[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
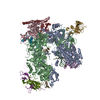
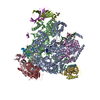
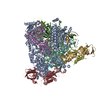
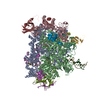
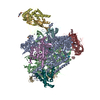
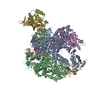
Yorodumi- PDB-7vbb: Structure of the post state human RNA Polymerase I Elongation Complex -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7vbb | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the post state human RNA Polymerase I Elongation Complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION/DNA/RNA / RNA Polymerase I / transcription / post state / TRANSCRIPTION-DNA-RNA complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRNA polymerase I transcription regulator complex / nucleologenesis / negative regulation of protein localization to nucleolus / neural crest formation / RNA Polymerase III Chain Elongation / DNA/RNA hybrid binding / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Termination / RNA polymerase I general transcription initiation factor binding / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / RPAP3/R2TP/prefoldin-like complex ...RNA polymerase I transcription regulator complex / nucleologenesis / negative regulation of protein localization to nucleolus / neural crest formation / RNA Polymerase III Chain Elongation / DNA/RNA hybrid binding / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Termination / RNA polymerase I general transcription initiation factor binding / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / RPAP3/R2TP/prefoldin-like complex / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 1 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 3 Promoter / RNA polymerase I preinitiation complex assembly / RNA Polymerase III Abortive And Retractive Initiation / Cytosolic sensors of pathogen-associated DNA / nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process / Abortive elongation of HIV-1 transcript in the absence of Tat / FGFR2 alternative splicing / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Termination / MicroRNA (miRNA) biogenesis / Viral Messenger RNA Synthesis / Signaling by FGFR2 IIIa TM / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE during HIV infection / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Formation of the HIV-1 Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription / HIV Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II HIV Promoter Escape / Transcription of the HIV genome / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) biogenesis / nucleolar large rRNA transcription by RNA polymerase I / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase I promoter / rRNA transcription / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / transcription by RNA polymerase III / Pausing and recovery of Tat-mediated HIV elongation / Tat-mediated HIV elongation arrest and recovery / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / HIV elongation arrest and recovery / Pausing and recovery of HIV elongation / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / RNA polymerase I complex / RNA polymerase III complex / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I / Formation of HIV elongation complex in the absence of HIV Tat / RNA polymerase II, core complex / tRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III / transcription by RNA polymerase I / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / embryo implantation / cell surface receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / DNA-templated transcription initiation / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / protein-DNA complex / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / ribonucleoside binding / Transcription-Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair (TC-NER) / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / fibrillar center / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / single-stranded DNA binding / chromosome / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / nucleic acid binding / transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein dimerization activity / protein stabilization / chromatin binding / chromatin / nucleolus / magnesium ion binding / mitochondrion / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.81 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao, D. / Liu, W. / Chen, K. / Yang, H. / Xu, Y. | ||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Discov / Year: 2021 Journal: Cell Discov / Year: 2021Title: Structure of the human RNA polymerase I elongation complex. Authors: Dan Zhao / Weida Liu / Ke Chen / Zihan Wu / Huirong Yang / Yanhui Xu /  Abstract: Eukaryotic RNA polymerase I (Pol I) transcribes ribosomal DNA and generates RNA for ribosome synthesis. Pol I accounts for the majority of cellular transcription activity and dysregulation of Pol I ...Eukaryotic RNA polymerase I (Pol I) transcribes ribosomal DNA and generates RNA for ribosome synthesis. Pol I accounts for the majority of cellular transcription activity and dysregulation of Pol I transcription leads to cancers and ribosomopathies. Despite extensive structural studies of yeast Pol I, structure of human Pol I remains unsolved. Here we determined the structures of the human Pol I in the pre-translocation, post-translocation, and backtracked states at near-atomic resolution. The single-subunit peripheral stalk lacks contacts with the DNA-binding clamp and is more flexible than the two-subunit stalk in yeast Pol I. Compared to yeast Pol I, human Pol I possesses a more closed clamp, which makes more contacts with DNA. The Pol I structure in the post-cleavage backtracked state shows that the C-terminal zinc ribbon of RPA12 inserts into an open funnel and facilitates "dinucleotide cleavage" on mismatched DNA-RNA hybrid. Critical disease-associated mutations are mapped on Pol I regions that are involved in catalysis and complex organization. In summary, the structures provide new sights into human Pol I complex organization and efficient proofreading. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7vbb.cif.gz 7vbb.cif.gz | 770.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7vbb.ent.gz pdb7vbb.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7vbb.json.gz 7vbb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vb/7vbb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vb/7vbb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vb/7vbb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vb/7vbb | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  31877MC  7vbaC  7vbcC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase I subunit ... , 6 types, 6 molecules ABINGM
| #1: Protein | Mass: 194911.859 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1A / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1A / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O95602, DNA-directed RNA polymerase Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O95602, DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 128379.219 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1B / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1B / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9H9Y6, DNA-directed RNA polymerase Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9H9Y6, DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 13917.695 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1H, RPA12, ZNRD1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1H, RPA12, ZNRD1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9P1U0 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9P1U0 |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 55065.523 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1G, ASE1, CAST, CD3EAP, PAF49 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1G, ASE1, CAST, CD3EAP, PAF49 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15446 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15446 |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 37490.379 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1F, TWISTNB / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1F, TWISTNB / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q3B726 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q3B726 |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 47330.234 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1E, PAF53, PRAF1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1E, PAF53, PRAF1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9GZS1 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9GZS1 |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerases I and III subunit ... , 2 types, 2 molecules CK
| #3: Protein | Mass: 39301.672 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1C, POLR1E / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1C, POLR1E / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15160 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15160 |
|---|---|
| #9: Protein | Mass: 15259.222 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1D / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1D / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DPB6 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DPB6 |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit ... , 5 types, 5 molecules EFHJL
| #4: Protein | Mass: 24584.223 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2E / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2E / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P19388 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P19388 |
|---|---|
| #5: Protein | Mass: 14491.026 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2F, POLRF / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2F, POLRF / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P61218 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P61218 |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 17162.273 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2H / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2H / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P52434 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P52434 |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 7655.123 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2L / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2L / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62875 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62875 |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 7018.244 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2K / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2K / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P53803 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P53803 |
-RNA chain , 1 types, 1 molecules R
| #14: RNA chain | Mass: 2503.521 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules TU
| #15: DNA chain | Mass: 7727.002 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|---|
| #16: DNA chain | Mass: 4247.753 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 6 molecules 


| #17: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #18: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: post state of human RNA Polymerase I Elongation Complex Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#16 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: NONE |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.81 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 183087 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj















































