEDTGKA CGVDYEVKAF CAENLEEKIH K RNSVRLVI ...String: MGDKGTRVFK KASPNGKLTV YLGKRDFVDH IDLVDPVDGV VLVDPEYLKE RRVYVTLTCA FRYGREDLDV LGLTFRKDLF VANVQSFPP APEDKKPLTR LQERLIKKLG EHAYPFTFEI PPNLPCSVTL QPGPEDTGKA CGVDYEVKAF CAENLEEKIH K RNSVRLVI RKVQYAPERP GPQPTAETTR QFLMSDKPLH LEASLDKEIY YHGEPISVNV HVTNNTNKTV KKIKISVRQY AD ICLFNTA QYKCPVAMEE ADDTVAPSST FCKVYTLTPF LANNREKRGL ALDGKLKHED TNLASSTLLR EGANREILGI IVS YKVKVK LVVSRGGLLG DLASSDVAVE LPFTLMHPKP KEEPPHREVP ESETPVDTNL IELDTNDDDI VFEDFARQRL KGMK DDKDE EDDGTGSPHL NNR UniProtKB: Beta-arrestin-1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Fab30 Heavy Chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab30 Heavy Chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.512354 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EISEVQLVES GGGLVQPGGS LRLSCAASGF NVYSSSIHWV RQAPGKGLEW VASISSYYGY TYYADSVKGR FTISADTSKN TAYLQMNSL RAEDTAVYYC ARSRQFWYSG LDYWGQGTLV TVSSASTKGP SVFPLAPSSK STSGGTAALG CLVKDYFPEP V TVSWNSGA ...String: EISEVQLVES GGGLVQPGGS LRLSCAASGF NVYSSSIHWV RQAPGKGLEW VASISSYYGY TYYADSVKGR FTISADTSKN TAYLQMNSL RAEDTAVYYC ARSRQFWYSG LDYWGQGTLV TVSSASTKGP SVFPLAPSSK STSGGTAALG CLVKDYFPEP V TVSWNSGA LTSGVHTFPA VLQSSGLYSL SSVVTVPSSS LGTQTYICNV NHKPSNTKVD KKVEPKSCDK THHHHHHHH |
-Macromolecule #3: Fab30 Light Chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab30 Light Chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.435064 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SDIQMTQSPS SLSASVGDRV TITCRASQSV SSAVAWYQQK PGKAPKLLIY SASSLYSGVP SRFSGSRSGT DFTLTISSLQ PEDFATYYC QQYKYVPVTF GQGTKVEIKR TVAAPSVFIF PPSDSQLKSG TASVVCLLNN FYPREAKVQW KVDNALQSGN S QESVTEQD ...String: SDIQMTQSPS SLSASVGDRV TITCRASQSV SSAVAWYQQK PGKAPKLLIY SASSLYSGVP SRFSGSRSGT DFTLTISSLQ PEDFATYYC QQYKYVPVTF GQGTKVEIKR TVAAPSVFIF PPSDSQLKSG TASVVCLLNN FYPREAKVQW KVDNALQSGN S QESVTEQD SKDSTYSLSS TLTLSKADYE KHKVYACEVT HQGLSSPVTK SFNRGEC |
-Macromolecule #4: Atypical chemokine receptor 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Atypical chemokine receptor 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.352668 KDa |
| Sequence | String: G(TPO)AQA(SEP)L(SEP)(SEP)C (SEP)E(SEP)(SEP)IL(TPO)A UniProtKB: Atypical chemokine receptor 2 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Number real images: 9698 / Average electron dose: 53.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 46000 |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)