[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
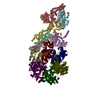
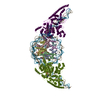
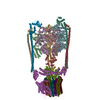
Yorodumi- PDB-6r0w: Thermus thermophilus V/A-type ATPase/synthase, rotational state 2 -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6r0w | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Thermus thermophilus V/A-type ATPase/synthase, rotational state 2 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ATP hydrolysis/synthesis / proton translocation / rotary catalysis | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, catalytic domain / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / vacuolar acidification / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ATPase binding ...proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, catalytic domain / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / vacuolar acidification / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ATPase binding / ATP binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhou, L. / Sazanov, L. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2019 Journal: Science / Year: 2019Title: Structure and conformational plasticity of the intact V/A-type ATPase. Authors: Long Zhou / Leonid A Sazanov /  Abstract: V (vacuolar)/A (archaeal)-type adenosine triphosphatases (ATPases), found in archaea and eubacteria, couple ATP hydrolysis or synthesis to proton translocation across the plasma membrane using the ...V (vacuolar)/A (archaeal)-type adenosine triphosphatases (ATPases), found in archaea and eubacteria, couple ATP hydrolysis or synthesis to proton translocation across the plasma membrane using the rotary-catalysis mechanism. They belong to the V-type ATPase family, which differs from the mitochondrial/chloroplast F-type ATP synthases in overall architecture. We solved cryo-electron microscopy structures of the intact V/A-ATPase, reconstituted into lipid nanodiscs, in three rotational states and two substates. These structures indicate substantial flexibility between V and V in a working enzyme, which results from mechanical competition between central shaft rotation and resistance from the peripheral stalks. We also describe details of adenosine diphosphate inhibition release, V-V torque transmission, and proton translocation, which are relevant for the entire V-type ATPase family. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6r0w.cif.gz 6r0w.cif.gz | 1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6r0w.ent.gz pdb6r0w.ent.gz | 817.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6r0w.json.gz 6r0w.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r0/6r0w https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r0/6r0w ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r0/6r0w ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r0/6r0w | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4699MC  4640C  4700C  4702C  4703C  6qumC  6r0yC  6r0zC  6r10C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-V-type ATP synthase ... , 7 types, 12 molecules ABCDEFGHJLMN
| #1: Protein | Mass: 63699.980 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56403, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #2: Protein | Mass: 53219.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q56404 #3: Protein | | Mass: 24715.566 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)References: UniProt: O87880 #4: Protein | | Mass: 11294.904 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)References: UniProt: P74903 #6: Protein | Mass: 20645.582 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)References: UniProt: P74901 #7: Protein | | Mass: 35968.570 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)References: UniProt: P74902 #8: Protein | | Mass: 72204.289 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q5SIT6 |
|---|
-V-type ATP synthase, subunit ... , 2 types, 14 molecules IKOPQRSTUVWXYZ
| #5: Protein | Mass: 13166.218 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q5SIT5 #9: Protein | Mass: 9841.714 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q5SIT7 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 3 molecules 


| #10: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
|---|---|
| #11: Chemical |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Thermus Thermophlius V/A-type ATPase/ATP synthase / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#9 / Source: NATURAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.65 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 5.4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R0.6/1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 75000 X / Calibrated magnification: 129032 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 500 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 1780 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 63 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 2700 |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 14 µm / Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.13_2998: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 181245 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 26565 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 96.3 / Space: REAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Accession code: 5Y5Y / Initial refinement model-ID: 1 / PDB-ID: 5Y5Y / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj





