+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23850 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
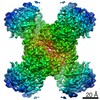
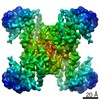
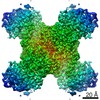
| Title | Human CTPS1 bound to inhibitor T35 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Human CTPS1 bound to inhibitor T35 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | glutaminase / amidoligase / nucleotide metabolism / LIGASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytoophidium / CTP synthase (glutamine hydrolysing) / CTP synthase activity / 'de novo' CTP biosynthetic process / pyrimidine nucleobase biosynthetic process / Interconversion of nucleotide di- and triphosphates / CTP biosynthetic process / nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process / B cell proliferation / T cell proliferation ...cytoophidium / CTP synthase (glutamine hydrolysing) / CTP synthase activity / 'de novo' CTP biosynthetic process / pyrimidine nucleobase biosynthetic process / Interconversion of nucleotide di- and triphosphates / CTP biosynthetic process / nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process / B cell proliferation / T cell proliferation / response to xenobiotic stimulus / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lynch EM / Dimattia MA | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021Title: Structural basis for isoform-specific inhibition of human CTPS1. Authors: Eric M Lynch / Michael A DiMattia / Steven Albanese / Gydo C P van Zundert / Jesse M Hansen / Joel D Quispe / Madison A Kennedy / Andreas Verras / Kenneth Borrelli / Angela V Toms / Neelu ...Authors: Eric M Lynch / Michael A DiMattia / Steven Albanese / Gydo C P van Zundert / Jesse M Hansen / Joel D Quispe / Madison A Kennedy / Andreas Verras / Kenneth Borrelli / Angela V Toms / Neelu Kaila / Kevin D Kreutter / Joshua J McElwee / Justin M Kollman /  Abstract: Cytidine triphosphate synthase 1 (CTPS1) is necessary for an effective immune response, as revealed by severe immunodeficiency in CTPS1-deficient individuals [E. Martin ], [] [510], [288-292] ([2014]) ...Cytidine triphosphate synthase 1 (CTPS1) is necessary for an effective immune response, as revealed by severe immunodeficiency in CTPS1-deficient individuals [E. Martin ], [] [510], [288-292] ([2014]). CTPS1 expression is up-regulated in activated lymphocytes to expand CTP pools [E. Martin ], [] [510], [288-292] ([2014]), satisfying increased demand for nucleic acid and lipid synthesis [L. D. Fairbanks, M. Bofill, K. Ruckemann, H. A. Simmonds], [ ] [270], [29682-29689] ([1995]). Demand for CTP in other tissues is met by the CTPS2 isoform and nucleoside salvage pathways [E. Martin ], [] [510], [288-292] ([2014]). Selective inhibition of the proliferative CTPS1 isoform is therefore desirable in the treatment of immune disorders and lymphocyte cancers, but little is known about differences in regulation of the isoforms or mechanisms of known inhibitors. We show that CTP regulates both isoforms by binding in two sites that clash with substrates. CTPS1 is less sensitive to CTP feedback inhibition, consistent with its role in increasing CTP levels in proliferation. We also characterize recently reported small-molecule inhibitors, both CTPS1 selective and nonselective. Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures reveal these inhibitors mimic CTP binding in one inhibitory site, where a single amino acid substitution explains selectivity for CTPS1. The inhibitors bind to CTPS assembled into large-scale filaments, which for CTPS1 normally represents a hyperactive form of the enzyme [E. M. Lynch ], [] [24], [507-514] ([2017]). This highlights the utility of cryo-EM in drug discovery, particularly for cases in which targets form large multimeric assemblies not amenable to structure determination by other techniques. Both inhibitors also inhibit the proliferation of human primary T cells. The mechanisms of selective inhibition of CTPS1 lay the foundation for the design of immunosuppressive therapies. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23850.map.gz emd_23850.map.gz | 6.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23850-v30.xml emd-23850-v30.xml emd-23850.xml emd-23850.xml | 11.9 KB 11.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_23850.png emd_23850.png | 194.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-23850.cif.gz emd-23850.cif.gz | 5.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23850 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23850 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23850 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23850 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7migMC  7mgzC  7mh0C  7mh1C  7mifC  7mihC  7miiC  7mipC  7miuC  7mivC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23850.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23850.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Human CTPS1 bound to inhibitor T35 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.05 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : CTPS1 tetramer
| Entire | Name: CTPS1 tetramer |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: CTPS1 tetramer
| Supramolecule | Name: CTPS1 tetramer / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: CTP synthase 1
| Macromolecule | Name: CTP synthase 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: CTP synthase (glutamine hydrolysing) |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 66.777297 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  unidentified baculovirus unidentified baculovirus |
| Sequence | String: MKYILVTGGV ISGIGKGIIA SSVGTILKSC GLHVTSIKID PYINIDAGTF SPYEHGEVFV LDDGGEVDLD LGNYERFLDI RLTKDNNLT TGKIYQYVIN KERKGDYLGK TVQVVPHITD AIQEWVMRQA LIPVDEDGLE PQVCVIELGG TVGDIESMPF I EAFRQFQF ...String: MKYILVTGGV ISGIGKGIIA SSVGTILKSC GLHVTSIKID PYINIDAGTF SPYEHGEVFV LDDGGEVDLD LGNYERFLDI RLTKDNNLT TGKIYQYVIN KERKGDYLGK TVQVVPHITD AIQEWVMRQA LIPVDEDGLE PQVCVIELGG TVGDIESMPF I EAFRQFQF KVKRENFCNI HVSLVPQPSS TGEQKTKPTQ NSVRELRGLG LSPDLVVCRC SNPLDTSVKE KISMFCHVEP EQ VICVHDV SSIYRVPLLL EEQGVVDYFL RRLDLPIERQ PRKMLMKWKE MADRYDRLLE TCSIALVGKY TKFSDSYASV IKA LEHSAL AINHKLEIKY IDSADLEPIT SQEEPVRYHE AWQKLCSAHG VLVPGGFGVR GTEGKIQAIA WARNQKKPFL GVCL GMQLA VVEFSRNVLG WQDANSTEFD PTTSHPVVVD MPEHNPGQMG GTMRLGKRRT LFQTKNSVMR KLYGDADYLE ERHRH RFEV NPVWKKCLEE QGLKFVGQDV EGERMEIVEL EDHPFFVGVQ YHPEFLSRPI KPSPPYFGLL LASVGRLSHY LQKGCR LSP RDTYSDRSGS SSPDSEITEL KFPSINHD UniProtKB: CTP synthase 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: 2-{2-[(cyclopropanesulfonyl)amino]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl}-2-methyl-N-{...
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-{2-[(cyclopropanesulfonyl)amino]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl}-2-methyl-N-{5-[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrazin-2-yl]pyridin-2-yl}propanamide type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZFY |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 512.528 Da |
| Chemical component information | 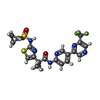 ChemComp-ZFY: |
-Macromolecule #3: GLUTAMINE
| Macromolecule | Name: GLUTAMINE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: GLN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 146.144 Da |
| Chemical component information | 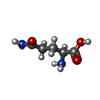 ChemComp-GLN: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: URIDINE 5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: URIDINE 5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: UTP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 484.141 Da |
| Chemical component information | 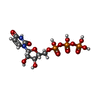 ChemComp-UTP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.9 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 90.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: EMDB MAP |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 3.1) / Number images used: 144655 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 3.1) |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 3.1) |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




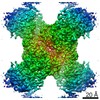
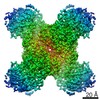
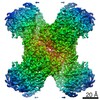
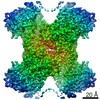



 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)





















