+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structure and function of the AAA+ protein CbbX, a red-type Rubisco activase. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nature, Vol. 479, Issue 7372, Page 194-199, Year 2011 |
| 掲載日 | 2011年11月2日 |
 著者 著者 | Oliver Mueller-Cajar / Mathias Stotz / Petra Wendler / F Ulrich Hartl / Andreas Bracher / Manajit Hayer-Hartl /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) catalyses the fixation of atmospheric CO(2) in photosynthesis, but tends to form inactive complexes with its substrate ribulose 1,5- ...Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) catalyses the fixation of atmospheric CO(2) in photosynthesis, but tends to form inactive complexes with its substrate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP). In plants, Rubisco is reactivated by the AAA(+) (ATPases associated with various cellular activities) protein Rubisco activase (Rca), but no such protein is known for the Rubisco of red algae. Here we identify the protein CbbX as an activase of red-type Rubisco. The 3.0-Å crystal structure of unassembled CbbX from Rhodobacter sphaeroides revealed an AAA(+) protein architecture. Electron microscopy and biochemical analysis showed that ATP and RuBP must bind to convert CbbX into functionally active, hexameric rings. The CbbX ATPase is strongly stimulated by RuBP and Rubisco. Mutational analysis suggests that CbbX functions by transiently pulling the carboxy-terminal peptide of the Rubisco large subunit into the hexamer pore, resulting in the release of the inhibitory RuBP. Understanding Rubisco activation may facilitate efforts to improve CO(2) uptake and biomass production by photosynthetic organisms. |
 リンク リンク |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:22048315 PubMed:22048315 |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) / X線回折 |
| 解像度 | 3 - 21.0 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-1932, PDB-3zuh: 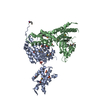 PDB-3syk: 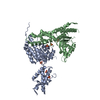 PDB-3syl: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-SO4:  ChemComp-HOH: 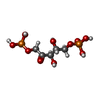 ChemComp-RUB:  ChemComp-ADP: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | CHAPERONE / photosynthesis / Rubisco activase / AAA+ protein / Calvin cycle / ATP BINDING PROTEIN |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について




 rhodobacter sphaeroides (バクテリア)
rhodobacter sphaeroides (バクテリア)