[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7jrj: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii radial spoke head and neck (recombinant) -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7jrj | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii radial spoke head and neck (recombinant) | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Cilia / Radial spoke / Mechano-regulation | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationradial spoke head / radial spoke / positive regulation of cilium-dependent cell motility / cilium movement involved in cell motility / axoneme assembly / motile cilium assembly / Oxidoreductases / Set1C/COMPASS complex / UTP biosynthetic process / CTP biosynthetic process ...radial spoke head / radial spoke / positive regulation of cilium-dependent cell motility / cilium movement involved in cell motility / axoneme assembly / motile cilium assembly / Oxidoreductases / Set1C/COMPASS complex / UTP biosynthetic process / CTP biosynthetic process / nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity / GTP biosynthetic process / motile cilium / cilium assembly / axoneme / cytoskeleton / calmodulin binding / oxidoreductase activity / hydrolase activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.03 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Grossman-Haham, I. / Coudray, N. / Yu, Z. / Wang, F. / Zhang, N. / Bhabha, G. / Vale, R.D. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2021Title: Structure of the radial spoke head and insights into its role in mechanoregulation of ciliary beating. Authors: Iris Grossman-Haham / Nicolas Coudray / Zanlin Yu / Feng Wang / Nan Zhang / Gira Bhabha / Ronald D Vale /  Abstract: Motile cilia power cell locomotion and drive extracellular fluid flow by propagating bending waves from their base to tip. The coordinated bending of cilia requires mechanoregulation by the radial ...Motile cilia power cell locomotion and drive extracellular fluid flow by propagating bending waves from their base to tip. The coordinated bending of cilia requires mechanoregulation by the radial spoke (RS) protein complexes and the microtubule central pair (CP). Despite their importance for ciliary motility across eukaryotes, the molecular function of the RSs is unknown. Here, we reconstituted the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii RS head that abuts the CP and determined its structure using single-particle cryo-EM to 3.1-Å resolution, revealing a flat, negatively charged surface supported by a rigid core of tightly intertwined proteins. Mutations in this core, corresponding to those involved in human ciliopathies, compromised the stability of the recombinant complex, providing a molecular basis for disease. Partially reversing the negative charge on the RS surface impaired motility in C. reinhardtii. We propose that the RS-head architecture is well-suited for mechanoregulation of ciliary beating through physical collisions with the CP. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
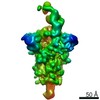
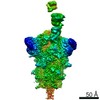
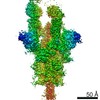
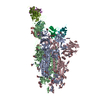
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7jrj.cif.gz 7jrj.cif.gz | 548.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7jrj.ent.gz pdb7jrj.ent.gz | 423.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7jrj.json.gz 7jrj.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jr/7jrj https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jr/7jrj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jr/7jrj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jr/7jrj | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  22446MC  7jr9C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 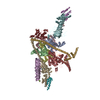
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Radial spoke protein ... , 2 types, 3 molecules EAB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 23553.943 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #8: Protein | Mass: 29572.348 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-Flagellar radial spoke protein ... , 10 types, 10 molecules FIGHCDLMNO
| #2: Protein | Mass: 87873.445 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 77445.297 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 39361.293 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP residues 159-516 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 55928.180 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 49900.820 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 48884.551 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #11: Protein/peptide | Mass: 528.644 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #12: Protein/peptide | Mass: 443.539 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 7592.350 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #14: Protein | Mass: 5890.252 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-Protein / Protein/peptide , 2 types, 2 molecules KJ
| #3: Protein | Mass: 61422.211 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #5: Protein/peptide | Mass: 358.434 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii radial spoke head and neck / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 / Details: 30 mM HEPES, 300 mM NaCl, 1 mM TCEP |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 70 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 / Num. of real images: 7572 |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 35 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 942591 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.03 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 136659 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 7JR9 Accession code: 7JR9 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



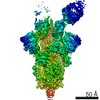
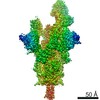
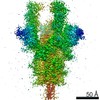
 PDBj
PDBj


