+Search query
-Structure paper
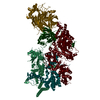
| Title | Cryo-EM structures of Gid12-bound GID E3 reveal steric blockade as a mechanism inhibiting substrate ubiquitylation. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 13, Issue 1, Page 3041, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Jun 1, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Shuai Qiao / Chia-Wei Lee / Dawafuti Sherpa / Jakub Chrustowicz / Jingdong Cheng / Maximilian Duennebacke / Barbara Steigenberger / Ozge Karayel / Duc Tung Vu / Susanne von Gronau / Matthias Mann / Florian Wilfling / Brenda A Schulman /    |
| PubMed Abstract | Protein degradation, a major eukaryotic response to cellular signals, is subject to numerous layers of regulation. In yeast, the evolutionarily conserved GID E3 ligase mediates glucose-induced ...Protein degradation, a major eukaryotic response to cellular signals, is subject to numerous layers of regulation. In yeast, the evolutionarily conserved GID E3 ligase mediates glucose-induced degradation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (Fbp1), malate dehydrogenase (Mdh2), and other gluconeogenic enzymes. "GID" is a collection of E3 ligase complexes; a core scaffold, RING-type catalytic core, and a supramolecular assembly module together with interchangeable substrate receptors select targets for ubiquitylation. However, knowledge of additional cellular factors directly regulating GID-type E3s remains rudimentary. Here, we structurally and biochemically characterize Gid12 as a modulator of the GID E3 ligase complex. Our collection of cryo-EM reconstructions shows that Gid12 forms an extensive interface sealing the substrate receptor Gid4 onto the scaffold, and remodeling the degron binding site. Gid12 also sterically blocks a recruited Fbp1 or Mdh2 from the ubiquitylation active sites. Our analysis of the role of Gid12 establishes principles that may more generally underlie E3 ligase regulation. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:35650207 / PubMed:35650207 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.3 - 31.2 Å |
| Structure data |  EMDB-14323: Structure of Chelator-GIDSR4 bound to Mdh2  EMDB-14324: Structure of Cage-GIDSR4 bound to PHSVTP-Fbp1 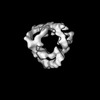 EMDB-14338: Structure of endogenous Cage-GIDAnt complex EMDB-32830, PDB-7wug:  EMDB-32831: Gid12 bound GIDSR4 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex 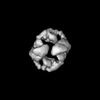 EMDB-32833: Gid12 bound Chelator-GIDSR4 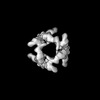 EMDB-32834: Cage assembly GID E3 ubiquitin ligase  EMDB-32835: Gid12 bound Cage-GIDSR3 |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | LIGASE / E3 ubiquitin Ligase / beta-propellor |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers