[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-25493: Human NALCN-FAM155A-UNC79-UNC80 channelosome with CaM bound, conf... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-25493 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
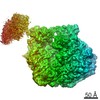
| Title | Human NALCN-FAM155A-UNC79-UNC80 channelosome with CaM bound, conformation 2/2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | sharpened map used for model refinements | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ion channel / calmodulin / HEAT repeat protein / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmonoatomic cation homeostasis / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, cholinergic / leak channel activity / regulation of resting membrane potential / cation channel complex / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / voltage-gated sodium channel activity / Calmodulin induced events ...monoatomic cation homeostasis / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, cholinergic / leak channel activity / regulation of resting membrane potential / cation channel complex / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / voltage-gated sodium channel activity / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / PKA activation / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / presynaptic endocytosis / sodium channel activity / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / monoatomic ion channel complex / DARPP-32 events / Smooth Muscle Contraction / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / catalytic complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / monoatomic cation channel activity / calcium channel inhibitor activity / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / presynaptic cytosol / cellular response to interferon-beta / Protein methylation / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / titin binding / eNOS activation / Ion homeostasis / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / calcium channel complex / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / sodium ion transmembrane transport / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / calyx of Held / bioluminescence / adenylate cyclase activator activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / sarcomere / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / regulation of cytokinesis / spindle microtubule / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / generation of precursor metabolites and energy / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / calcium channel regulator activity / sperm midpiece / RAF activation / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / response to calcium ion / calcium ion transmembrane transport / cellular response to type II interferon / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / Stimuli-sensing channels / spindle pole / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / calcium-dependent protein binding / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kschonsak M / Chua HC | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Structural architecture of the human NALCN channelosome. Authors: Marc Kschonsak / Han Chow Chua / Claudia Weidling / Nourdine Chakouri / Cameron L Noland / Katharina Schott / Timothy Chang / Christine Tam / Nidhi Patel / Christopher P Arthur / Alexander ...Authors: Marc Kschonsak / Han Chow Chua / Claudia Weidling / Nourdine Chakouri / Cameron L Noland / Katharina Schott / Timothy Chang / Christine Tam / Nidhi Patel / Christopher P Arthur / Alexander Leitner / Manu Ben-Johny / Claudio Ciferri / Stephan Alexander Pless / Jian Payandeh /    Abstract: Depolarizing sodium (Na) leak currents carried by the NALCN channel regulate the resting membrane potential of many neurons to modulate respiration, circadian rhythm, locomotion and pain sensitivity. ...Depolarizing sodium (Na) leak currents carried by the NALCN channel regulate the resting membrane potential of many neurons to modulate respiration, circadian rhythm, locomotion and pain sensitivity. NALCN requires FAM155A, UNC79 and UNC80 to function, but the role of these auxiliary subunits is not understood. NALCN, UNC79 and UNC80 are essential in rodents, and mutations in human NALCN and UNC80 cause severe developmental and neurological disease. Here we determined the structure of the NALCN channelosome, an approximately 1-MDa complex, as fundamental aspects about the composition, assembly and gating of this channelosome remain obscure. UNC79 and UNC80 are massive HEAT-repeat proteins that form an intertwined anti-parallel superhelical assembly, which docks intracellularly onto the NALCN-FAM155A pore-forming subcomplex. Calmodulin copurifies bound to the carboxy-terminal domain of NALCN, identifying this region as a putative modulatory hub. Single-channel analyses uncovered a low open probability for the wild-type complex, highlighting the tightly closed S6 gate in the structure, and providing a basis to interpret the altered gating properties of disease-causing variants. Key constraints between the UNC79-UNC80 subcomplex and the NALCN DI-DII and DII-DIII linkers were identified, leading to a model of channelosome gating. Our results provide a structural blueprint to understand the physiology of the NALCN channelosome and a template for drug discovery to modulate the resting membrane potential. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_25493.map.gz emd_25493.map.gz | 226.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-25493-v30.xml emd-25493-v30.xml emd-25493.xml emd-25493.xml | 29.9 KB 29.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_25493.png emd_25493.png | 85 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-25493.cif.gz emd-25493.cif.gz | 12.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_25493_additional_1.map.gz emd_25493_additional_1.map.gz | 226.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25493 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25493 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25493 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25493 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7sx4MC  7sx3C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_25493.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_25493.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | sharpened map used for model refinements | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1732 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: map (non-sharpened) of overall NALCN-FAM-UNC79-UNC80-CAM
| File | emd_25493_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | map (non-sharpened) of overall NALCN-FAM-UNC79-UNC80-CAM | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Pentameric complex of the leak channel NALCN with FAM155A, Calmod...
+Supramolecule #1: Pentameric complex of the leak channel NALCN with FAM155A, Calmod...
+Macromolecule #1: Sodium leak channel non-selective protein,Enhanced green fluoresc...
+Macromolecule #2: Transmembrane protein FAM155A
+Macromolecule #3: Calmodulin-1
+Macromolecule #4: UNC79,Protein unc-79 homolog
+Macromolecule #5: Protein unc-80 homolog
+Macromolecule #6: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
+Macromolecule #7: (1S)-2-{[(2-AMINOETHOXY)(HYDROXY)PHOSPHORYL]OXY}-1-[(PALMITOYLOXY...
+Macromolecule #8: (1R)-2-{[{[(2S)-2,3-DIHYDROXYPROPYL]OXY}(HYDROXY)PHOSPHORYL]OXY}-...
+Macromolecule #9: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.65 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| |||||||||
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R0.6/1 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Details: 3.5 sec blotting. | |||||||||
| Details | NALCN was reconstituted into lipid nanodiscs and mildly crosslinkned with 0.05% EM grade glutaraldehyde for 10 min at room temperature. Cross-linking was quenched with 9 mM Tris pH 7.5 |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 2 / Number real images: 26550 / Average exposure time: 3.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 64.009 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)