[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-42405: Preliminary map of the Prothrombin-prothrombinase complex on nano... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 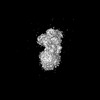 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Preliminary map of the Prothrombin-prothrombinase complex on nano discs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Unsharpened map | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Coagulation / Prothrombin / Prothrombinase / nanodisc / complex / BLOOD CLOTTING | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationresponse to vitamin K / coagulation factor Xa / platelet alpha granule / Cargo concentration in the ER / Defective factor IX causes thrombophilia / Defective cofactor function of FVIIIa variant / Defective F9 variant does not activate FX / COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle / Extrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / COPII-mediated vesicle transport ...response to vitamin K / coagulation factor Xa / platelet alpha granule / Cargo concentration in the ER / Defective factor IX causes thrombophilia / Defective cofactor function of FVIIIa variant / Defective F9 variant does not activate FX / COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle / Extrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / blood circulation / cytolysis by host of symbiont cells / thrombospondin receptor activity / thrombin-activated receptor signaling pathway / Defective factor XII causes hereditary angioedema / thrombin / negative regulation of astrocyte differentiation / regulation of blood coagulation / positive regulation of phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / neutrophil-mediated killing of gram-negative bacterium / Defective F8 cleavage by thrombin / Platelet Aggregation (Plug Formation) / ligand-gated ion channel signaling pathway / positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process / negative regulation of platelet activation / negative regulation of blood coagulation / positive regulation of blood coagulation / negative regulation of fibrinolysis / positive regulation of TOR signaling / regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / Transport of gamma-carboxylated protein precursors from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus / Gamma-carboxylation of protein precursors / Common Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / Removal of aminoterminal propeptides from gamma-carboxylated proteins / fibrinolysis / Intrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / negative regulation of proteolysis / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response / positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / Peptide ligand-binding receptors / platelet alpha granule lumen / Regulation of Complement cascade / acute-phase response / Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / Post-translational protein phosphorylation / lipopolysaccharide binding / growth factor activity / phospholipid binding / positive regulation of insulin secretion / platelet activation / response to wounding / Golgi lumen / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process / blood coagulation / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / Platelet degranulation / extracellular vesicle / regulation of cell shape / heparin binding / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / : / positive regulation of cell growth / blood microparticle / G alpha (q) signalling events / cell surface receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / positive regulation of cell migration / receptor ligand activity / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / copper ion binding / signaling receptor binding / serine-type endopeptidase activity / external side of plasma membrane / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / calcium ion binding / proteolysis / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.47 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Stojanovski BM / Mohammed BM / Di Cera E | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 8 items United States, 8 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Subcell Biochem / Year: 2024 Journal: Subcell Biochem / Year: 2024Title: The Prothrombin-Prothrombinase Interaction. Authors: Bosko M Stojanovski / Bassem M Mohammed / Enrico Di Cera /  Abstract: The hemostatic response to vascular injury entails a sequence of proteolytic events where several inactive zymogens of the trypsin family are converted to active proteases. The cascade starts with ...The hemostatic response to vascular injury entails a sequence of proteolytic events where several inactive zymogens of the trypsin family are converted to active proteases. The cascade starts with exposure of tissue factor from the damaged endothelium and culminates with conversion of prothrombin to thrombin in a reaction catalyzed by the prothrombinase complex composed of the enzyme factor Xa, cofactor Va, Ca, and phospholipids. This cofactor-dependent activation is paradigmatic of analogous reactions of the blood coagulation and complement cascades, which makes elucidation of its molecular mechanism of broad significance to the large class of trypsin-like zymogens to which prothrombin belongs. Because of its relevance as the most important reaction in the physiological response to vascular injury, as well as the main trigger of pathological thrombotic complications, the mechanism of prothrombin activation has been studied extensively. However, a molecular interpretation of this mechanism has become available only recently from important developments in structural biology. Here we review current knowledge on the prothrombin-prothrombinase interaction and outline future directions for the study of this key reaction of the coagulation cascade. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_42405.map.gz emd_42405.map.gz | 253.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-42405-v30.xml emd-42405-v30.xml emd-42405.xml emd-42405.xml | 22.3 KB 22.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_42405_fsc.xml emd_42405_fsc.xml | 16.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_42405.png emd_42405.png | 109.7 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_42405_msk_1.map emd_42405_msk_1.map | 512 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-42405.cif.gz emd-42405.cif.gz | 5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_42405_additional_1.map.gz emd_42405_additional_1.map.gz emd_42405_additional_2.map.gz emd_42405_additional_2.map.gz emd_42405_half_map_1.map.gz emd_42405_half_map_1.map.gz emd_42405_half_map_2.map.gz emd_42405_half_map_2.map.gz | 474.3 MB 474.3 MB 474.8 MB 474.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42405 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42405 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42405 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42405 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_42405_validation.pdf.gz emd_42405_validation.pdf.gz | 885.2 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_42405_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_42405_full_validation.pdf.gz | 884.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_42405_validation.xml.gz emd_42405_validation.xml.gz | 26.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_42405_validation.cif.gz emd_42405_validation.cif.gz | 35.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42405 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42405 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42405 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42405 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9cthMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_42405.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_42405.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unsharpened map | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.94 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Prothrombin_Prothrombinase complex on lipid nanodiscs.
| Entire | Name: Prothrombin_Prothrombinase complex on lipid nanodiscs. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Prothrombin_Prothrombinase complex on lipid nanodiscs.
| Supramolecule | Name: Prothrombin_Prothrombinase complex on lipid nanodiscs. type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 Details: The complex is made of coagulation factor Va (derived from human plasma), coagulation factor Xa (Recombinantly expressed in BHK cells) and Prothrombin (Recombinantly expressed in BHK cells). ...Details: The complex is made of coagulation factor Va (derived from human plasma), coagulation factor Xa (Recombinantly expressed in BHK cells) and Prothrombin (Recombinantly expressed in BHK cells). The nanodisc component of the complex is made of the scaffold protein MSP1E3D1 (Recombinantly expressed in bacteria) and the phospholipid component was Porcine Brain phosphatidylserine. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: Blood Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: Blood |
-Supramolecule #2: Coagulation Factor Va
| Supramolecule | Name: Coagulation Factor Va / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: Blood Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: Blood |
-Supramolecule #3: Coagulation Factor Xa
| Supramolecule | Name: Coagulation Factor Xa / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 Details: Catalytically inactive full length mutant S379A with C-terminus HPC4 tag. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: Blood Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: Blood |
-Supramolecule #4: Prothrombin
| Supramolecule | Name: Prothrombin / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 Details: Catalytically inactive full length mutant S525A with C-terminus HPC4 tag |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: Blood Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: Blood |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.01 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 / Details: 20 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, and 5 mM CaCl2 |
| Grid | Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
| Details | Prothrombin:FVa:FXa were mixed in 2:1:2 ratio. 0.01 mg/mL total protein was used for freezing. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 2390 / Average electron dose: 51.28 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-9cth: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


















