[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
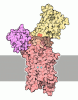
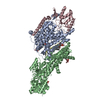
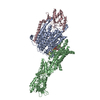
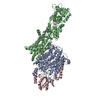
Yorodumi- PDB-6hra: Cryo-EM structure of the KdpFABC complex in an E1 outward-facing ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6hra | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the KdpFABC complex in an E1 outward-facing state (state 1) | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / P-type ATPase superfamily of K+ transporters (SKT) potassium uptake system four subunit complex | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationP-type K+ transporter / P-type potassium transmembrane transporter activity / potassium:proton antiporter complex / potassium ion-transporting ATPase complex / potassium ion binding / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / potassium ion transmembrane transport / potassium ion transport / magnesium ion binding / ATP hydrolysis activity ...P-type K+ transporter / P-type potassium transmembrane transporter activity / potassium:proton antiporter complex / potassium ion-transporting ATPase complex / potassium ion binding / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / potassium ion transmembrane transport / potassium ion transport / magnesium ion binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Stock, C. / Hielkema, L. / Tascon, I. / Wunnicke, D. / Oostergetel, G.T. / Azkargorta, M. / Paulino, C. / Haenelt, I. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, Germany,  Netherlands, 3items Netherlands, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2018 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2018Title: Cryo-EM structures of KdpFABC suggest a K transport mechanism via two inter-subunit half-channels. Authors: C Stock / L Hielkema / I Tascón / D Wunnicke / G T Oostergetel / M Azkargorta / C Paulino / I Hänelt /    Abstract: P-type ATPases ubiquitously pump cations across biological membranes to maintain vital ion gradients. Among those, the chimeric K uptake system KdpFABC is unique. While ATP hydrolysis is accomplished ...P-type ATPases ubiquitously pump cations across biological membranes to maintain vital ion gradients. Among those, the chimeric K uptake system KdpFABC is unique. While ATP hydrolysis is accomplished by the P-type ATPase subunit KdpB, K has been assumed to be transported by the channel-like subunit KdpA. A first crystal structure uncovered its overall topology, suggesting such a spatial separation of energizing and transporting units. Here, we report two cryo-EM structures of the 157 kDa, asymmetric KdpFABC complex at 3.7 Å and 4.0 Å resolution in an E1 and an E2 state, respectively. Unexpectedly, the structures suggest a translocation pathway through two half-channels along KdpA and KdpB, uniting the alternating-access mechanism of actively pumping P-type ATPases with the high affinity and selectivity of K channels. This way, KdpFABC would function as a true chimeric complex, synergizing the best features of otherwise separately evolved transport mechanisms. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6hra.cif.gz 6hra.cif.gz | 250.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6hra.ent.gz pdb6hra.ent.gz | 197.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6hra.json.gz 6hra.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hr/6hra https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hr/6hra ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hr/6hra ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hr/6hra | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  0257MC  0258C  6hrbC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 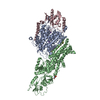
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 59218.613 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: K12 / Gene: kdpA, b0698, JW0686 / Production host:  | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 20281.035 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: K12 / Gene: kdpC, b0696, JW0684 / Production host:  | ||
| #3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 3071.714 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: K12 / Gene: kdpF, b4513, JW0687 / Production host:  | ||
| #4: Protein | Mass: 72347.844 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: K12 / Gene: kdpB, b0697, JW0685 / Production host:  | ||
| #5: Chemical | | Has protein modification | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: KdpFABC / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.157 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 Details: 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 8, 10 mM MgCl2, 10 mM NaCl and 0.012% DDM |
| Specimen | Conc.: 3.1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: at 5mA / Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 293 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 49407 X / Calibrated magnification: 49407 X / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 300 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 300 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 3000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 105 K / Temperature (min): 90 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 9 sec. / Electron dose: 52 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 9 / Num. of real images: 7327 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Width: 3838 / Height: 3710 / Movie frames/image: 60 / Used frames/image: 1-60 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.11.1_2575: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 826403 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 219897 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 5MRW Accession code: 5MRW / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj