[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-9050: In situ structure of transcriptional enzyme complex and asymmetri... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-9050 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
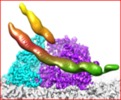
| Title | In situ structure of transcriptional enzyme complex and asymmetric inner capsid protein of aquareovirus at primed state | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
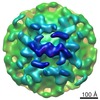
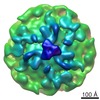
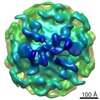
 Map data Map data | Grass Carp reovirus TEC structure at primed state | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample | transcriptional enzyme complex and asymmetric inner capsid protein != Grass carp reovirus transcriptional enzyme complex and asymmetric inner capsid protein
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Reovirus / transcriptional enzyme complex / polymerase / RdRp / NTPase / VIRAL PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhost cytoskeleton / viral inner capsid / 7-methylguanosine mRNA capping / viral genome replication / viral capsid / viral nucleocapsid / host cell cytoplasm / RNA helicase activity / RNA helicase / hydrolase activity ...host cytoskeleton / viral inner capsid / 7-methylguanosine mRNA capping / viral genome replication / viral capsid / viral nucleocapsid / host cell cytoplasm / RNA helicase activity / RNA helicase / hydrolase activity / RNA-directed RNA polymerase / RNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / structural molecule activity / RNA binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Grass carp reovirus Grass carp reovirus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ding K / Zhou ZH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 8 items United States, 8 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2018 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2018Title: Structures of the Polymerase Complex and RNA Genome Show How Aquareovirus Transcription Machineries Respond to Uncoating. Authors: Ke Ding / Lisa Nguyen / Z Hong Zhou /  Abstract: Reoviruses carry out genomic RNA transcription within intact viruses to synthesize plus-sense RNA strands, which are capped prior to their release as mRNA. The structures of the transcriptional ...Reoviruses carry out genomic RNA transcription within intact viruses to synthesize plus-sense RNA strands, which are capped prior to their release as mRNA. The structures of the transcriptional enzyme complex (TEC) containing the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) and NTPase are known for the single-layered reovirus cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus (CPV), but not for multilayered reoviruses, such as aquareoviruses (ARV), which possess a primed stage that CPV lacks. Consequently, how the RNA genome and TEC respond to priming in reoviruses is unknown. Here, we determined the near-atomic-resolution asymmetric structure of ARV in the primed state by cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), revealing the structures of 11 TECs inside each capsid and their interactions with the 11 surrounding double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) genome segments and with the 120 enclosing capsid shell protein (CSP) VP3 subunits. The RdRp VP2 and the NTPase VP4 associate with each other and with capsid vertices; both bind RNA in multiple locations, including a novel C-terminal domain of VP4. Structural comparison between the primed and quiescent states showed translocation of the dsRNA end from the NTPase to the RdRp during priming. The RNA template channel was open in both states, suggesting that channel blocking is not a regulating mechanism between these states in ARV. Instead, the NTPase C-terminal domain appears to regulate RNA translocation between the quiescent and primed states. Taking the data together, dsRNA viruses appear to have adapted divergent mechanisms to regulate genome transcription while retaining similar mechanisms to coassemble their genome segments, TEC, and capsid proteins into infectious virions. Viruses in the family are characterized by the ability to endogenously synthesize nascent RNA within the virus. However, the mechanisms for assembling their RNA genomes with transcriptional enzymes into a multilayered virion and for priming such a virion for transcription are poorly understood. By cryo-EM and novel asymmetric reconstruction, we determined the atomic structure of the transcription complex inside aquareoviruses (ARV) that are primed for infection. The transcription complex is anchored by the N-terminal segments of enclosing capsid proteins and contains an NTPase and a polymerase. The NTPase has a newly discovered domain that translocates the 5' end of plus-sense RNA in segmented dsRNA genomes from the NTPase to polymerase VP2 when the virus changes from the inactive (quiescent) to the primed state. Conformation changes in capsid proteins and transcriptional complexes suggest a mechanism for relaying information from the outside to the inside of the virus during priming. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_9050.map.gz emd_9050.map.gz | 95.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-9050-v30.xml emd-9050-v30.xml emd-9050.xml emd-9050.xml | 18.6 KB 18.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_9050.png emd_9050.png | 192.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-9050.cif.gz emd-9050.cif.gz | 7.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_9050_additional.map.gz emd_9050_additional.map.gz | 1.1 GB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9050 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9050 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9050 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9050 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6m99MC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_9050.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_9050.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Grass Carp reovirus TEC structure at primed state | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.33 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: True asymmetric reconstruction
| File | emd_9050_additional.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | True asymmetric reconstruction | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
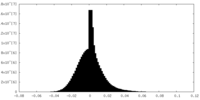
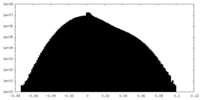
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : transcriptional enzyme complex and asymmetric inner capsid protein
| Entire | Name: transcriptional enzyme complex and asymmetric inner capsid protein |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Grass carp reovirus
| Supramolecule | Name: Grass carp reovirus / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 / NCBI-ID: 128987 / Sci species name: Grass carp reovirus / Virus type: VIRION / Virus isolate: STRAIN / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: No |
|---|---|
| Host (natural) | Organism:  Ctenopharyngodon idella (grass carp) Ctenopharyngodon idella (grass carp) |
-Macromolecule #1: VP2
| Macromolecule | Name: VP2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Grass carp reovirus Grass carp reovirus |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 141.685438 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MEELFNALPQ PLQQLSLALA GEIPLTDHIF EQAASTWHVQ PRSLTYKLLD HIPFATPVVV PPSIYHSLDW SKCFAVNQDR VERIPTIDN PDDVYVPNSD IGPLLTSLHT IPDYGFLHPT IENDATTLRA ERARCASTFY KIASSQARQV KLDPIRMLGF L LLVQARPR ...String: MEELFNALPQ PLQQLSLALA GEIPLTDHIF EQAASTWHVQ PRSLTYKLLD HIPFATPVVV PPSIYHSLDW SKCFAVNQDR VERIPTIDN PDDVYVPNSD IGPLLTSLHT IPDYGFLHPT IENDATTLRA ERARCASTFY KIASSQARQV KLDPIRMLGF L LLVQARPR VPSGLVTDQP TRRDPTLSPA LHAIWQVMQY YKVAGVYYAP ALVVPSGAIW WIPPPGKRNV VSVQYLLTDL IS LAILAHM TDMSPTLELT GVLMYLRAAS SHSYAYTLLQ MKSVFPALSL RSMYRNKGFG GKAPAIEWTE PRSKYKFRWT GVT QLHDGL RPRSPSMDVP TLETLAKYEL VDIGHTIIRE RNAHPQHNHD SVRFVRDVMA LTSGMYLVRQ PTMSVLREYS QVPD IKDPI PPSAWTGPIG NVRYLLPSVQ GPARHLYDTW RAAARQIAQD PQWHDPLNQA IMRAQYVTAR GGSSASLKFA LKVTG IVLP EYDDSKVKKS SKIYQAAQIA RIAFMLLIAA IHAEVTMGIR NQVQRRARSI MPLNVIQQAI SAPHTLVANY INKHMN LST TSGSVVTDKV IPLILYASTP PNTVVNVDIK ACDASITYNY FLSVICGAMH EGFEVGNADA AFMGVPSTIV SDRRSPV AP YSRPISGLQT MVQHLADLYA AGFRYSVSDA FSSGNKFSFP TSTFPSGSTA TSTEHTANNS TMMEYFLNVH APSHVKSA S LKRILTDMTI QRNYVCQGDD GILLLPHEAA SKISADDMNE LLTCLRDYGQ LFGWNYDIDW SDTAEYLKLY ALMGCRIPN TSRHPPVGKE YAAPQTDEIW PSLIDIVIGH HLNGVTDVLN WREWLRFSWA FACYSSRGGY TNPRGQSFSA QYPWWTFVYL GIPPILLPG QTPFIHSCYM PPGDQGMFSI LNGWRDWLIS HASTTLPPLR HNHPVWGLSD VPSLLSQFGV YAGYHAAQHY R RPKPAPET ASSDSINQIT SDLTEYLFYD SALKARVMKG RYNWERLSSS LSLNVGSRVP SLFDVPGKWV AAGRDAEKPP PS SVEDMFT SLNRCIRRPT HSFSRLLELY LRVHVALGES IPLAIDPDVP QVAGADPAND DHWFKYTCLG DIPSATRNYF GES LFVGRV VSGLDVEAVD ATLLRLKILG APPEAFIAVL NGIGMSDSEA HQIAGRISLA NAQLVQIARV VHLSIPSSWM TLNT GPYIH HHAYDFKPGI TQPSAKSRDK SIWMSPILKL LCTSYAMTVA GPVRTSIVTE IDGSAAALSG NLRVWMRDV UniProtKB: RNA-directed RNA polymerase |
-Macromolecule #2: Putative core protein NTPase/VP5
| Macromolecule | Name: Putative core protein NTPase/VP5 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Grass carp reovirus Grass carp reovirus |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 80.381516 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MITIVVIPTA HFSWTDTNFL NSVDYRLTSQ PKIRDRFAVY APGWLRRQLD EFSASLTASE LLQALQTIPI PVKARCLLLP KPKRFAQWL LDVPSANIWH IPVTTLRATV ASKHPSSDVY NYIPDHVPPN AEFDTVTRRV AAGRDIYVRS TKVIGAPLCL A APAKYYAG ...String: MITIVVIPTA HFSWTDTNFL NSVDYRLTSQ PKIRDRFAVY APGWLRRQLD EFSASLTASE LLQALQTIPI PVKARCLLLP KPKRFAQWL LDVPSANIWH IPVTTLRATV ASKHPSSDVY NYIPDHVPPN AEFDTVTRRV AAGRDIYVRS TKVIGAPLCL A APAKYYAG YLSTHQLDGI YPENWAPDNF HKREFCLTIL PSLLGPRTFL LDVDADRDAS YPLSVLWPQL RALALKSRLL LP PVALLRR VVDPGLKPTW SADSDAAFRA LRLSRPSSAS KPVGFDFSAL PVVDIICLLE SEPDDHGRIA PGTRLTIHSV PTD LLTSLS IQEGVRYPLR QESGMFVHWV LLALLMSDDV TISGTRRSVK LETAHASARP FVHITVERCA SARIIDVRGS PAMY ANAVC LTLPKGSYKS TIIDTLPAMF SDLPILEQAA VIDSDALGDS LRPSFETQFL ERLENLDPNL LDRAVASILS PTSDT SDDA VTTVLDAFNA LYREIMTPAQ RARLPLLTQQ GRVLAFAHSD YELLSANIPI QVVRGSIPID HVVNLLARRN RVGGTA LQV LLDYCYRTQA SPLAPTPAGR LYKQLFGPWL MVPRLSEPLI KLRLVASAPA KVLRAAGWTI DGDPPLEVSC LCAYVTD RA AATALIERRL DSRALVTVGG DQLMFVEYAP PLPLVSIPRT FLLPVTYVVH WVPPQRVLLN GGNVSFTSGL EWTFDDDP Q VVTSTGV UniProtKB: Putative core protein NTPase/VP5 |
-Macromolecule #3: VP3
| Macromolecule | Name: VP3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 10 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Grass carp reovirus Grass carp reovirus |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 132.203312 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MPRRSARKAQ SAIASPADTN VVPAKDAPTT NSPPSTTSPN QAAADANQQQ AGIVSSQSGP NAVGDSAPSS SVNNDGDIIT RPTSDSIAA VANATKPAAV VSDPQSMKVT PIVNPSSYVC NVCNARFSTM SALSEHLRSD HRDDASTLLA TPMINNAIRS F LTAWDDIR ...String: MPRRSARKAQ SAIASPADTN VVPAKDAPTT NSPPSTTSPN QAAADANQQQ AGIVSSQSGP NAVGDSAPSS SVNNDGDIIT RPTSDSIAA VANATKPAAV VSDPQSMKVT PIVNPSSYVC NVCNARFSTM SALSEHLRSD HRDDASTLLA TPMINNAIRS F LTAWDDIR ILSPDVSSKS LSAYLDSAVA NGPELIIEDT GLCTSFMLLD NIPSAHLTKE LIGFTWFMQM YQMTPPLPEG AV NRIVCMT NWASLGDEGR GLEVRLPPPT DSSVHAYKTV LSRGYIDNAQ FNPLALRSNV LLMLLQFTLS NLKINKSSTF TSD VTTITS GRMIRAFEGR PELLALAYPG RAVLPTQTKN AQFLSTAIAD RIGRLDRANL IGGEVSAMVE CMELCDALTL HIRE TYIML LRSMHQDPTQ IVQIVNECAN NLLNSTIPIS LRPTILCPWF ASSEDLRLQQ VMHLVNISSN TAAALPLVEA LSTLL RSVT PLVLDPTVLT NAITTISEST TQTISPISEI LRLLQPMGND YAAFWKCIAS WAYNGLVTTV LSEDAFPDSS QSITHL PSM WKCLFLTLAG PMTSDPHSPV KVFMALANLL AQPEPIAIGV PGMHQTTPAS QFSHPGVWPP GFLNPQLINP QQAPLLR AF AEHIRANWPQ PSEFGYGSTL QGSANLFIPS NRMVYPWPNQ PLPRLTVAPT YDSAMSNWIS TTIAFFIRVV NSVNMTAT V NDLTRRTMTG VMTAMRQVKT MTPFYIQHMC PTELSVLASV TVTPPFQVPF TRLVQNDVIT NVLVARVDPA QRGDAAVDI RATHATFAAA LPVDPAAIVV AMLCGQTETN LIPSHHYGKA FAPLFASNAM FTRNQRAVIT REAFVCARSA VAQCQDAGFL VPRPLDALR QFDVTSAAAA EIMHAVNDAF KTAFDLDGAL LDGLALYGDP RIADLSAAYL QYGGNVVREH VPPGPSHIHR A LQQVESTF MAEMNLFNVA RGNLYLVQTA TNGNWSPMAP VAAPPFVRGG PNVRVVGRFG TIVPRPNGLE PQLIDDGNVP RD IAGDWVY PSDVLQVSVA VFRDYVWPMV KAGRTRVLVE LGHYVYTLHY YDPQISLDEA PILEEWLSKI NPAGIPPVPF CIP IPQVYP CITARRVHYA FTSENNNDSL FSTNAASIDT AFGENAAVSP LRWPGLVDPN YRVGTNDLPN RITLYNSLYR YNFT YPTLD GIMYVRSAT UniProtKB: RNA helicase |
-Macromolecule #4: PHOSPHATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 94.971 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PO4: |
-Macromolecule #5: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 25.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 73472 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)