+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure and autoinhibitory regulation of MET1 in the maintenance of plant CG methylation. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Plant Cell, Vol. 37, Issue 11, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Oct 31, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Jiuwei Lu / Xinyi Chen / Jian Fang / Daniel Li / Huy Le / Xuehua Zhong / Jikui Song /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Plant DNA methyltransferase 1 (MET1) is responsible for maintaining genome-wide cytosine-phosphate-guanine (CG) methylation. Its dysregulation has been linked to profound biological disruptions, ...Plant DNA methyltransferase 1 (MET1) is responsible for maintaining genome-wide cytosine-phosphate-guanine (CG) methylation. Its dysregulation has been linked to profound biological disruptions, including genomic instability and developmental defects. However, the exact mechanism by which MET1 orchestrates these vital functions and coordinates its various domains to shape the plant-specific epigenome remains unknown. Here, we report the cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of Arabidopsis thaliana MET1 (AtMET1), revealing an autoinhibitory mechanism that governs its DNA methylation activity. Between the 2 replication foci target sequence (RFTS) domains in AtMET1, the second RFTS domain (RFTS2) directly associates with the methyltransferase (MTase) domain, thereby inhibiting substrate-binding activity. Compared with DNMT1, AtMET1 lacks the CXXC domain and its downstream autoinhibitory linker, featuring only limited RFTS2-MTase interactions, resulting in a much-reduced autoinhibitory contact. In line with this difference, the DNA methylation activity of AtMET1 displays less temperature dependence than that of DNMT1, potentially allowing MET1 to maintain its activity across diverse temperature conditions. We further report the structure of AtMET1 bound to hemimethylated CG DNA, unveiling the molecular basis for substrate binding and CG recognition by AtMET1, and an activation mechanism that involves a coordinated conformational shift between 2 structural elements of its active site. In addition, our combined structural and biochemical analysis highlights distinct functionalities between the 2 RFTS domains of AtMET1, unraveling their evolutionary divergence from the DNMT1 RFTS domain. Together, this study offers a framework for understanding the structure and mechanism of AtMET1, with profound implications for the maintenance of CG methylation in plants. |
 External links External links |  Plant Cell / Plant Cell /  PubMed:41082549 PubMed:41082549 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.9 - 3.29 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-71556, PDB-9peb: EMDB-71557, PDB-9pec: EMDB-71558, PDB-9ped: |
| Chemicals | 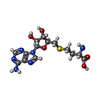 ChemComp-SAH:  ChemComp-ZN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase / TRANSFERASE/DNA / TRANSFERASE-DNA complex |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers










