[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-32584: CryoEM structure of human low-voltage activated T-type calcium ch... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CryoEM structure of human low-voltage activated T-type calcium channel CaV3.3 (apo) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | apo state / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhigh voltage-gated calcium channel activity / sleep / NCAM1 interactions / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / neuronal action potential / Smooth Muscle Contraction / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / signal transduction / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | He L / Yu Z | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structure, gating, and pharmacology of human Ca3.3 channel. Authors: Lingli He / Zhuoya Yu / Ze Geng / Zhuo Huang / Changjiang Zhang / Yanli Dong / Yiwei Gao / Yuhang Wang / Qihao Chen / Le Sun / Xinyue Ma / Bo Huang / Xiaoqun Wang / Yan Zhao /  Abstract: The low-voltage activated T-type calcium channels regulate cellular excitability and oscillatory behavior of resting membrane potential which trigger many physiological events and have been ...The low-voltage activated T-type calcium channels regulate cellular excitability and oscillatory behavior of resting membrane potential which trigger many physiological events and have been implicated with many diseases. Here, we determine structures of the human T-type Ca3.3 channel, in the absence and presence of antihypertensive drug mibefradil, antispasmodic drug otilonium bromide and antipsychotic drug pimozide. Ca3.3 contains a long bended S6 helix from domain III, with a positive charged region protruding into the cytosol, which is critical for T-type Ca channel activation at low voltage. The drug-bound structures clearly illustrate how these structurally different compounds bind to the same central cavity inside the Ca3.3 channel, but are mediated by significantly distinct interactions between drugs and their surrounding residues. Phospholipid molecules penetrate into the central cavity in various extent to shape the binding pocket and play important roles in stabilizing the inhibitor. These structures elucidate mechanisms of channel gating, drug recognition, and actions, thus pointing the way to developing potent and subtype-specific drug for therapeutic treatments of related disorders. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_32584.map.gz emd_32584.map.gz | 59.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-32584-v30.xml emd-32584-v30.xml emd-32584.xml emd-32584.xml | 12.5 KB 12.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_32584.png emd_32584.png | 69.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-32584.cif.gz emd-32584.cif.gz | 6.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32584 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32584 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32584 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32584 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_32584_validation.pdf.gz emd_32584_validation.pdf.gz | 485.3 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_32584_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_32584_full_validation.pdf.gz | 484.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_32584_validation.xml.gz emd_32584_validation.xml.gz | 6.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_32584_validation.cif.gz emd_32584_validation.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-32584 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-32584 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-32584 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-32584 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7wliMC  7wljC  7wlkC  7wllC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_32584.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_32584.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.04 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
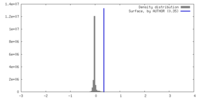
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : CaV3.3
| Entire | Name: CaV3.3 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: CaV3.3
| Supramolecule | Name: CaV3.3 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Voltage-dependent T-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1I
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent T-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1I type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 245.373031 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAESASPPSS SAAAPAAEPG VTTEQPGPRS PPSSPPGLEE PLDGADPHVP HPDLAPIAFF CLRQTTSPRN WCIKMVCNPW FECVSMLVI LLNCVTLGMY QPCDDMDCLS DRCKILQVFD DFIFIFFAME MVLKMVALGI FGKKCYLGDT WNRLDFFIVM A GMVEYSLD ...String: MAESASPPSS SAAAPAAEPG VTTEQPGPRS PPSSPPGLEE PLDGADPHVP HPDLAPIAFF CLRQTTSPRN WCIKMVCNPW FECVSMLVI LLNCVTLGMY QPCDDMDCLS DRCKILQVFD DFIFIFFAME MVLKMVALGI FGKKCYLGDT WNRLDFFIVM A GMVEYSLD LQNINLSAIR TVRVLRPLKA INRVPSMRIL VNLLLDTLPM LGNVLLLCFF VFFIFGIIGV QLWAGLLRNR CF LEENFTI QGDVALPPYY QPEEDDEMPF ICSLSGDNGI MGCHEIPPLK EQGRECCLSK DDVYDFGAGR QDLNASGLCV NWN RYYNVC RTGSANPHKG AINFDNIGYA WIVIFQVITL EGWVEIMYYV MDAHSFYNFI YFILLIIVGS FFMINLCLVV IATQ FSETK QREHRLMLEQ RQRYLSSSTV ASYAEPGDCY EEIFQYVCHI LRKAKRRALG LYQALQSRRQ ALGPEAPAPA KPGPH AKEP RHYHGKTKGQ GDEGRHLGSR HCQTLHGPAS PGNDHSGREL CPQHSPLDAT PHTLVQPIPA TLASDPASCP CCQHED GRR PSGLGSTDSG QEGSGSGSSA GGEDEADGDG ARSSEDGASS ELGKEEEEEE QADGAVWLCG DVWRETRAKL RGIVDSK YF NRGIMMAILV NTVSMGIEHH EQPEELTNIL EICNVVFTSM FALEMILKLA AFGLFDYLRN PYNIFDSIIV IISIWEIV G QADGGLSVLR TFRLLRVLKL VRFMPALRRQ LVVLMKTMDN VATFCMLLML FIFIFSILGM HIFGCKFSLR TDTGDTVPD RKNFDSLLWA IVTVFQILTQ EDWNVVLYNG MASTSPWASL YFVALMTFGN YVLFNLLVAI LVEGFQAEGD ANRSYSDEDQ SSSNIEEFD KLQEGLDSSG DPKLCPIPMT PNGHLDPSLP LGGHLGPAGA AGPAPRLSLQ PDPMLVALGS RKSSVMSLGR M SYDQRSLS SSRSSYYGPW GRSAAWASRR SSWNSLKHKP PSAEHESLLS AERGGGARVC EVAADEGPPR AAPLHTPHAH HI HHGPHLA HRHRHHRRTL SLDNRDSVDL AELVPAVGAH PRAAWRAAGP APGHEDCNGR MPSIAKDVFT KMGDRGDRGE DEE EIDYTL CFRVRKMIDV YKPDWCEVRE DWSVYLFSPE NRFRVLCQTI IAHKLFDYVV LAFIFLNCIT IALERPQIEA GSTE RIFLT VSNYIFTAIF VGEMTLKVVS LGLYFGEQAY LRSSWNVLDG FLVFVSIIDI VVSLASAGGA KILGVLRVLR LLRTL RPLR VISRAPGLKL VVETLISSLK PIGNIVLICC AFFIIFGILG VQLFKGKFYH CLGVDTRNIT NRSDCMAANY RWVHHK YNF DNLGQALMSL FVLASKDGWV NIMYNGLDAV AVDQQPVTNH NPWMLLYFIS FLLIVSFFVL NMFVGVVVEN FHKCRQH QE AEEARRREEK RLRRLEKKRR KAQRLPYYAT YCHTRLLIHS MCTSHYLDIF ITFIICLNVV TMSLEHYNQP TSLETALK Y CNYMFTTVFV LEAVLKLVAF GLRRFFKDRW NQLDLAIVLL SVMGITLEEI EINAALPINP TIIRIMRVLR IARVLKLLK MATGMRALLD TVVQALPQVG NLGLLFMLLF FIYAALGVEL FGKLVCNDEN PCEGMSRHAT FENFGMAFLT LFQVSTGDNW NGIMKDTLR DCTHDERSCL SSLQFVSPLY FVSFVLTAQF VLINVVVAVL MKHLDDSNKE AQEDAEMDAE LELEMAHGLG P GPRLPTGS PGAPGRGPGG AGGGGDTEGG LCRRCYSPAQ ENLWLDSVSL IIKDSLEGEL TIIDNLSGSI FHHYSSPAGC KK CHHDKQE VQLAETEAFS LNSDRSSSIL LGDDLSLEDP TACPPGRKDS KGELDPPEPM RVGDLGECFF PLSSTAVSPD PEN FLCEME EIPFNPVRSW LKHDSSQAPP SPFSPDASSP LLPMPAEFFH PAVSASQKGP EKGTGTGTLP KIALQGSWAS LRSP RVNCT LLRQATGSDT SLDASPSSSA GSLQTTLEDS LTLSDSPRRA LGPPAPAPGP RAGLSPAARR RLSLRGRGLF SLRGL RAHQ RSHSSGGSTS PGCTHHDSMD PSDEEGRGGA GGGGAGSEHS ETLSSLSLTS LFCPPPPPPA PGLTPARKFS STSSLA APG RPHAAALAHG LARSPSWAAD RSKDPPGRAP LPMGLGPLAP PPQPLPGELE PGDAASKRKR UniProtKB: Voltage-dependent T-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1I |
-Macromolecule #2: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #3: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #4: 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycerophosphoethanolamine
| Macromolecule | Name: 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycerophosphoethanolamine / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 11 / Formula: 3PE |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 748.065 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-3PE: |
-Macromolecule #5: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: Y01 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 486.726 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-Y01: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 9.6 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 93988 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)