+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of human exostosin-like 3 (EXTL3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | glycosyltransferase / heparan / n-acetylglucosaminyltransferase / TRANSFERASE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglucuronosyl-galactosyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase / glucuronyl-galactosyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity / positive regulation of detection of glucose / protein-hormone receptor activity / positive regulation of keratinocyte proliferation / heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process / negative regulation of keratinocyte differentiation / negative regulation of inflammatory response to wounding / XBP1(S) activates chaperone genes / : ...glucuronosyl-galactosyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase / glucuronyl-galactosyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity / positive regulation of detection of glucose / protein-hormone receptor activity / positive regulation of keratinocyte proliferation / heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process / negative regulation of keratinocyte differentiation / negative regulation of inflammatory response to wounding / XBP1(S) activates chaperone genes / : / glycosyltransferase activity / negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response / negative regulation of inflammatory response / positive regulation of cell growth / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / magnesium ion binding / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / nucleus / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.43 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wilson LFL / Dendooven T | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  Sweden, 8 items Sweden, 8 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: The structure of EXTL3 helps to explain the different roles of bi-domain exostosins in heparan sulfate synthesis. Authors: L F L Wilson / T Dendooven / S W Hardwick / A Echevarría-Poza / T Tryfona / K B R M Krogh / D Y Chirgadze / B F Luisi / D T Logan / K Mani / P Dupree /     Abstract: Heparan sulfate is a highly modified O-linked glycan that performs diverse physiological roles in animal tissues. Though quickly modified, it is initially synthesised as a polysaccharide of ...Heparan sulfate is a highly modified O-linked glycan that performs diverse physiological roles in animal tissues. Though quickly modified, it is initially synthesised as a polysaccharide of alternating β-D-glucuronosyl and N-acetyl-α-D-glucosaminyl residues by exostosins. These enzymes generally possess two glycosyltransferase domains (GT47 and GT64)-each thought to add one type of monosaccharide unit to the backbone. Although previous structures of murine exostosin-like 2 (EXTL2) provide insight into the GT64 domain, the rest of the bi-domain architecture is yet to be characterised; hence, how the two domains co-operate is unknown. Here, we report the structure of human exostosin-like 3 (EXTL3) in apo and UDP-bound forms. We explain the ineffectiveness of EXTL3's GT47 domain to transfer β-D-glucuronosyl units, and we observe that, in general, the bi-domain architecture would preclude a processive mechanism of backbone extension. We therefore propose that heparan sulfate backbone polymerisation occurs by a simple dissociative mechanism. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_11923.map.gz emd_11923.map.gz | 264.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-11923-v30.xml emd-11923-v30.xml emd-11923.xml emd-11923.xml | 13.4 KB 13.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_11923_fsc.xml emd_11923_fsc.xml | 14.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_11923.png emd_11923.png | 216.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-11923.cif.gz emd-11923.cif.gz | 6.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11923 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11923 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11923 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11923 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7au2MC  7auaC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_11923.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 282.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_11923.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 282.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.6667 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
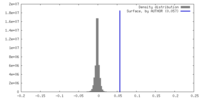
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Homodimer of EXTL3 globular domain
| Entire | Name: Homodimer of EXTL3 globular domain |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Homodimer of EXTL3 globular domain
| Supramolecule | Name: Homodimer of EXTL3 globular domain / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 170 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Exostosin-like 3
| Macromolecule | Name: Exostosin-like 3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: glucuronosyl-galactosyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 101.705117 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: APQLHHHHHH DLYENLYFQG KLTTLDEADE AGKRIFGPRV GNELCEVKHV LDLCRIRESV SEELLQLEAK RQELNSEIAK LNLKIEACK KSIENAKQDL LQLKNVISQT EHSYKELMAQ NQPKLSLPIR LLPEKDDAGL PPPKATRGCR LHNCFDYSRC P LTSGFPVY ...String: APQLHHHHHH DLYENLYFQG KLTTLDEADE AGKRIFGPRV GNELCEVKHV LDLCRIRESV SEELLQLEAK RQELNSEIAK LNLKIEACK KSIENAKQDL LQLKNVISQT EHSYKELMAQ NQPKLSLPIR LLPEKDDAGL PPPKATRGCR LHNCFDYSRC P LTSGFPVY VYDSDQFVFG SYLDPLVKQA FQATARANVY VTENADIACL YVILVGEMQE PVVLRPAELE KQLYSLPHWR TD GHNHVII NLSRKSDTQN LLYNVSTGRA MVAQSTFYTV QYRPGFDLVV SPLVHAMSEP NFMEIPPQVP VKRKYLFTFQ GEK IESLRS SLQEARSFEE EMEGDPPADY DDRIIATLKA VQDSKLDQVL VEFTCKNQPK PSLPTEWALC GEREDRLELL KLST FALII TPGDPRLVIS SGCATRLFEA LEVGAVPVVL GEQVQLPYQD MLQWNEAALV VPKPRVTEVH FLLRSLSDSD LLAMR RQGR FLWETYFSTA DSIFNTVLAM IRTRIQIPAA PIREEAAAEI PHRSGKAAGT DPNMADNGDL DLGPVETEPP YASPRY LRN FTLTVTDFYR SWNCAPGPFH LFPHTPFDPV LPSEAKFLGS GTGFRPIGGG AGGSGKEFQA ALGGNVPREQ FTVVMLT YE REEVLMNSLE RLNGLPYLNK VVVVWNSPKL PSEDLLWPDI GVPIMVVRTE KNSLNNRFLP WNEIETEAIL SIDDDAHL R HDEIMFGFRV WREARDRIVG FPGRYHAWDI PHQSWLYNSN YSCELSMVLT GAAFFHKYYA YLYSYVMPQA IRDMVDEYI NCEDIAMNFL VSHITRKPPI KVTSRWTFRC PGCPQALSHD DSHFHERHKC INFFVKVYGY MPLLYTQFRV DSVLFKTRLP HDKTKCFKF I UniProtKB: Exostosin-like 3 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil / Material: COPPER / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Average electron dose: 71.4 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7au2: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)