[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-9617: Structure of the human voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.4 in com... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-9617 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the human voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.4 in complex with beta1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | sodium channel / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of skeletal muscle contraction by action potential / corticospinal neuron axon guidance / positive regulation of voltage-gated sodium channel activity / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane depolarization / membrane depolarization during Purkinje myocyte cell action potential / cardiac conduction / membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / membrane depolarization during action potential / positive regulation of sodium ion transport / regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transport ...regulation of skeletal muscle contraction by action potential / corticospinal neuron axon guidance / positive regulation of voltage-gated sodium channel activity / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane depolarization / membrane depolarization during Purkinje myocyte cell action potential / cardiac conduction / membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / membrane depolarization during action potential / positive regulation of sodium ion transport / regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transport / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / node of Ranvier / voltage-gated sodium channel complex / sodium channel inhibitor activity / locomotion / neuronal action potential propagation / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / voltage-gated sodium channel activity / sodium ion transport / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / intercalated disc / sodium channel regulator activity / membrane depolarization / cardiac muscle contraction / T-tubule / axon guidance / muscle contraction / sodium ion transmembrane transport / positive regulation of neuron projection development / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / perikaryon / transmembrane transporter binding / cell adhesion / extracellular region / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Pan XJ / li ZQ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 6 items China, 6 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2018 Journal: Science / Year: 2018Title: Structure of the human voltage-gated sodium channel Na1.4 in complex with β1. Authors: Xiaojing Pan / Zhangqiang Li / Qiang Zhou / Huaizong Shen / Kun Wu / Xiaoshuang Huang / Jiaofeng Chen / Juanrong Zhang / Xuechen Zhu / Jianlin Lei / Wei Xiong / Haipeng Gong / Bailong Xiao / Nieng Yan /  Abstract: Voltage-gated sodium (Na) channels, which are responsible for action potential generation, are implicated in many human diseases. Despite decades of rigorous characterization, the lack of a structure ...Voltage-gated sodium (Na) channels, which are responsible for action potential generation, are implicated in many human diseases. Despite decades of rigorous characterization, the lack of a structure of any human Na channel has hampered mechanistic understanding. Here, we report the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the human Na1.4-β1 complex at 3.2-Å resolution. Accurate model building was made for the pore domain, the voltage-sensing domains, and the β1 subunit, providing insight into the molecular basis for Na permeation and kinetic asymmetry of the four repeats. Structural analysis of reported functional residues and disease mutations corroborates an allosteric blocking mechanism for fast inactivation of Na channels. The structure provides a path toward mechanistic investigation of Na channels and drug discovery for Na channelopathies. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_9617.map.gz emd_9617.map.gz | 49.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-9617-v30.xml emd-9617-v30.xml emd-9617.xml emd-9617.xml | 16.8 KB 16.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_9617.png emd_9617.png | 69.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-9617.cif.gz emd-9617.cif.gz | 7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9617 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9617 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9617 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9617 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 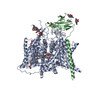 6agfMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_9617.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_9617.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.091 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of human sodium channel protein type 4 subunit alpha and ...
| Entire | Name: Complex of human sodium channel protein type 4 subunit alpha and human sodium channel subunit beta-1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of human sodium channel protein type 4 subunit alpha and ...
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of human sodium channel protein type 4 subunit alpha and human sodium channel subunit beta-1 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 200 KDa |
-Supramolecule #2: Human sodium channel protein type 4 subunit alpha
| Supramolecule | Name: Human sodium channel protein type 4 subunit alpha / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: Human sodium channel subunit beta-1
| Supramolecule | Name: Human sodium channel subunit beta-1 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Sodium channel protein type 4 subunit alpha
| Macromolecule | Name: Sodium channel protein type 4 subunit alpha / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 212.836375 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MASWSHPQFE KGGGARGGSG GGSWSHPQFE KGFDYKDDDD KGTMARPSLC TLVPLGPECL RPFTRESLAA IEQRAVEEEA RLQRNKQME IEEPERKPRS DLEAGKNLPM IYGDPPPEVI GIPLEDLDPY YSNKKTFIVL NKGKAIFRFS ATPALYLLSP F SVVRRGAI ...String: MASWSHPQFE KGGGARGGSG GGSWSHPQFE KGFDYKDDDD KGTMARPSLC TLVPLGPECL RPFTRESLAA IEQRAVEEEA RLQRNKQME IEEPERKPRS DLEAGKNLPM IYGDPPPEVI GIPLEDLDPY YSNKKTFIVL NKGKAIFRFS ATPALYLLSP F SVVRRGAI KVLIHALFSM FIMITILTNC VFMTMSDPPP WSKNVEYTFT GIYTFESLIK ILARGFCVDD FTFLRDPWNW LD FSVIMMA YLTEFVDLGN ISALRTFRVL RALKTITVIP GLKTIVGALI QSVKKLSDVM ILTVFCLSVF ALVGLQLFMG NLR QKCVRW PPPFNDTNTT WYSNDTWYGN DTWYGNEMWY GNDSWYANDT WNSHASWATN DTFDWDAYIS DEGNFYFLEG SNDA LLCGN SSDAGHCPEG YECIKTGRNP NYGYTSYDTF SWAFLALFRL MTQDYWENLF QLTLRAAGKT YMIFFVVIIF LGSFY LINL ILAVVAMAYA EQNEATLAED KEKEEEFQQM LEKFKKHQEE LEKAKAAQAL EGGEADGDPA HGKDCNGSLD TSQGEK GAP RQSSSGDSGI SDAMEELEEA HQKCPPWWYK CAHKVLIWNC CAPWLKFKNI IHLIVMDPFV DLGITICIVL NTLFMAM EH YPMTEHFDNV LTVGNLVFTG IFTAEMVLKL IAMDPYEYFQ QGWNIFDSII VTLSLVELGL ANVQGLSVLR SFRLLRVF K LAKSWPTLNM LIKIIGNSVG ALGNLTLVLA IIVFIFAVVG MQLFGKSYKE CVCKIALDCN LPRWHMHDFF HSFLIVFRI LCGEWIETMW DCMEVAGQAM CLTVFLMVMV IGNLVVLNLF LALLLSSFSA DSLAASDEDG EMNNLQIAIG RIKLGIGFAK AFLLGLLHG KILSPKDIML SLGEADGAGE AGEAGETAPE DEKKEPPEED LKKDNHILNH MGLADGPPSS LELDHLNFIN N PYLTIQVP IASEESDLEM PTEEETDTFS EPEDSKKPPQ PLYDGNSSVC STADYKPPEE DPEEQAEENP EGEQPEECFT EA CVQRWPC LYVDISQGRG KKWWTLRRAC FKIVEHNWFE TFIVFMILLS SGALAFEDIY IEQRRVIRTI LEYADKVFTY IFI MEMLLK WVAYGFKVYF TNAWCWLDFL IVDVSIISLV ANWLGYSELG PIKSLRTLRA LRPLRALSRF EGMRVVVNAL LGAI PSIMN VLLVCLIFWL IFSIMGVNLF AGKFYYCINT TTSERFDISE VNNKSECESL MHTGQVRWLN VKVNYDNVGL GYLSL LQVA TFKGWMDIMY AAVDSREKEE QPQYEVNLYM YLYFVIFIIF GSFFTLNLFI GVIIDNFNQQ KKKLGGKDIF MTEEQK KYY NAMKKLGSKK PQKPIPRPQN KIQGMVYDLV TKQAFDITIM ILICLNMVTM MVETDNQSQL KVDILYNINM IFIIIFT GE CVLKMLALRQ YYFTVGWNIF DFVVVILSIV GLALSDLIQK YFVSPTLFRV IRLARIGRVL RLIRGAKGIR TLLFALMM S LPALFNIGLL LFLVMFIYSI FGMSNFAYVK KESGIDDMFN FETFGNSIIC LFEITTSAGW DGLLNPILNS GPPDCDPNL ENPGTSVKGD CGNPSIGICF FCSYIIISFL IVVNMYIAII LENFNVATEE SSEPLGEDDF EMFYETWEKF DPDATQFIAY SRLSDFVDT LQEPLRIAKP NKIKLITLDL PMVPGDKIHC LDILFALTKE VLGDSGEMDA LKQTMEEKFM AANPSKVSYE P ITTTLKRK HEEVCAIKIQ RAYRRHLLQR SMKQASYMYR HSHDGSGDDA PEKEGLLANT MSKMYGHENG NSSSPSPEEK GE AGDAGPT MGLMPISPSD TAWPPAPPPG QTVRPGVKES LV UniProtKB: Sodium channel protein type 4 subunit alpha |
-Macromolecule #2: Sodium channel subunit beta-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Sodium channel subunit beta-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.732115 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGRLLALVVG AALVSSACGG CVEVDSETEA VYGMTFKILC ISCKRRSETN AETFTEWTFR QKGTEEFVKI LRYENEVLQL EEDERFEGR VVWNGSRGTK DLQDLSIFIT NVTYNHSGDY ECHVYRLLFF ENYEHNTSVV KKIHIEVVDK ANRDMASIVS E IMMYVLIV ...String: MGRLLALVVG AALVSSACGG CVEVDSETEA VYGMTFKILC ISCKRRSETN AETFTEWTFR QKGTEEFVKI LRYENEVLQL EEDERFEGR VVWNGSRGTK DLQDLSIFIT NVTYNHSGDY ECHVYRLLFF ENYEHNTSVV KKIHIEVVDK ANRDMASIVS E IMMYVLIV VLTIWLVAEM IYCYKKIAAA TETAAQENAS EYLAITSESK ENCTGVQVAE UniProtKB: Sodium channel regulatory subunit beta-1 |
-Macromolecule #5: [(2~{R})-1-[2-azanylethoxy(oxidanyl)phosphoryl]oxy-3-hexadecanoyl...
| Macromolecule | Name: [(2~{R})-1-[2-azanylethoxy(oxidanyl)phosphoryl]oxy-3-hexadecanoyloxy-propan-2-yl] (~{Z})-octadec-9-enoate type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: 6OU |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 717.996 Da |
| Chemical component information | 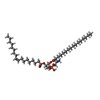 ChemComp-6OU: |
-Macromolecule #6: (3beta,14beta,17beta,25R)-3-[4-methoxy-3-(methoxymethyl)butoxy]sp...
| Macromolecule | Name: (3beta,14beta,17beta,25R)-3-[4-methoxy-3-(methoxymethyl)butoxy]spirost-5-en type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: 9Z9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 544.805 Da |
| Chemical component information | 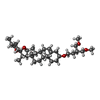 ChemComp-9Z9: |
-Macromolecule #7: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 5.9 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 48.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






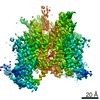





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















