+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 6lvb | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
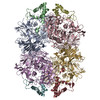
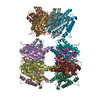
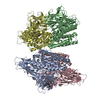
| タイトル | Structure of Dimethylformamidase, tetramer | ||||||||||||
 要素 要素 |
| ||||||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | HYDROLASE / ab polypeptide / mononuclear iron / amidohydrolase / tetramer | ||||||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報 | ||||||||||||
| 生物種 |  Paracoccus sp. SSG05 (バクテリア) Paracoccus sp. SSG05 (バクテリア) | ||||||||||||
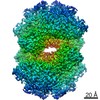
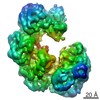
| 手法 | 電子顕微鏡法 / 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 2.8 Å | ||||||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Arya, C.A. / Yadav, S. / Fine, J. / Casanal, A. / Chopra, G. / Ramanathan, G. / Subramanian, R. / Vinothkumar, K.R. | ||||||||||||
| 資金援助 |  インド, 3件 インド, 3件
| ||||||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Angew Chem Int Ed Engl / 年: 2020 ジャーナル: Angew Chem Int Ed Engl / 年: 2020タイトル: A 2-Tyr-1-carboxylate Mononuclear Iron Center Forms the Active Site of a Paracoccus Dimethylformamidase. 著者: Chetan Kumar Arya / Swati Yadav / Jonathan Fine / Ana Casanal / Gaurav Chopra / Gurunath Ramanathan / Kutti R Vinothkumar / Ramaswamy Subramanian /    要旨: N,N-dimethyl formamide (DMF) is an extensively used organic solvent but is also a potent pollutant. Certain bacterial species from genera such as Paracoccus, Pseudomonas, and Alcaligenes have evolved ...N,N-dimethyl formamide (DMF) is an extensively used organic solvent but is also a potent pollutant. Certain bacterial species from genera such as Paracoccus, Pseudomonas, and Alcaligenes have evolved to use DMF as a sole carbon and nitrogen source for growth via degradation by a dimethylformamidase (DMFase). We show that DMFase from Paracoccus sp. strain DMF is a halophilic and thermostable enzyme comprising a multimeric complex of the α β or (α β ) type. One of the three domains of the large subunit and the small subunit are hitherto undescribed protein folds of unknown evolutionary origin. The active site consists of a mononuclear iron coordinated by two Tyr side-chain phenolates and one carboxylate from Glu. The Fe ion in the active site catalyzes the hydrolytic cleavage of the amide bond in DMF. Kinetic characterization reveals that the enzyme shows cooperativity between subunits, and mutagenesis and structural data provide clues to the catalytic mechanism. #1: ジャーナル: Prog Biophys Mol Biol / 年: 2021 タイトル: Comparison of CryoEM and X-ray structures of dimethylformamidase. 著者: Kutti R Vinothkumar / Chetan Kumar Arya / Gurunath Ramanathan / Ramaswamy Subramanian /   要旨: Dimethylformamidase (DMFase) catalyzes the hydrolysis of dimethylformamide, an industrial solvent, introduced into the environment by humans. Recently, we determined the structures of ...Dimethylformamidase (DMFase) catalyzes the hydrolysis of dimethylformamide, an industrial solvent, introduced into the environment by humans. Recently, we determined the structures of dimethylformamidase by electron cryo microscopy and X-ray crystallography revealing a tetrameric enzyme with a mononuclear iron at the active site. DMFase from Paracoccus sp. isolated from a waste water treatment plant around the city of Kanpur in India shows maximal activity at 54 °C and is halotolerant. The structures determined by both techniques are mostly identical and the largest difference is in a loop near the active site. This loop could play a role in co-operativity between the monomers. A number of non-protein densities are observed in the EM map, which are modelled as water molecules. Comparison of the structures determined by the two methods reveals conserved water molecules that could play a structural role. The higher stability, unusual active site and negligible activity at low temperature makes this a very good model to study enzyme mechanism by cryoEM. | ||||||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  6lvb.cif.gz 6lvb.cif.gz | 610.6 KB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb6lvb.ent.gz pdb6lvb.ent.gz | 503.7 KB | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  6lvb.json.gz 6lvb.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lv/6lvb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lv/6lvb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lv/6lvb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lv/6lvb | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
| 登録構造単位 | 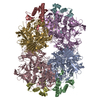
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- 要素
要素
| #1: タンパク質 | 分子量: 86341.758 Da / 分子数: 4 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 由来: (組換発現)  Paracoccus sp. SSG05 (バクテリア) Paracoccus sp. SSG05 (バクテリア)遺伝子: dmfase2 / 発現宿主:  #2: タンパク質 | 分子量: 16083.823 Da / 分子数: 4 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 由来: (組換発現)  Paracoccus sp. SSG05 (バクテリア) Paracoccus sp. SSG05 (バクテリア)遺伝子: dmfase1 / 発現宿主:  #3: 化合物 | ChemComp-FE / #4: 水 | ChemComp-HOH / | 研究の焦点であるリガンドがあるか | Y | |
|---|
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法: 電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
| EM実験 | 試料の集合状態: PARTICLE / 3次元再構成法: 単粒子再構成法 |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 構成要素 | 名称: Dimethylformamidase / タイプ: COMPLEX / 詳細: Tetramer, 2x(a2b2) / Entity ID: #1-#2 / 由来: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分子量 | 値: 0.4 MDa / 実験値: NO | ||||||||||||
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Paracoccus sp. SSG05 (バクテリア) Paracoccus sp. SSG05 (バクテリア) | ||||||||||||
| 由来(組換発現) | 生物種:  | ||||||||||||
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.2 | ||||||||||||
| 緩衝液成分 |
| ||||||||||||
| 試料 | 濃度: 3 mg/ml / 包埋: NO / シャドウイング: NO / 染色: NO / 凍結: YES / 詳細: Sample at higher salt exists mostly as tetramer | ||||||||||||
| 試料支持 | 詳細: Glow discharge was carried out in Quorum Glocube instrument at 25mA for 90 seconds. グリッドの材料: GOLD / グリッドのサイズ: 300 divisions/in. / グリッドのタイプ: Quantifoil R0.6/1 | ||||||||||||
| 急速凍結 | 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / 凍結剤: ETHANE / 湿度: 100 % / 凍結前の試料温度: 291 K 詳細: Blot force was 0 and blotting was done for 3.5 seconds |
- 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| 顕微鏡 | モデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| 電子銃 | 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM |
| 電子レンズ | モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 倍率(公称値): 75000 X / 倍率(補正後): 130841 X / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 4145.7 nm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 931.5 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 931.5 nm / 最大 デフォーカス(補正後): 4145.7 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2レンズ絞り径: 50 µm / アライメント法: COMA FREE |
| 試料ホルダ | 凍結剤: NITROGEN 試料ホルダーモデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER 最高温度: 77.7 K / 最低温度: 77.7 K |
| 撮影 | 平均露光時間: 60 sec. / 電子線照射量: 27 e/Å2 / 検出モード: COUNTING フィルム・検出器のモデル: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) 撮影したグリッド数: 1 / 実像数: 793 詳細: A total of 25 frames were saved from the 60 second exposure, resulting in ~1.08 electron/frame |
| 画像スキャン | サンプリングサイズ: 14 µm / 横: 4096 / 縦: 4096 |
- 解析
解析
| EMソフトウェア |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF補正 | 詳細: CTF correction was done with Relion, during refinement and reconstruction タイプ: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 粒子像の選択 | 選択した粒子像数: 89183 詳細: Two rounds of 2D classification was performed prior to angular assignment and reconstruction | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 点対称性: C2 (2回回転対称) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3次元再構成 | 解像度: 2.8 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 粒子像の数: 59191 / アルゴリズム: BACK PROJECTION / 対称性のタイプ: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 原子モデル構築 | B value: 38.8 / プロトコル: OTHER / 空間: REAL |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー










 PDBj
PDBj