+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | Wild type P53 dimer structure from human cancer cells | ||||||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | P53 dimer structure | ||||||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| ||||||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | cancer / tumor suppressor / cell cycle / apoptosis / DNA repair / ANTITUMOR PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報Loss of function of TP53 in cancer due to loss of tetramerization ability / Regulation of TP53 Expression / signal transduction by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of G1 to G0 transition / regulation of fibroblast apoptotic process / negative regulation of glucose catabolic process to lactate via pyruvate / Transcriptional activation of cell cycle inhibitor p21 / regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / Activation of NOXA and translocation to mitochondria / negative regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt ...Loss of function of TP53 in cancer due to loss of tetramerization ability / Regulation of TP53 Expression / signal transduction by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of G1 to G0 transition / regulation of fibroblast apoptotic process / negative regulation of glucose catabolic process to lactate via pyruvate / Transcriptional activation of cell cycle inhibitor p21 / regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / Activation of NOXA and translocation to mitochondria / negative regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt / ATP-dependent DNA/DNA annealing activity / negative regulation of helicase activity / regulation of cell cycle G2/M phase transition / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to hypoxia / oxidative stress-induced premature senescence / oligodendrocyte apoptotic process / negative regulation of miRNA processing / positive regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process / regulation of tissue remodeling / glucose catabolic process to lactate via pyruvate / positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability / negative regulation of mitophagy / positive regulation of programmed necrotic cell death / circadian behavior / mRNA transcription / bone marrow development / regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability involved in apoptotic process / histone deacetylase regulator activity / germ cell nucleus / T cell lineage commitment / RUNX3 regulates CDKN1A transcription / regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / TP53 regulates transcription of additional cell cycle genes whose exact role in the p53 pathway remain uncertain / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Death Receptors and Ligands / Activation of PUMA and translocation to mitochondria / DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in transcription of p21 class mediator / B cell lineage commitment / thymocyte apoptotic process / negative regulation of glial cell proliferation / negative regulation of neuroblast proliferation / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Association with Co-factors / mitochondrial DNA repair / positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Caspase Activators and Caspases / ER overload response / negative regulation of DNA replication / positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria / TP53 regulates transcription of several additional cell death genes whose specific roles in p53-dependent apoptosis remain uncertain / entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod / cardiac septum morphogenesis / PI5P Regulates TP53 Acetylation / positive regulation of execution phase of apoptosis / Association of TriC/CCT with target proteins during biosynthesis / necroptotic process / Zygotic genome activation (ZGA) / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in Cytochrome C Release / TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding / rRNA transcription / negative regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / SUMOylation of transcription factors / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / general transcription initiation factor binding / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / response to X-ray / Transcriptional Regulation by VENTX / DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / Pyroptosis / replicative senescence / mitophagy / cellular response to UV-C / positive regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / neuroblast proliferation / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / somitogenesis / embryonic organ development / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / chromosome organization / T cell proliferation involved in immune response / hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation / glial cell proliferation / type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway / cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G1 Cell Cycle Arrest / cellular response to glucose starvation / viral process / cellular response to actinomycin D / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / negative regulation of stem cell proliferation / mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation / gastrulation / MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding / tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / response to salt stress / cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Acetylation / 14-3-3 protein binding 類似検索 - 分子機能 | ||||||||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | ||||||||||||
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 4.2 Å | ||||||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Solares M / Kelly DF | ||||||||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 3件 米国, 3件
| ||||||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Chembiochem / 年: 2022 ジャーナル: Chembiochem / 年: 2022タイトル: High-Resolution Imaging of Human Cancer Proteins Using Microprocessor Materials. 著者: Maria J Solares / G M Jonaid / William Y Luqiu / Samantha Berry / Janki Khadela / Yanping Liang / Madison C Evans / Kevin J Pridham / William J Dearnaley / Zhi Sheng / Deborah F Kelly /  要旨: Mutations in tumor suppressor genes, such as Tumor Protein 53 (TP53), are heavily implicated in aggressive cancers giving rise to gain- and loss-of-function phenotypes. While individual domains of ...Mutations in tumor suppressor genes, such as Tumor Protein 53 (TP53), are heavily implicated in aggressive cancers giving rise to gain- and loss-of-function phenotypes. While individual domains of the p53 protein have been studied extensively, structural information for full-length p53 remains incomplete. Functionalized microprocessor chips (microchips) with properties amenable to electron microscopy permitted us to visualize complete p53 assemblies for the first time. The new structures revealed p53 in an inactive dimeric state independent of DNA binding. Residues located at the protein-protein interface corresponded with modification sites in cancer-related hot spots. Changes in these regions may amplify the toxic effects of clinical mutations. Taken together, these results contribute advances in technology and imaging approaches to decode native protein models in different states of activation. | ||||||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 添付画像 |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_28816.map.gz emd_28816.map.gz | 2.4 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-28816-v30.xml emd-28816-v30.xml emd-28816.xml emd-28816.xml | 17.5 KB 17.5 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| 画像 |  emd_28816.png emd_28816.png | 233.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-28816.cif.gz emd-28816.cif.gz | 5.9 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_28816_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28816_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28816_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28816_half_map_2.map.gz | 2.2 MB 2.3 MB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28816 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28816 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28816 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28816 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_28816_validation.pdf.gz emd_28816_validation.pdf.gz | 762.6 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_28816_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_28816_full_validation.pdf.gz | 762.2 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_28816_validation.xml.gz emd_28816_validation.xml.gz | 6.4 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_28816_validation.cif.gz emd_28816_validation.cif.gz | 7.7 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28816 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28816 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28816 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28816 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  8f2hMC  8f2iC M: このマップから作成された原子モデル C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | 類似検索 - 機能・相同性  F&H 検索 F&H 検索 |
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| 「今月の分子」の関連する項目 |
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_28816.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 2.7 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_28816.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 2.7 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
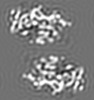
| 注釈 | P53 dimer structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 これらの図は立方格子座標系で作成されたものです | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
|
-添付データ
-ハーフマップ: Half Map 1
| ファイル | emd_28816_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
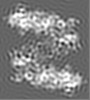
| 注釈 | Half Map 1 | ||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: Half Map 2
| ファイル | emd_28816_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | Half Map 2 | ||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : P53 dimer isolated from U87-MG cells
| 全体 | 名称: P53 dimer isolated from U87-MG cells |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: P53 dimer isolated from U87-MG cells
| 超分子 | 名称: P53 dimer isolated from U87-MG cells / タイプ: cell / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: all / 詳細: Native protein, wild-type with no tags |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 器官: Brain / 組織: Brain tumor Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 器官: Brain / 組織: Brain tumor |
-分子 #1: Cellular tumor antigen p53
| 分子 | 名称: Cellular tumor antigen p53 / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / コピー数: 2 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 器官: brain tumor / 組織: brain Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 器官: brain tumor / 組織: brain |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 43.711176 KDa |
| 配列 | 文字列: MEEPQSDPSV EPPLSQETFS DLWKLLPENN VLSPLPSQAM DDLMLSPDDI EQWFTEDPGP DEAPRMPEAA PPVAPAPAAP TPAAPAPAP SWPLSSSVPS QKTYQGSYGF RLGFLHSGTA KSVTCTYSPA LNKMFCQLAK TCPVQLWVDS TPPPGTRVRA M AIYKQSQH ...文字列: MEEPQSDPSV EPPLSQETFS DLWKLLPENN VLSPLPSQAM DDLMLSPDDI EQWFTEDPGP DEAPRMPEAA PPVAPAPAAP TPAAPAPAP SWPLSSSVPS QKTYQGSYGF RLGFLHSGTA KSVTCTYSPA LNKMFCQLAK TCPVQLWVDS TPPPGTRVRA M AIYKQSQH MTEVVRRCPH HERCSDSDGL APPQHLIRVE GNLRVEYLDD RNTFRHSVVV PYEPPEVGSD CTTIHYNYMC NS SCMGGMN RRPILTIITL EDSSGNLLGR NSFEVRVCAC PGRDRRTEEE NLRKKGEPHH ELPPGSTKRA LPNNTSSSPQ PKK KPLDGE YFTLQIRGRE RFEMFRELNE ALELKDAQAG KEPGGSRAHS SHLKSKKGQS TSRHKKLMFK TEGPDSD UniProtKB: Cellular tumor antigen p53 |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 濃度 | 0.2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.5 詳細: 20 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 140 mM NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 2 mM CaCl2, 5 mM imidazole |
| グリッド | モデル: Homemade / 材質: SILICON NITRIDE 詳細: Silicon nitride chips coated with Ni-NTA layers prior to sample application |
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE / チャンバー内湿度: 90 % / チャンバー内温度: 298 K / 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK III 詳細: The microchip samples were loaded into a FEI Mark III Vitrobot and flash-frozen into liquid ethane.. |
| 詳細 | Sample was placed on Silicon nitride chips coated with Ni-NTA layers |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | TFS TALOS F200C |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: FEI CETA (4k x 4k) / 撮影したグリッド数: 10 / 実像数: 300 / 平均露光時間: 1.0 sec. / 平均電子線量: 5.0 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 200 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | C2レンズ絞り径: 100.0 µm / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 5.0 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 1.0 µm / 倍率(公称値): 142000 |
| 試料ステージ | 試料ホルダーモデル: GATAN 626 SINGLE TILT LIQUID NITROGEN CRYO TRANSFER HOLDER ホルダー冷却材: NITROGEN |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Tecnai F20 / 画像提供: FEI Company |
+ 画像解析
画像解析
-原子モデル構築 1
| 精密化 | 空間: REAL / プロトコル: FLEXIBLE FIT / 温度因子: 50 |
|---|---|
| 得られたモデル |  PDB-8f2h: |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー



















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)