+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | E. coli ATP synthase imaged in 10mM MgATP State1 "half-up | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Energy / ATP hyrolysis / ATP synthesis / Motor / Membrane protein / cryoEM | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / : / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / hydrolase activity / lipid binding / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sobti M / Stewart AG | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1 items Australia, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2023Title: Changes within the central stalk of E. coli FF ATP synthase observed after addition of ATP. Authors: Meghna Sobti / Yi C Zeng / James L Walshe / Simon H J Brown / Robert Ishmukhametov / Alastair G Stewart /   Abstract: FF ATP synthase functions as a biological generator and makes a major contribution to cellular energy production. Proton flow generates rotation in the F motor that is transferred to the F motor to ...FF ATP synthase functions as a biological generator and makes a major contribution to cellular energy production. Proton flow generates rotation in the F motor that is transferred to the F motor to catalyze ATP production, with flexible F/F coupling required for efficient catalysis. FF ATP synthase can also operate in reverse, hydrolyzing ATP and pumping protons, and in bacteria this function can be regulated by an inhibitory ε subunit. Here we present cryo-EM data showing E. coli FF ATP synthase in different rotational and inhibited sub-states, observed following incubation with 10 mM MgATP. Our structures demonstrate how structural transitions within the inhibitory ε subunit induce torsional movement in the central stalk, thereby enabling its rotation within the F motor. This highlights the importance of the central rotor for flexible coupling of the F and F motors and provides further insight into the regulatory mechanism mediated by subunit ε. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_27297.map.gz emd_27297.map.gz | 152.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-27297-v30.xml emd-27297-v30.xml emd-27297.xml emd-27297.xml | 28.7 KB 28.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_27297_fsc.xml emd_27297_fsc.xml | 12.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_27297.png emd_27297.png | 99.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-27297.cif.gz emd-27297.cif.gz | 7.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_27297_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27297_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27297_half_map_2.map.gz emd_27297_half_map_2.map.gz | 132.3 MB 132.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27297 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27297 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27297 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27297 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8dbpMC  8dbqC  8dbrC  8dbsC  8dbtC  8dbuC 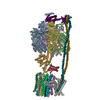 8dbvC  8dbwC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_27297.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_27297.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.079 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_27297_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_27297_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : ATP synthase
+Supramolecule #1: ATP synthase
+Macromolecule #1: ATP synthase subunit c
+Macromolecule #2: ATP synthase subunit alpha
+Macromolecule #3: ATP synthase subunit beta
+Macromolecule #4: ATP synthase gamma chain
+Macromolecule #5: ATP synthase epsilon chain
+Macromolecule #6: ATP synthase subunit delta
+Macromolecule #7: ATP synthase subunit b
+Macromolecule #8: ATP synthase subunit a
+Macromolecule #9: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #10: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #11: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 48.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










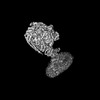
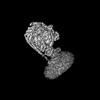


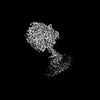








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)