+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-22523 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of a 12 base pair RecA-D loop complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | consensus reconstruction postprocessed with relion | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Recombination / DNA repair / DNA BINDING PROTEIN / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDNA polymerase V complex / homologous recombination / SOS response / recombinational repair / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / response to ionizing radiation / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / translesion synthesis / cell motility / single-stranded DNA binding ...DNA polymerase V complex / homologous recombination / SOS response / recombinational repair / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / response to ionizing radiation / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / translesion synthesis / cell motility / single-stranded DNA binding / DNA recombination / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / damaged DNA binding / DNA repair / DNA damage response / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Pavletich NP | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Mechanism of strand exchange from RecA-DNA synaptic and D-loop structures. Authors: Haijuan Yang / Chun Zhou / Ankita Dhar / Nikola P Pavletich /   Abstract: The strand-exchange reaction is central to homologous recombination. It is catalysed by the RecA family of ATPases, which form a helical filament with single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and ATP. This ...The strand-exchange reaction is central to homologous recombination. It is catalysed by the RecA family of ATPases, which form a helical filament with single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and ATP. This filament binds to a donor double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) to form synaptic filaments, which search for homology and then catalyse the exchange of the complementary strand, forming either a new heteroduplex or-if homology is limited-a D-loop. How synaptic filaments form, search for homology and catalyse strand exchange is poorly understood. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy analysis of synaptic mini-filaments with both non-complementary and partially complementary dsDNA, and structures of RecA-D-loop complexes containing a 10- or a 12-base-pair heteroduplex. The C-terminal domain of RecA binds to dsDNA and directs it to the RecA L2 loop, which inserts into and opens up the duplex. The opening propagates through RecA sequestering the homologous strand at a secondary DNA-binding site, which frees the complementary strand to sample pairing with the ssDNA. At each RecA step, there is a roughly 20% probability that duplex opening will terminate and the as-yet-unopened dsDNA portion will bind to another C-terminal domain. Homology suppresses this process, through the cooperation of heteroduplex pairing with the binding of ssDNA to the secondary site, to extend dsDNA opening. This mechanism locally limits the length of ssDNA sampled for pairing if homology is not encountered, and could allow for the formation of multiple, widely separated synapses on the donor dsDNA, which would increase the likelihood of encountering homology. These findings provide key mechanistic insights into homologous recombination. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_22523.map.gz emd_22523.map.gz | 59.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-22523-v30.xml emd-22523-v30.xml emd-22523.xml emd-22523.xml | 19 KB 19 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_22523.png emd_22523.png | 190 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-22523.cif.gz emd-22523.cif.gz | 5.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_22523_additional_1.map.gz emd_22523_additional_1.map.gz emd_22523_additional_2.map.gz emd_22523_additional_2.map.gz emd_22523_additional_3.map.gz emd_22523_additional_3.map.gz | 1.9 MB 4.4 MB 4.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22523 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22523 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22523 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22523 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7jy7MC  7jy6C  7jy8C  7jy9C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_22523.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_22523.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | consensus reconstruction postprocessed with relion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.096 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
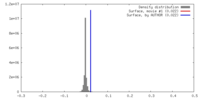
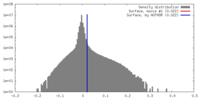
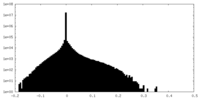
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
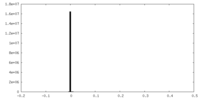
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: composite REFMAC5 map (masked) used in coordinate refinement
| File | emd_22523_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | composite REFMAC5 map (masked) used in coordinate refinement | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: reconstruction (masked) focused at 5' end postprocessed with relion
| File | emd_22523_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | reconstruction (masked) focused at 5' end postprocessed with relion | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: reconstruction (masked) focused at 3' end postprocessed with relion
| File | emd_22523_additional_3.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | reconstruction (masked) focused at 3' end postprocessed with relion | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Structure of a 12 base pair RecA-D loop complex.
| Entire | Name: Structure of a 12 base pair RecA-D loop complex. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Structure of a 12 base pair RecA-D loop complex.
| Supramolecule | Name: Structure of a 12 base pair RecA-D loop complex. / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Protein RecA
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein RecA / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 9 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 35.960281 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAIDENKQKA LAAALGQIEK QFGKGSIMRL GEDRSMDVET ISTGSLSLDI ALGAGGLPMG RIVEIYGPES SGKTTLTLQV IAAAQREGK TCAFIDAEHA LDPIYARKLG VDIDNLLCSQ PDTGEQALEI CDALARSGAV DVIVVDSVAA LTPKAEIEGE I GDSHMGLA ...String: MAIDENKQKA LAAALGQIEK QFGKGSIMRL GEDRSMDVET ISTGSLSLDI ALGAGGLPMG RIVEIYGPES SGKTTLTLQV IAAAQREGK TCAFIDAEHA LDPIYARKLG VDIDNLLCSQ PDTGEQALEI CDALARSGAV DVIVVDSVAA LTPKAEIEGE I GDSHMGLA ARMMSQAMRK LAGNLKQSNT LLIFINQIRM KIGVMFGNPE TTTGGNALKF YASVRLDIRR IGAVKEGENV VG SETRVKV VKNKIAAPFK QAEFQILYGE GINFYGELVD LGVKEKLIEK AGAWYSYKGE KIGQGKANAT AWLKDNPETA KEI EKKVRE LLLSNPNS UniProtKB: Protein RecA |
-Macromolecule #2: DNA (27-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (27-MER) / type: dna / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8.147223 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #3: DNA (48-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (48-MER) / type: dna / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.85651 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DT) (DC)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG) |
-Macromolecule #4: DNA (48-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (48-MER) / type: dna / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.735464 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DC) |
-Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 9 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #6: PHOSPHOTHIOPHOSPHORIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOTHIOPHOSPHORIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 9 / Formula: AGS |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 523.247 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-AGS: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 67.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 222426 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







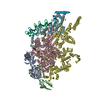
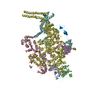

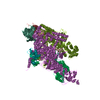
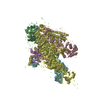
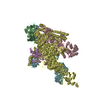


 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)