[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7eor: Structure of the human GluN1/GluN2A NMDA receptor in the glycine/... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7eor | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
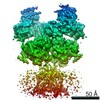
| Title | Structure of the human GluN1/GluN2A NMDA receptor in the glycine/glutamate/GNE-6901 bound state | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / NMDA receptor | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglycine-gated cation channel activity / excitatory chemical synaptic transmission / directional locomotion / Synaptic adhesion-like molecules / protein localization to postsynaptic membrane / serotonin metabolic process / sleep / propylene metabolic process / response to glycine / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors ...glycine-gated cation channel activity / excitatory chemical synaptic transmission / directional locomotion / Synaptic adhesion-like molecules / protein localization to postsynaptic membrane / serotonin metabolic process / sleep / propylene metabolic process / response to glycine / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / regulation of monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / Neurexins and neuroligins / NMDA glutamate receptor activity / NMDA selective glutamate receptor complex / glutamate binding / neurotransmitter receptor complex / ligand-gated sodium channel activity / glutamate receptor signaling pathway / calcium ion transmembrane import into cytosol / protein heterotetramerization / glycine binding / startle response / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / dopamine metabolic process / positive regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / positive regulation of calcium ion transport into cytosol / Long-term potentiation / regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity / monoatomic cation transport / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / synaptic cleft / calcium ion homeostasis / MECP2 regulates neuronal receptors and channels / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / neurogenesis / excitatory synapse / sensory perception of pain / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / synaptic membrane / sodium ion transmembrane transport / positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / response to amphetamine / protein catabolic process / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / excitatory postsynaptic potential / regulation of membrane potential / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / regulation of synaptic plasticity / brain development / visual learning / postsynaptic density membrane / response to wounding / calcium ion transmembrane transport / memory / terminal bouton / synaptic vesicle / long-term synaptic potentiation / signaling receptor activity / amyloid-beta binding / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / presynaptic membrane / dendritic spine / response to ethanol / chemical synaptic transmission / learning or memory / postsynaptic membrane / calmodulin binding / neuron projection / postsynaptic density / positive regulation of apoptotic process / response to xenobiotic stimulus / calcium ion binding / synapse / dendrite / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein-containing complex binding / glutamatergic synapse / cell surface / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / zinc ion binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, H. / Zhu, S. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, European Union, 6items China, European Union, 6items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Neuron / Year: 2021 Journal: Neuron / Year: 2021Title: Gating mechanism and a modulatory niche of human GluN1-GluN2A NMDA receptors. Authors: Han Wang / Shiyun Lv / David Stroebel / Jinbao Zhang / Yijie Pan / Xuejing Huang / Xing Zhang / Pierre Paoletti / Shujia Zhu /   Abstract: N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors are glutamate-gated calcium-permeable ion channels that are widely implicated in synaptic transmission and plasticity. Here, we report a gallery of cryo-electron ...N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors are glutamate-gated calcium-permeable ion channels that are widely implicated in synaptic transmission and plasticity. Here, we report a gallery of cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of the human GluN1-GluN2A NMDA receptor at an overall resolution of 4 Å in complex with distinct ligands or modulators. In the full-length context of GluN1-GluN2A receptors, we visualize the competitive antagonists bound to the ligand-binding domains (LBDs) of GluN1 and GluN2A subunits, respectively. We reveal that the binding of positive allosteric modulator shortens the distance between LBDs and the transmembrane domain (TMD), which further stretches the opening of the gate. In addition, we unexpectedly visualize the binding cavity of the "foot-in-the-door" blocker 9-aminoacridine within the LBD-TMD linker region, differing from the conventional "trapping" blocker binding site at the vestibule within the TMD. Our study provides molecular insights into the crosstalk between LBDs and TMD during channel activation, inhibition, and allosteric transition. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
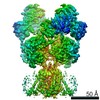
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7eor.cif.gz 7eor.cif.gz | 538.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7eor.ent.gz pdb7eor.ent.gz | 439.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7eor.json.gz 7eor.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/eo/7eor https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/eo/7eor ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/eo/7eor ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/eo/7eor | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  31228MC  7eoqC  7eosC  7eotC  7eouC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
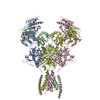
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 95537.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: L794C Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GRIN2A, NMDAR2A / Cell line (production host): HEK293S / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GRIN2A, NMDAR2A / Cell line (production host): HEK293S / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q12879 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q12879#2: Protein | Mass: 95210.102 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: E698C Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GRIN1, NMDAR1 / Cell line (production host): HEK293S / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GRIN1, NMDAR1 / Cell line (production host): HEK293S / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q05586 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q05586#3: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / #4: Chemical | Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Structure of the human GluN1/GluN2A NMDA receptor in the glycine/glutamate/GNE-6901 bound state Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293S Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293S |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19_4092: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 69419 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6IRA Accession code: 6IRA / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj