[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-3j3v: Atomic model of the immature 50S subunit from Bacillus subtilis (... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3j3v | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Atomic model of the immature 50S subunit from Bacillus subtilis (state I-a) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / Ribosome biogenesis / ribosome assembly / RNA folding / YlqF | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of rRNA processing / nucleoid / rRNA processing / regulation of translation / large ribosomal subunit / transferase activity / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit ...positive regulation of rRNA processing / nucleoid / rRNA processing / regulation of translation / large ribosomal subunit / transferase activity / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / response to antibiotic / mRNA binding / DNA binding / RNA binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 13.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Li, N. / Guo, Q. / Zhang, Y. / Yuan, Y. / Ma, C. / Lei, J. / Gao, N. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2013 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2013Title: Cryo-EM structures of the late-stage assembly intermediates of the bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit. Authors: Ningning Li / Yuling Chen / Qiang Guo / Yixiao Zhang / Yi Yuan / Chengying Ma / Haiteng Deng / Jianlin Lei / Ning Gao /  Abstract: Ribosome assembly is a process fundamental for all cellular activities. The efficiency and accuracy of the subunit assembly are tightly regulated and closely monitored. In the present work, we ...Ribosome assembly is a process fundamental for all cellular activities. The efficiency and accuracy of the subunit assembly are tightly regulated and closely monitored. In the present work, we characterized, both compositionally and structurally, a set of in vivo 50S subunit precursors (45S), isolated from a mutant bacterial strain. Our qualitative mass spectrometry data indicate that L28, L16, L33, L36 and L35 are dramatically underrepresented in the 45S particles. This protein spectrum shows interesting similarity to many qualitatively analyzed 50S precursors from different genetic background, indicating the presence of global rate-limiting steps in the late-stage assembly of 50S subunit. Our structural data reveal two major intermediate states for the 45S particles. Consistently, both states severally lack those proteins, but they also differ in the stability of the functional centers of the 50S subunit, demonstrating that they are translationally inactive. Detailed analysis indicates that the orientation of H38 accounts for the global conformational differences in these intermediate structures, and suggests that the reorientation of H38 to its native position is rate-limiting during the late-stage assembly. Especially, H38 plays an essential role in stabilizing the central protuberance, through the interaction with the 5S rRNA, and the correctly orientated H38 is likely a prerequisite for further maturation of the 50S subunit. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3j3v.cif.gz 3j3v.cif.gz | 2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3j3v.ent.gz pdb3j3v.ent.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3j3v.json.gz 3j3v.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j3/3j3v https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j3/3j3v ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j3/3j3v ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j3/3j3v | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 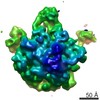 5642MC 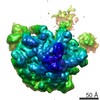 5643C  3j3wC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
+50S ribosomal protein ... , 22 types, 22 molecules 0256CDEFGJKLNOPQRSTUXY
-Ribosome RNA ... , 2 types, 2 molecules AB
| #5: RNA chain | Mass: 949324.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #6: RNA chain | Mass: 38423.863 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Immature 50S subunit from YlqF-deficient Bacillus subtilis strain Type: RIBOSOME |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 100mM NH4Cl, 20mM Tris-HCl, 10mM MgOAc2, 1mM TCEP. / pH: 7.5 / Details: 100mM NH4Cl, 20mM Tris-HCl, 10mM MgOAc2, 1mM TCEP. |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Method: Blot for 20 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS / Date: Dec 6, 2011 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 59000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / Camera length: 0 mm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Tilt angle max: 0 ° / Tilt angle min: 0 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI EAGLE (4k x 4k) |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: Each particle | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Method: Reference projections / Resolution: 13.3 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Num. of particles: 21020 Details: (Single particle details: This is one of the classified groups with the software RELION) (Single particle--Applied symmetry: C1) Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj






























