[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-28378: Structure of the C3bB proconvertase in complex with lufaxin and f... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the C3bB proconvertase in complex with lufaxin and factor Xa | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Complement / Alternative pathway / inhibitor / sand fly / IMMUNE SYSTEM | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationalternative-complement-pathway C3/C5 convertase / C5L2 anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor binding / oviduct epithelium development / regulation of triglyceride biosynthetic process / complement binding / positive regulation of activation of membrane attack complex / vertebrate eye-specific patterning / positive regulation of apoptotic cell clearance / complement-mediated synapse pruning / Alternative complement activation ...alternative-complement-pathway C3/C5 convertase / C5L2 anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor binding / oviduct epithelium development / regulation of triglyceride biosynthetic process / complement binding / positive regulation of activation of membrane attack complex / vertebrate eye-specific patterning / positive regulation of apoptotic cell clearance / complement-mediated synapse pruning / Alternative complement activation / coagulation factor Xa / positive regulation of phagocytosis, engulfment / Activation of C3 and C5 / positive regulation of lipid storage / positive regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of type IIa hypersensitivity / complement receptor mediated signaling pathway / Defective factor IX causes thrombophilia / Defective cofactor function of FVIIIa variant / Defective F9 variant does not activate FX / complement-dependent cytotoxicity / positive regulation of D-glucose transmembrane transport / complement activation / complement activation, alternative pathway / Extrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / endopeptidase inhibitor activity / neuron remodeling / amyloid-beta clearance / B cell activation / positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production / complement activation, classical pathway / positive regulation of TOR signaling / Transport of gamma-carboxylated protein precursors from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus / Gamma-carboxylation of protein precursors / Common Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / Removal of aminoterminal propeptides from gamma-carboxylated proteins / Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection / Intrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / Peptide ligand-binding receptors / Regulation of Complement cascade / Post-translational protein phosphorylation / response to bacterium / fatty acid metabolic process / phospholipid binding / positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis / Golgi lumen / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / positive regulation of angiogenesis / Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / blood coagulation / azurophil granule lumen / toxin activity / secretory granule lumen / blood microparticle / G alpha (i) signalling events / immune response / positive regulation of cell migration / receptor ligand activity / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / inflammatory response / signaling receptor binding / external side of plasma membrane / serine-type endopeptidase activity / calcium ion binding / Neutrophil degranulation / cell surface / signal transduction / protein-containing complex / proteolysis / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  Lutzomyia longipalpis (insect) Lutzomyia longipalpis (insect) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.53 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Andersen JF / Lei H | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Blood / Year: 2023 Journal: Blood / Year: 2023Title: A bispecific inhibitor of complement and coagulation blocks activation in complementopathy models via a novel mechanism. Authors: John F Andersen / Haotian Lei / Ethan C Strayer / Tapan Kanai / Van Pham / Xiang-Zuo Pan / Patricia Hessab Alvarenga / Gloria F Gerber / Oluwatoyin A Asojo / Ivo M B Francischetti / Robert A ...Authors: John F Andersen / Haotian Lei / Ethan C Strayer / Tapan Kanai / Van Pham / Xiang-Zuo Pan / Patricia Hessab Alvarenga / Gloria F Gerber / Oluwatoyin A Asojo / Ivo M B Francischetti / Robert A Brodsky / Jesus G Valenzuela / José M C Ribeiro /  Abstract: Inhibitors of complement and coagulation are present in the saliva of a variety of blood-feeding arthropods that transmit parasitic and viral pathogens. Here, we describe the structure and mechanism ...Inhibitors of complement and coagulation are present in the saliva of a variety of blood-feeding arthropods that transmit parasitic and viral pathogens. Here, we describe the structure and mechanism of action of the sand fly salivary protein lufaxin, which inhibits the formation of the central alternative C3 convertase (C3bBb) and inhibits coagulation factor Xa (fXa). Surface plasmon resonance experiments show that lufaxin stabilizes the binding of serine protease factor B (FB) to C3b but does not detectably bind either C3b or FB alone. The crystal structure of the inhibitor reveals a novel all β-sheet fold containing 2 domains. A structure of the lufaxin-C3bB complex obtained via cryo-electron microscopy (EM) shows that lufaxin binds via its N-terminal domain at an interface containing elements of both C3b and FB. By occupying this spot, the inhibitor locks FB into a closed conformation in which proteolytic activation of FB by FD cannot occur. C3bB-bound lufaxin binds fXa at a separate site in its C-terminal domain. In the cryo-EM structure of a C3bB-lufaxin-fXa complex, the inhibitor binds to both targets simultaneously, and lufaxin inhibits fXa through substrate-like binding of a C-terminal peptide at the active site as well as other interactions in this region. Lufaxin inhibits complement activation in ex vivo models of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) as well as thrombin generation in plasma, providing a rationale for the development of a bispecific inhibitor to treat complement-related diseases in which thrombosis is a prominent manifestation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_28378.map.gz emd_28378.map.gz | 96.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-28378-v30.xml emd-28378-v30.xml emd-28378.xml emd-28378.xml | 23.8 KB 23.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_28378.png emd_28378.png | 108.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-28378.cif.gz emd-28378.cif.gz | 8.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_28378_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28378_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28378_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28378_half_map_2.map.gz | 80.9 MB 80.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28378 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28378 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28378 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28378 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8eokMC  8enuC  8eo2C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_28378.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_28378.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.92 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
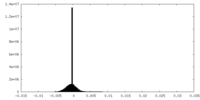
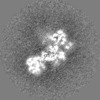
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: half map 1
| File | emd_28378_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
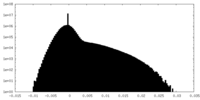
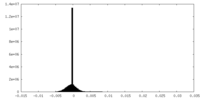
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half map 2
| File | emd_28378_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
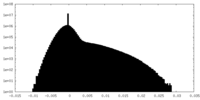
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : The C3 proconvertase from the alternative pathway of complement i...
| Entire | Name: The C3 proconvertase from the alternative pathway of complement in complex with lufaxin, a complement/coagulation inhibitor and coagulation factor Xa |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: The C3 proconvertase from the alternative pathway of complement i...
| Supramolecule | Name: The C3 proconvertase from the alternative pathway of complement in complex with lufaxin, a complement/coagulation inhibitor and coagulation factor Xa type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3, #5-#6 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 348.3 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Complement C3 beta chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Complement C3 beta chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 71.39332 KDa |
| Sequence | String: SPMYSIITPN ILRLESEETM VLEAHDAQGD VPVTVTVHDF PGKKLVLSSE KTVLTPATNH MGNVTFTIPA NREFKSEKGR NKFVTVQAT FGTQVVEKVV LVSLQSGYLF IQTDKTIYTP GSTVLYRIFT VNHKLLPVGR TVMVNIENPE GIPVKQDSLS S QNQLGVLP ...String: SPMYSIITPN ILRLESEETM VLEAHDAQGD VPVTVTVHDF PGKKLVLSSE KTVLTPATNH MGNVTFTIPA NREFKSEKGR NKFVTVQAT FGTQVVEKVV LVSLQSGYLF IQTDKTIYTP GSTVLYRIFT VNHKLLPVGR TVMVNIENPE GIPVKQDSLS S QNQLGVLP LSWDIPELVN MGQWKIRAYY ENSPQQVFST EFEVKEYVLP SFEVIVEPTE KFYYIYNEKG LEVTITARFL YG KKVEGTA FVIFGIQDGE QRISLPESLK RIPIEDGSGE VVLSRKVLLD GVQNPRAEDL VGKSLYVSAT VILHSGSDMV QAE RSGIPI VTSPYQIHFT KTPKYFKPGM PFDLMVFVTN PDGSPAYRVP VAVQGEDTVQ SLTQGDGVAK LSINTHPSQK PLSI TVRTK KQELSEAEQA TRTMQALPYS TVGNSNNYLH LSVLRTELRP GETLNVNFLL RMDRAHEAKI RYYTYLIMNK GRLLK AGRQ VREPGQDLVV LPLSITTDFI PSFRLVAYYT LIGASGQREV VADSVWVDVK DSCVGSLVVK SGQSEDRQPV PGQQMT LKI EGDHGARVVL VAVDKGVFVL NKKNKLTQSK IWDVVEKADI GCTPGSGKDY AGVFSDAGLT FTSSSGQQTA QRAELQC PQ PAA UniProtKB: Complement C3 |
-Macromolecule #2: Complement C3b alpha' chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Complement C3b alpha' chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 104.073164 KDa |
| Sequence | String: SNLDEDIIAE ENIVSRSEFP ESWLWNVEDL KEPPKNGIST KLMNIFLKDS ITTWEILAVS MSDKKGICVA DPFEVTVMQD FFIDLRLPY SVVRNEQVEI RAVLYNYRQN QELKVRVELL HNPAFCSLAT TKRRHQQTVT IPPKSSLSVP YVIVPLKTGL Q EVEVKAAV ...String: SNLDEDIIAE ENIVSRSEFP ESWLWNVEDL KEPPKNGIST KLMNIFLKDS ITTWEILAVS MSDKKGICVA DPFEVTVMQD FFIDLRLPY SVVRNEQVEI RAVLYNYRQN QELKVRVELL HNPAFCSLAT TKRRHQQTVT IPPKSSLSVP YVIVPLKTGL Q EVEVKAAV YHHFISDGVR KSLKVVPEGI RMNKTVAVRT LDPERLGREG VQKEDIPPAD LSDQVPDTES ETRILLQGTP VA QMTEDAV DAERLKHLIV TPSGCGEQNM IGMTPTVIAV HYLDETEQWE KFGLEKRQGA LELIKKGYTQ QLAFRQPSSA FAA FVKRAP STWLTAYVVK VFSLAVNLIA IDSQVLCGAV KWLILEKQKP DGVFQEDAPV IHQEMIGGLR NNNEKDMALT AFVL ISLQE AKDICEEQVN SLPGSITKAG DFLEANYMNL QRSYTVAIAG YALAQMGRLK GPLLNKFLTT AKDKNRWEDP GKQLY NVEA TSYALLALLQ LKDFDFVPPV VRWLNEQRYY GGGYGSTQAT FMVFQALAQY QKDAPDHQEL NLDVSLQLPS RSSKIT HRI HWESASLLRS EETKENEGFT VTAEGKGQGT LSVVTMYHAK AKDQLTCNKF DLKVTIKPAP ETEKRPQDAK NTMILEI CT RYRGDQDATM SILDISMMTG FAPDTDDLKQ LANGVDRYIS KYELDKAFSD RNTLIIYLDK VSHSEDDCLA FKVHQYFN V ELIQPGAVKV YAYYNLEESC TRFYHPEKED GKLNKLCRDE LCRCAEENCF IQKSDDKVTL EERLDKACEP GVDYVYKTR LVKVQLSNDF DEYIMAIEQT IKSGSDEVQV GQQRTFISPI KCREALKLEE KKHYLMWGLS SDFWGEKPNL SYIIGKDTWV EHWPEEDEC QDEENQKQCQ DLGAFTESMV VFGCPN UniProtKB: Complement C3 |
-Macromolecule #3: Complement factor B
| Macromolecule | Name: Complement factor B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: alternative-complement-pathway C3/C5 convertase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 85.510617 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GSNLSPQLCL MPFILGLLSG GVTTTPWSLA RPQGSCSLEG VEIKGGSFRL LQEGQALEYV CPSGFYPYPV QTRTCRSTGS WSTLKTQDQ KTVRKAECRA IHCPRPHDFE NGEYWPRSPY YNVSDEISFH CYDGYTLRGS ANRTCQVNGR WSGQTAICDN G AGYCSNPG ...String: GSNLSPQLCL MPFILGLLSG GVTTTPWSLA RPQGSCSLEG VEIKGGSFRL LQEGQALEYV CPSGFYPYPV QTRTCRSTGS WSTLKTQDQ KTVRKAECRA IHCPRPHDFE NGEYWPRSPY YNVSDEISFH CYDGYTLRGS ANRTCQVNGR WSGQTAICDN G AGYCSNPG IPIGTRKVGS QYRLEDSVTY HCSRGLTLRG SQRRTCQEGG SWSGTEPSCQ DSFMYDTPQE VAEAFLSSLT ET IEGVDAE DGHGPGEQQK RKIVLDPSGS MNIYLVLDGS DSIGASNFTG AKKCLVNLIE KVASYGVKPR YGLVTYATYP KIW VKVSEA DSSNADWVTK QLNEINYEDH KLKSGTNTKK ALQAVYSMMS WPDDVPPEGW NRTRHVIILM TDGLHNMGGD PITV IDEIR DLLYIGKDRK NPREDYLDVY VFGVGPLVNQ VNINALASKK DNEQHVFKVK DMENLEDVFY QMIDESQSLS LCGMV WEHR KGTDYHKQPW QAKISVIRPS KGHESCMGAV VSEYFVLTAA HCFTVDDKEH SIKVSVGGEK RDLEIEVVLF HPNYNI NGK KEAGIPEFYD YDVALIKLKN KLKYGQTIRP ICLPCTEGTT RALRLPPTTT CQQQKEELLP AQDIKALFVS EEEKKLT RK EVYIKNGDKK GSCERDAQYA PGYDKVKDIS EVVTPRFLCT GGVSPYADPN TCRGDSGGPL IVHKRSRFIQ VGVISWGV V DVCKNQKRQK QVPAHARDFH INLFQVLPWL KEKLQDEDLG FL UniProtKB: Complement factor B |
-Macromolecule #4: Lufaxin
| Macromolecule | Name: Lufaxin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Lutzomyia longipalpis (insect) Lutzomyia longipalpis (insect) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 33.354586 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: DGDEYFIGKY KEKDETLFFA SYGLKRDPCQ IVLGYKCSNN QTHFVLNFKT NKKSCISAIK LTSYPKINQN SDLTRNLYCQ TGGIGTDNC KLVFKKRKRQ IAANIEIYGI PAKKCSFKDR YIGADPLHVD SYGLSYQFDQ EHGWNLERNN IFKDTRFSTE V FYHKNGLF ...String: DGDEYFIGKY KEKDETLFFA SYGLKRDPCQ IVLGYKCSNN QTHFVLNFKT NKKSCISAIK LTSYPKINQN SDLTRNLYCQ TGGIGTDNC KLVFKKRKRQ IAANIEIYGI PAKKCSFKDR YIGADPLHVD SYGLSYQFDQ EHGWNLERNN IFKDTRFSTE V FYHKNGLF NTQITYLAEE DSFSEAREIT AKDIKKKFSI ILPNEEYKRI SFLDVYWFQE TMRKKPKYPY IHYNGECSNE NK TCELVFD TDELMTYALV KVFTNPESDG SRLKEEDLGR GHHHHHH UniProtKB: Lufaxin |
-Macromolecule #5: Factor X light chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Factor X light chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.210793 KDa |
| Sequence | String: EEMKKGHLER ECMEETCSYE EAREVFEDSD KTNEFWNKYK DGDQCETSPC QNQGKCKDGL GEYTCTCLEG FEGKNCELFT RKLCSLDNG DCDQFCHEEQ NSVVCSCARG YTLADNGKAC IPTGPYPCGK QTLER UniProtKB: Coagulation factor X |
-Macromolecule #6: Activated factor Xa heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Activated factor Xa heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 28.550596 KDa |
| Sequence | String: IVGGQECKDG ECPWQALLIN EENEGFCGGT ILSEFYILTA AHCLYQAKRF KVRVGDRNTE QEEGGEAVHE VEVVIKHNRF TKETYDFDI AVLRLKTPIT FRMNVAPACL PERDWAESTL MTQKTGIVSG FGRTHEKGRQ STRLKMLEVP YVDRNSCKLS S SFIITQNM ...String: IVGGQECKDG ECPWQALLIN EENEGFCGGT ILSEFYILTA AHCLYQAKRF KVRVGDRNTE QEEGGEAVHE VEVVIKHNRF TKETYDFDI AVLRLKTPIT FRMNVAPACL PERDWAESTL MTQKTGIVSG FGRTHEKGRQ STRLKMLEVP YVDRNSCKLS S SFIITQNM FCAGYDTKQE DACQGDSGGP HVTRFKDTYF VTGIVSWGEG CARKGKYGIY TKVTAFLKWI DRSMKTRGLP KA KSHAPEV ITSSPLK UniProtKB: Coagulation factor X |
-Macromolecule #8: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #9: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 9 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.5 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: C-flat-1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE | ||||||||||||
| Details | The sample was monodisperse |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 58.31 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.3 µm / Nominal magnification: 45000 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)