+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3882 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
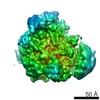
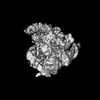
| Title | 'Thermus thermophilus PilF ATPase (apoprotein form) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Thermus thermophilus PilF ATPase (apoprotein form) | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | type IV pilus / type II secretion / macromolecular machine / MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) /   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 8.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Derrick JP / Collins RF | |||||||||
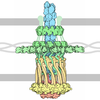
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2018 Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2018Title: Structural cycle of the Thermus thermophilus PilF ATPase: the powering of type IVa pilus assembly. Authors: Richard Collins / Vijaykumar Karuppiah / C Alistair Siebert / Rana Dajani / Angela Thistlethwaite / Jeremy P Derrick /  Abstract: Type IV pili are responsible for a diverse range of functions, including twitching motility and cell adhesion. Assembly of the pilus fiber is driven by a cytoplasmic ATPase: it interacts with an ...Type IV pili are responsible for a diverse range of functions, including twitching motility and cell adhesion. Assembly of the pilus fiber is driven by a cytoplasmic ATPase: it interacts with an inner membrane complex of biogenesis proteins which, in turn, bind to nascent pilin subunits and mediate fiber assembly. Here we report the structural characterization of the PilF TFP assembly ATPase from Thermus thermophilus. The crystal structure of a recombinant C-terminal fragment of PilF revealed bound, unhydrolysed ATP, although the full length complex was enzymatically active. 3D reconstructions were carried out by single particle cryoelectron microscopy for full length apoprotein PilF and in complex with AMPPNP. The structure forms an hourglass-like shape, with the ATPase domains in one half and the N1 domains in the second half which, we propose, interact with the other pilus biogenesis components. Molecular models for both forms were generated: binding of AMPPNP causes an upward shift of the N1 domains towards the ATPase domains of ~8 Å. We advocate a model in which ATP hydrolysis is linked to displacement of the N1 domains which is associated with lifting pilin subunits out of the inner membrane, and provide the activation energy needed to form the pilus fiber. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3882.map.gz emd_3882.map.gz | 3.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3882-v30.xml emd-3882-v30.xml emd-3882.xml emd-3882.xml | 12.9 KB 12.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_3882.png emd_3882.png | 72.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-3882.cif.gz emd-3882.cif.gz | 5.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3882 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3882 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3882 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3882 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6ejfMC  4194C  5oiuC  6f8lC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3882.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 27 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3882.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 27 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Thermus thermophilus PilF ATPase (apoprotein form) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
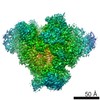
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.6 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
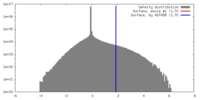
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Thermus thermophilus PilF ATPase (AMPPNP-bound form)
| Entire | Name: Thermus thermophilus PilF ATPase (AMPPNP-bound form) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Thermus thermophilus PilF ATPase (AMPPNP-bound form)
| Supramolecule | Name: Thermus thermophilus PilF ATPase (AMPPNP-bound form) / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Type IV pilus assembly protein PilF
| Macromolecule | Name: Type IV pilus assembly protein PilF / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: Domain is part of the larger protein but connectivity to other domains cannot be confirmed. Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.249751 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: LPRAKPLGEI LVELGLARPE DVEEALQKQR RGGGRLEDTL VQSGKLRPEA LAQAVATQLG YPYVDPEEDP PDPGAPLLLP EDLCRRYGV FPHRLEGNRL VLLMKDPRNI LALDDVRLAL KRKGLNYEVA PAVATEAAIT KLIERFY UniProtKB: Type IV pilus assembly ATPase PilB |
-Macromolecule #2: Type IV pilus assembly protein PilF
| Macromolecule | Name: Type IV pilus assembly protein PilF / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 Details: Domain is part of the larger protein but connectivity to other domains cannot be confirmed. Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.440708 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: QKDLKLGELL LQKGWISREA LEEALVEQEK TGDLLGRILV RKGLPEEALY RALAEQKGLE FLESTEGIVP DPSAALLLLR SDALRYGAV PIGFQNGEVE VVLSDPRHKE AVAQLLNRPA RFYLALPQAW EELFRRAY UniProtKB: Type IV pilus assembly ATPase PilB |
-Macromolecule #3: Type IV pilus assembly protein PilF
| Macromolecule | Name: Type IV pilus assembly protein PilF / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 45.203906 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SAAQKFVKQV IREAFLQDAS DIHIEPRQND VQVRLRIDGA LRPYSTLPKG ALNAVISVVK IMGGLNIAEK RLPQDGRVRY REGAIDVDL RLSTLPTVYG EKAVMRLLKK ASDIPEIEDL GFAPGVFERF KEVISKPYGI FLITGPTGSG KSFTTFSILK R IATPDKNT ...String: SAAQKFVKQV IREAFLQDAS DIHIEPRQND VQVRLRIDGA LRPYSTLPKG ALNAVISVVK IMGGLNIAEK RLPQDGRVRY REGAIDVDL RLSTLPTVYG EKAVMRLLKK ASDIPEIEDL GFAPGVFERF KEVISKPYGI FLITGPTGSG KSFTTFSILK R IATPDKNT QTIEDPVEYE IPGINQTQVN PQAGLTFARA LRAFLRQDPD IIMVGEIRDS ETAKIATEAA LTGHLVIATL HT NDAAQAI TRLDEMGVEP FNISAALIGV LSQRLVRRVC EHCKVEVKPD PETLRRLGLS EAEIQGARLY KGMGCERCGG TGY KGRYAI HELLVVDDEI RHAIVAGKSA TEIKEIARRK GMKTLREDGL YKALQGITTL EEVLARTIEA AAELALVPRG SSAH HHHHH HHHH UniProtKB: Type IV pilus assembly ATPase PilB |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: 25 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2 and 5 % glycerol (v/v) |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
| Details | Monodisperse |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 BASE (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 45.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated defocus max: 4.5 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 1.0 µm / Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: OTHER / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 4.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: ORTHOGONAL TILT |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 8.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 45000 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6ejf: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)