+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7p1g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
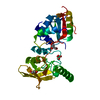
| Title | Structure of the P. aeruginosa ExoY-F-actin complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TOXIN / Bacterial toxin / F-actin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcalcium- and calmodulin-responsive adenylate cyclase activity / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / myosin heavy chain binding / detection of maltose stimulus / tropomyosin binding / maltose transport complex / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration ...calcium- and calmodulin-responsive adenylate cyclase activity / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / myosin heavy chain binding / detection of maltose stimulus / tropomyosin binding / maltose transport complex / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / carbohydrate transport / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / actin monomer binding / carbohydrate transmembrane transporter activity / maltose binding / maltose transport / maltodextrin transmembrane transport / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex, substrate-binding subunit-containing / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / titin binding / actin filament polymerization / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex / cell chemotaxis / actin filament / filopodium / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / calcium-dependent protein binding / lamellipodium / outer membrane-bounded periplasmic space / cell body / periplasmic space / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / calcium ion binding / DNA damage response / positive regulation of gene expression / magnesium ion binding / extracellular region / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria)  Amanita phalloides (death cap) Amanita phalloides (death cap) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Belyy, A. / Merino, F. / Raunser, S. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1items Germany, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Mechanism of actin-dependent activation of nucleotidyl cyclase toxins from bacterial human pathogens. Authors: Alexander Belyy / Felipe Merino / Undine Mechold / Stefan Raunser /   Abstract: Bacterial human pathogens secrete initially inactive nucleotidyl cyclases that become potent enzymes by binding to actin inside eukaryotic host cells. The underlying molecular mechanism of this ...Bacterial human pathogens secrete initially inactive nucleotidyl cyclases that become potent enzymes by binding to actin inside eukaryotic host cells. The underlying molecular mechanism of this activation is, however, unclear. Here, we report structures of ExoY from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Vibrio vulnificus bound to their corresponding activators F-actin and profilin-G-actin. The structures reveal that in contrast to the apo-state, two flexible regions become ordered and interact strongly with actin. The specific stabilization of these regions results in an allosteric stabilization of the nucleotide binding pocket and thereby to an activation of the enzyme. Differences in the sequence and conformation of the actin-binding regions are responsible for the selective binding to either F- or G-actin. Other nucleotidyl cyclase toxins that bind to calmodulin rather than actin undergo a similar disordered-to-ordered transition during activation, suggesting that the allosteric activation-by-stabilization mechanism of ExoY is conserved in these enzymes, albeit the different activator. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7p1g.cif.gz 7p1g.cif.gz | 669.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7p1g.ent.gz pdb7p1g.ent.gz | 524.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7p1g.json.gz 7p1g.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p1/7p1g https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p1/7p1g ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p1/7p1g ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p1/7p1g | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  13158MC  7p1hC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 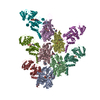
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 10 molecules MKLNOCABDE
| #1: Protein | Mass: 84941.797 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria)Gene: malE, b4034, JW3994, exoY, PA2191 / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 42096.953 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 5 molecules HFGIJ
| #3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 808.899 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Amanita phalloides (death cap) Amanita phalloides (death cap) |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 25 molecules 






| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-GH3 / #6: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / #7: Chemical | ChemComp-PO4 / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: The complex of P. aeruginosa ExoY with F-actin / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 400 nm |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1.5 sec. / Electron dose: 93 e/Å2 / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 12437 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2249589 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 1535755 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj