+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structures and therapeutic potential of anti-RBD human monoclonal antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Theranostics, Vol. 12, Issue 1, Page 1-17, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Jan 1, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Kuan-Ying A Huang / Daming Zhou / Tiong Kit Tan / Charles Chen / Helen M E Duyvesteyn / Yuguang Zhao / Helen M Ginn / Ling Qin / Pramila Rijal / Lisa Schimanski / Robert Donat / Adam Harding / Javier Gilbert-Jaramillo / William James / Julia A Tree / Karen Buttigieg / Miles Carroll / Sue Charlton / Chia-En Lien / Meei-Yun Lin / Cheng-Pin Chen / Shu-Hsing Cheng / Xiaorui Chen / Tzou-Yien Lin / Elizabeth E Fry / Jingshan Ren / Che Ma / Alain R Townsend / David I Stuart /    |
| PubMed Abstract | Administration of potent anti-receptor-binding domain (RBD) monoclonal antibodies has been shown to curtail viral shedding and reduce hospitalization in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. However, ... Administration of potent anti-receptor-binding domain (RBD) monoclonal antibodies has been shown to curtail viral shedding and reduce hospitalization in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. However, the structure-function analysis of potent human anti-RBD monoclonal antibodies and its links to the formulation of antibody cocktails remains largely elusive. Previously, we isolated a panel of neutralizing anti-RBD monoclonal antibodies from convalescent patients and showed their neutralization efficacy . Here, we elucidate the mechanism of action of antibodies and dissect antibodies at the epitope level, which leads to a formation of a potent antibody cocktail. We found that representative antibodies which target non-overlapping epitopes are effective against wild type virus and recently emerging variants of concern, whilst being encoded by antibody genes with few somatic mutations. Neutralization is associated with the inhibition of binding of viral RBD to ACE2 and possibly of the subsequent fusion process. Structural analysis of representative antibodies, by cryo-electron microscopy and crystallography, reveals that they have some unique aspects that are of potential value while sharing some features in common with previously reported neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. For instance, one has a common VH 3-53 public variable region yet is unusually resilient to mutation at residue 501 of the RBD. We evaluate the efficacy of an antibody cocktail consisting of two potent non-competing anti-RBD antibodies in a Syrian hamster model. We demonstrate that the cocktail prevents weight loss, reduces lung viral load and attenuates pulmonary inflammation in hamsters in both prophylactic and therapeutic settings. Although neutralization of one of these antibodies is abrogated by the mutations of variant B.1.351, it is also possible to produce a bi-valent cocktail of antibodies both of which are resilient to variants B.1.1.7, B.1.351 and B.1.617.2. These findings support the up-to-date and rational design of an anti-RBD antibody cocktail as a therapeutic candidate against COVID-19. |
 External links External links |  Theranostics / Theranostics /  PubMed:34987630 / PubMed:34987630 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2.92 - 4.8 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-13742, PDB-7q0a:  PDB-7pqy:  PDB-7pqz: 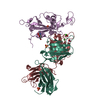 PDB-7pr0: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-PO4:  ChemComp-NAG:  ChemComp-SO4: 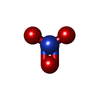 ChemComp-NO3:  ChemComp-CL:  ChemComp-GOL: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / SARS-CoV-2 antibody / receptor-binding-domain / RBD / spike / neutralisation / FI-3A / FD-11A / FD-5D / VIRAL PROTEIN/IMMUNE SYSTEM / SARS-CoV2 / ectodomain / fab / antibody / trimer / virus |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)