+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | The structure of bacteriorhodopsin at 3.0 A resolution based on electron crystallography: implication of the charge distribution. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | J Mol Biol, Vol. 286, Issue 3, Page 861-882, Year 1999 |
| Publish date | Feb 26, 1999 |
 Authors Authors | K Mitsuoka / T Hirai / K Murata / A Miyazawa / A Kidera / Y Kimura / Y Fujiyoshi /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Electron crystallography has the potential to visualise the charge status of atoms. This is due to the significantly different scattering factors of neutral and ionised atoms for electrons in the low- ...Electron crystallography has the potential to visualise the charge status of atoms. This is due to the significantly different scattering factors of neutral and ionised atoms for electrons in the low-resolution range (typically less than 5 A). In previous work, we observed two different types of densities around acidic residues in the experimental (|Fo|) map of bacteriorhodopsin (bR), a light-driven proton pump. We suggested that these might reflect different states of the acidic residues; namely, the protonated (neutral) and the deprotonated (negatively charged) state. To evaluate the observed charge more quantitatively, we refined the atomic model for bR and eight surrounding lipids using our electron crystallographic data set between 8.0 and 3.0 A resolution, where the charge effect is small. The refined model yielded an R-factor of 23.7% and a free R-factor of 33.0%. To evaluate the effect of charges on the density map, we calculated a difference (|Fo|-|Fc|) map including data of a resolution lower than 8.0 A resolution, where the charge effect is significant. We found strong peaks in the difference map mainly in the backbone region of the transmembrane helices. We interpreted these peaks to come from the polarisation of the polar groups in the main chain of the alpha-helices and we examined this by assuming a partial charge of 0.5 for the peptide carbonyl groups. The resulting R and free R-factors dropped from 0.250 and 0.341 to 0.246 and 0.336, respectively. Furthermore, we also observed some strong peaks around some side-chains, which could be assigned to positively charged atoms. Thus, we could show that Asp36 and Asp102 are likely to interact with cations nearby. In addition, peaks found around the acidic residues Glu74, Glu194 and Glu212 have different features and might represent positive charges on polarised water molecules or hydroxonium ions. |
 External links External links |  J Mol Biol / J Mol Biol /  PubMed:10024456 PubMed:10024456 |
| Methods | EM (electron crystallography) |
| Resolution | 3 Å |
| Structure data | 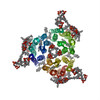 PDB-2at9: |
| Chemicals | 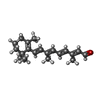 ChemComp-RET:  ChemComp-2DP:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | PHOTORECEPTOR / PROTON PUMP / MEMBRANE PROTEIN / RETINAL PROTEIN / TWO-DIMENSIONAL CRYSTAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



 halobacterium salinarum (Halophile)
halobacterium salinarum (Halophile)