+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural basis for activity switching in polymerases determining the fate of let-7 pre-miRNAs. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Struct Mol Biol, Vol. 31, Issue 9, Page 1426-1438, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Jul 25, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Gangshun Yi / Mingda Ye / Loic Carrique / Afaf El-Sagheer / Tom Brown / Chris J Norbury / Peijun Zhang / Robert J C Gilbert /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Tumor-suppressor let-7 pre-microRNAs (miRNAs) are regulated by terminal uridylyltransferases TUT7 and TUT4 that either promote let-7 maturation by adding a single uridine nucleotide to the pre-miRNA ...Tumor-suppressor let-7 pre-microRNAs (miRNAs) are regulated by terminal uridylyltransferases TUT7 and TUT4 that either promote let-7 maturation by adding a single uridine nucleotide to the pre-miRNA 3' end or mark them for degradation by the addition of multiple uridines. Oligo-uridylation is increased in cells by enhanced TUT7/4 expression and especially by the RNA-binding pluripotency factor LIN28A. Using cryogenic electron microscopy, we captured high-resolution structures of active forms of TUT7 alone, of TUT7 plus pre-miRNA and of both TUT7 and TUT4 bound with pre-miRNA and LIN28A. Our structures reveal that pre-miRNAs engage the enzymes in fundamentally different ways depending on the presence of LIN28A, which clamps them onto the TUTs to enable processive 3' oligo-uridylation. This study reveals the molecular basis for mono- versus oligo-uridylation by TUT7/4, as determined by the presence of LIN28A, and thus their mechanism of action in the regulation of cell fate and in cancer. |
 External links External links |  Nat Struct Mol Biol / Nat Struct Mol Biol /  PubMed:39054354 / PubMed:39054354 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.65 - 4.0 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-16825, PDB-8oef: EMDB-17084, PDB-8opp: EMDB-17086, PDB-8ops: EMDB-17087, PDB-8opt: EMDB-17164, PDB-8ost: |
| Chemicals | 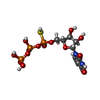 ChemComp-P5E:  ChemComp-ZN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | RNA / Polymerase / uridylation / RNA maturation and turnover control / RNA BINDING PROTEIN / CELL CYCLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers






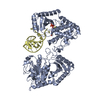

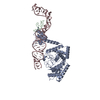

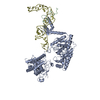


 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)