+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
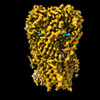
| Title | Cryo-EM map of squid sensory receptor CRB1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM structure of squid sensory receptor CRB1 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | pentameric ligand gated ion channel / squid sensory receptor / cys-loop receptor / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Sepioloidea lineolata (invertebrata) Sepioloidea lineolata (invertebrata) | |||||||||
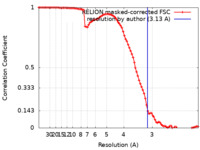
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.13 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kang G / Kim JJ / Allard CAH / Valencia-Montoya WA / van Giesen L / Kilian PB / Bai X / Bellono NW / Hibbs RE | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Sensory specializations drive octopus and squid behaviour. Authors: Guipeun Kang / Corey A H Allard / Wendy A Valencia-Montoya / Lena van Giesen / Jeong Joo Kim / Peter B Kilian / Xiaochen Bai / Nicholas W Bellono / Ryan E Hibbs /  Abstract: The evolution of new traits enables expansion into new ecological and behavioural niches. Nonetheless, demonstrated connections between divergence in protein structure, function and lineage-specific ...The evolution of new traits enables expansion into new ecological and behavioural niches. Nonetheless, demonstrated connections between divergence in protein structure, function and lineage-specific behaviours remain rare. Here we show that both octopus and squid use cephalopod-specific chemotactile receptors (CRs) to sense their respective marine environments, but structural adaptations in these receptors support the sensation of specific molecules suited to distinct physiological roles. We find that squid express ancient CRs that more closely resemble related nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, whereas octopuses exhibit a more recent expansion in CRs consistent with their elaborated 'taste by touch' sensory system. Using a combination of genetic profiling, physiology and behavioural analyses, we identify the founding member of squid CRs that detects soluble bitter molecules that are relevant in ambush predation. We present the cryo-electron microscopy structure of a squid CR and compare this with octopus CRs and nicotinic receptors. These analyses demonstrate an evolutionary transition from an ancestral aromatic 'cage' that coordinates soluble neurotransmitters or tastants to a more recent octopus CR hydrophobic binding pocket that traps insoluble molecules to mediate contact-dependent chemosensation. Thus, our study provides a foundation for understanding how adaptation of protein structure drives the diversification of organismal traits and behaviour. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_28167.map.gz emd_28167.map.gz | 41.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-28167-v30.xml emd-28167-v30.xml emd-28167.xml emd-28167.xml | 14.9 KB 14.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
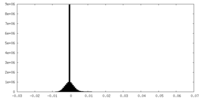
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_28167_fsc.xml emd_28167_fsc.xml | 9.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_28167.png emd_28167.png | 139.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-28167.cif.gz emd-28167.cif.gz | 5.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_28167_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28167_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28167_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28167_half_map_2.map.gz | 52.2 MB 51.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28167 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28167 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28167 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28167 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_28167.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 67 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_28167.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 67 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of squid sensory receptor CRB1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
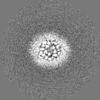
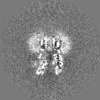
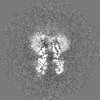
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.069 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
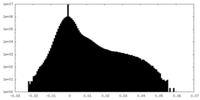
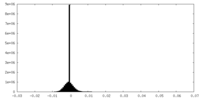
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half Map 1
| File | emd_28167_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half Map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
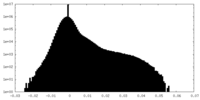
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half Map 2
| File | emd_28167_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half Map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
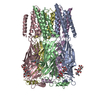
-Entire : Squid sensory receptor CRB1 in complex with denatonium
| Entire | Name: Squid sensory receptor CRB1 in complex with denatonium |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Squid sensory receptor CRB1 in complex with denatonium
| Supramolecule | Name: Squid sensory receptor CRB1 in complex with denatonium type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Sepioloidea lineolata (invertebrata) Sepioloidea lineolata (invertebrata) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 200 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: Squid sensory receptor CRB1
| Macromolecule | Name: Squid sensory receptor CRB1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Sepioloidea lineolata (invertebrata) Sepioloidea lineolata (invertebrata) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 45.038723 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: CWTYEEEYYF RSNFLQQYNK DIRPLNDLSK PISVGIHLEI AKMNDFNLAE GRLKIQTYLI LQWYDEKIFW NESTYPIPKL MVSSKKIWS PAISVYYTEN EMDSKDQFQM EIYKNGSVHQ WKSFYFNILC DVNARAFPFD KYTCETMFYF NDYDIQTAIF S SFRCISST ...String: CWTYEEEYYF RSNFLQQYNK DIRPLNDLSK PISVGIHLEI AKMNDFNLAE GRLKIQTYLI LQWYDEKIFW NESTYPIPKL MVSSKKIWS PAISVYYTEN EMDSKDQFQM EIYKNGSVHQ WKSFYFNILC DVNARAFPFD KYTCETMFYF NDYDIQTAIF S SFRCISST DLSRKAWYVS FSCDTKIGEE GSLGQLSLKL VRKVSLQCLS VLLPLFIFFI LNIMIGYLPI ESGEKVTFAT TV FLSNVIY IDNLSKQLPK ESSEIPLIFL CHIFLAFLSG LSAVGTIITS KIFCKYKSTE SAPSPSPAPA NNKIDVKKNS QIY SISKEG RVEKEANSSD GIKATTTTTT TTITEDLKKI CLSYAKIESA ILYIMTFISI LCALVFTSLF FESFLD |
-Macromolecule #3: N-benzyl-2-(2,6-dimethylanilino)-N,N-diethyl-2-oxoethan-1-aminium
| Macromolecule | Name: N-benzyl-2-(2,6-dimethylanilino)-N,N-diethyl-2-oxoethan-1-aminium type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: WK3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 325.468 Da |
| Chemical component information | 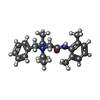 ChemComp-WK3: |
-Macromolecule #4: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 10 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)