[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-29657: Semi-synthetic CoA-alpha-Synuclein Constructs Trap N-terminal Ace... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Semi-synthetic CoA-alpha-Synuclein Constructs Trap N-terminal Acetyltransferase NatB for Binding Mechanism Studies | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | N-terminal acetyltransferase / TRANSFERASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationN-terminal peptidyl-glutamine acetylation / N-terminal methionine Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatB / N-terminal peptidyl-aspartic acid acetylation / N-terminal peptidyl-glutamic acid acetylation / NatB complex / N-terminal protein amino acid acetylation / protein N-terminal-methionine acetyltransferase activity / protein-N-terminal amino-acid acetyltransferase activity / acetyltransferase activator activity / negative regulation of mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone ...N-terminal peptidyl-glutamine acetylation / N-terminal methionine Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatB / N-terminal peptidyl-aspartic acid acetylation / N-terminal peptidyl-glutamic acid acetylation / NatB complex / N-terminal protein amino acid acetylation / protein N-terminal-methionine acetyltransferase activity / protein-N-terminal amino-acid acetyltransferase activity / acetyltransferase activator activity / negative regulation of mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone / : / neutral lipid metabolic process / regulation of acyl-CoA biosynthetic process / negative regulation of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / negative regulation of norepinephrine uptake / response to desipramine / positive regulation of SNARE complex assembly / positive regulation of hydrogen peroxide catabolic process / supramolecular fiber / regulation of synaptic vesicle recycling / negative regulation of chaperone-mediated autophagy / mitochondrial membrane organization / regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / positive regulation of protein localization to cell periphery / negative regulation of exocytosis / negative regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway / regulation of glutamate secretion / dopamine biosynthetic process / response to iron(II) ion / negative regulation of thrombin-activated receptor signaling pathway / SNARE complex assembly / positive regulation of neurotransmitter secretion / negative regulation of dopamine metabolic process / regulation of macrophage activation / positive regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process / regulation of locomotion / negative regulation of microtubule polymerization / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / synaptic vesicle transport / synaptic vesicle priming / transporter regulator activity / protein kinase inhibitor activity / dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / regulation of dopamine secretion / mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled electron transport / positive regulation of receptor recycling / dynein complex binding / cuprous ion binding / nuclear outer membrane / response to magnesium ion / positive regulation of exocytosis / synaptic vesicle exocytosis / positive regulation of endocytosis / synaptic vesicle endocytosis / kinesin binding / cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of serotonin uptake / response to type II interferon / regulation of presynapse assembly / alpha-tubulin binding / beta-tubulin binding / phospholipase binding / behavioral response to cocaine / supramolecular fiber organization / cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus / phospholipid metabolic process / inclusion body / cytoskeleton organization / cellular response to epinephrine stimulus / Hsp70 protein binding / enzyme inhibitor activity / response to interleukin-1 / axon terminus / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cellular response to copper ion / positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / SNARE binding / adult locomotory behavior / regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization / excitatory postsynaptic potential / protein tetramerization / phosphoprotein binding / microglial cell activation / ferrous iron binding / fatty acid metabolic process / synapse organization / PKR-mediated signaling / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / phospholipid binding / receptor internalization / protein destabilization / tau protein binding / terminal bouton / positive regulation of inflammatory response / long-term synaptic potentiation / synaptic vesicle membrane / actin cytoskeleton / actin binding / growth cone / cellular response to oxidative stress Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
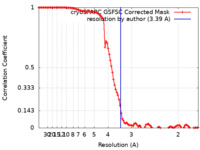
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.39 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gardner SM / Marmorstein R | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation | Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2023 Title: Semi-synthetic CoA-α-Synuclein Constructs Trap N-terminal Acetyltransferase NatB for Binding Mechanism Studies. Authors: Buyan Pan / Sarah Gardner / Kollin Schultz / Ryann M Perez / Sunbin Deng / Marie Shimogawa / Kohei Sato / Elizabeth Rhoades / Ronen Marmorstein / E James Petersson Abstract: N-terminal acetylation is a chemical modification carried out by N-terminal acetyltransferases (NATs). A major member of this enzyme family, NatB, acts on much of the human proteome, including α- ...N-terminal acetylation is a chemical modification carried out by N-terminal acetyltransferases (NATs). A major member of this enzyme family, NatB, acts on much of the human proteome, including α-synuclein (αS), a synaptic protein that mediates vesicle trafficking. NatB acetylation of αS modulates its lipid vesicle binding properties and amyloid fibril formation, which underlies its role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Although the molecular details of the interaction between human NatB (hNatB) and the N-terminus of αS have been resolved, whether the remainder of the protein plays a role in interacting with the enzyme is unknown. Here we execute the first synthesis, by native chemical ligation, of a bisubstrate inhibitor of NatB consisting of coenzyme A and full-length human αS, additionally incorporating two fluorescent probes for studies of conformational dynamics. We use cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to characterize the structural features of the hNatB/inhibitor complex and show that, beyond the first few residues, αS remains disordered when in complex with hNatB. We further probe changes in the αS conformation by single molecule Förster resonance energy transfer (smFRET) to reveal that the C-terminus expands when bound to hNatB. Computational models based on the cryo-EM and smFRET data help to explain the conformational changes and their implications for hNatB substrate recognition and specific inhibition of the interaction with αS. Beyond the study of αS and NatB, these experiments illustrate valuable strategies for the study of challenging structural biology targets through a combination of protein semi-synthesis, cryo-EM, smFRET, and computational modeling. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_29657.map.gz emd_29657.map.gz | 51.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-29657-v30.xml emd-29657-v30.xml emd-29657.xml emd-29657.xml | 18.6 KB 18.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_29657_fsc.xml emd_29657_fsc.xml | 9.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_29657.png emd_29657.png | 48.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-29657.cif.gz emd-29657.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_29657_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29657_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29657_half_map_2.map.gz emd_29657_half_map_2.map.gz | 95.5 MB 95.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29657 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29657 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29657 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29657 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 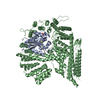 8g0lMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_29657.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_29657.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.86 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
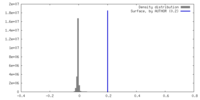
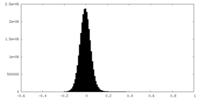
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_29657_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
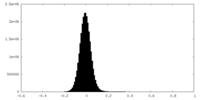
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_29657_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
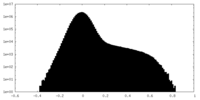
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Ternary complex of NAA20, NAA25 and CoA-alpha-Synuclein
| Entire | Name: Ternary complex of NAA20, NAA25 and CoA-alpha-Synuclein |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Ternary complex of NAA20, NAA25 and CoA-alpha-Synuclein
| Supramolecule | Name: Ternary complex of NAA20, NAA25 and CoA-alpha-Synuclein type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: N-alpha-acetyltransferase 20
| Macromolecule | Name: N-alpha-acetyltransferase 20 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: N-terminal methionine Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatB |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 20.390133 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MTTLRAFTCD DLFRFNNINL DPLTETYGIP FYLQYLAHWP EYFIVAEAPG GELMGYIMGK AEGSVAREEW HGHVTALSVA PEFRRLGLA AKLMELLEEI SERKGGFFVD LFVRVSNQVA VNMYKQLGYS VYRTVIEYYS ASNGEPDEDA YDMRKALSRD T EKKSIIPL PHPVRPEDIE UniProtKB: N-alpha-acetyltransferase 20 |
-Macromolecule #2: N-alpha-acetyltransferase 25, NatB auxiliary subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: N-alpha-acetyltransferase 25, NatB auxiliary subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 112.444258 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MATRGHVQDP NDRRLRPIYD YLDNGNNKMA IQQADKLLKK HKDLHCAKVL KAIGLQRTGK QEEAFTLAQE VAALEPTDDN SLQALTILY REMHRPELVT KLYEAAVKKV PNSEEYHSHL FMAYARVGEY KKMQQAGMAL YKIVPKNPYY FWSVMSLIMQ S ISAQDENL ...String: MATRGHVQDP NDRRLRPIYD YLDNGNNKMA IQQADKLLKK HKDLHCAKVL KAIGLQRTGK QEEAFTLAQE VAALEPTDDN SLQALTILY REMHRPELVT KLYEAAVKKV PNSEEYHSHL FMAYARVGEY KKMQQAGMAL YKIVPKNPYY FWSVMSLIMQ S ISAQDENL SKTMFLPLAE RMVEKMVKED KIEAEAEVEL YYMILERLGK YQEALDVIRG KLGEKLTSEI QSRENKCMAM YK KLSRWPE CNALSRRLLL KNSDDWQFYL TYFDSVFRLI EEAWSPPAEG EHSLEGEVHY SAEKAVKFIE DRITEESKSS RHL RGPHLA KLELIRRLRS QGCNDEYKLG DPEELMFQYF KKFGDKPCCF TDLKVFVDLL PATQCTKFIN QLLGVVPLST PTED KLALP ADIRALQQHL CVVQLTRLLG LYHTMDKNQK LSVVRELMLR YQHGLEFGKT CLKTELQFSD YYCLLAVHAL IDVWR ETGD ETTVWQALTL LEEGLTHSPS NAQFKLLLVR IYCMLGAFEP VVDLYSSLDA KHIQHDTIGY LLTRYAESLG QYAAAS QSC NFALRFFHSN QKDTSEYIIQ AYKYGAFEKI PEFIAFRNRL NNSLHFAQVR TERMLLDLLL EANISTSLAE SIKSMNL RP EEDDIPWEDL RDNRDLNVFF SWDPKDRDVS EEHKKLSLEE ETLWLRIRSL TLRLISGLPS LNHPVEPKNS EKTAENGV S SRIDILRLLL QQLEATLETG KRFIEKDIQY PFLGPVPTRM GGFFNSGCSQ CQISSFYLVN DIYELDTSGL EDTMEIQER IENSFKSLLD QLKDVFSKCK GDLLEVKDGN LKTHPTLLEN LVFFVETISV ILWVSSYCES VLRPYKLNLQ KKKKKKKETS IIMPPVFTS FQDYVTGLQT LISNVVDHIK GLETHLIALK LEELILEDTS LSPEERKFSK TVQGKVQSSY LHSLLEMGEL L KKRLETTK KLKI UniProtKB: N-alpha-acetyltransferase 25, NatB auxiliary subunit |
-Macromolecule #3: Alpha-synuclein
| Macromolecule | Name: Alpha-synuclein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 641.799 Da |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDVFM UniProtKB: Alpha-synuclein |
-Macromolecule #4: CARBOXYMETHYL COENZYME *A
| Macromolecule | Name: CARBOXYMETHYL COENZYME *A / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: CMC |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 825.57 Da |
| Chemical component information | 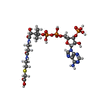 ChemComp-CMC: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 4 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 5470 / Average electron dose: 43.9 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)