+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Protein nanoparticle vaccines induce potent neutralizing antibody responses against MERS-CoV. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Cell Rep, Vol. 43, Issue 12, Page 115036, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Dec 24, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Cara W Chao / Kaitlin R Sprouse / Marcos C Miranda / Nicholas J Catanzaro / Miranda L Hubbard / Amin Addetia / Cameron Stewart / Jack T Brown / Annie Dosey / Adian Valdez / Rashmi Ravichandran / Grace G Hendricks / Maggie Ahlrichs / Craig Dobbins / Alexis Hand / Jackson McGowan / Boston Simmons / Catherine Treichel / Isabelle Willoughby / Alexandra C Walls / Andrew T McGuire / Elizabeth M Leaf / Ralph S Baric / Alexandra Schäfer / David Veesler / Neil P King /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is a betacoronavirus that causes severe respiratory illness in humans. There are no licensed vaccines against MERS-CoV and only a few ...Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is a betacoronavirus that causes severe respiratory illness in humans. There are no licensed vaccines against MERS-CoV and only a few candidates in phase I clinical trials. Here, we develop MERS-CoV vaccines utilizing a computationally designed protein nanoparticle platform that has generated safe and immunogenic vaccines against various enveloped viruses, including a licensed vaccine for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Two-component nanoparticles displaying spike (S)-derived antigens induce neutralizing responses and protect mice against challenge with mouse-adapted MERS-CoV. Epitope mapping reveals the dominant responses elicited by immunogens displaying the prefusion-stabilized S-2P trimer, receptor binding domain (RBD), or N-terminal domain (NTD). An RBD nanoparticle elicits antibodies targeting multiple non-overlapping epitopes in the RBD. Our findings demonstrate the potential of two-component nanoparticle vaccine candidates for MERS-CoV and suggest that this platform technology could be broadly applicable to betacoronavirus vaccine development. |
 External links External links |  Cell Rep / Cell Rep /  PubMed:39644492 / PubMed:39644492 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 15.0 Å |
| Structure data | 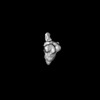 EMDB-47577: Negative stain EM map of polyclonal serum from mouse immunized with MERS-CoV NTD-I53-50 in complex with MERS S-2P  EMDB-47580: Negative stain EM map of polyclonal serum from mouse immunized with MERS-CoV S-2P in complex with MERS S-2P  EMDB-47583: Negative stain EM map of polyclonal serum from mouse immunized with MERS-CoV S-2P in complex with MERS S-2P  EMDB-47584: Negative stain EM map of polyclonal serum from mouse immunized with MERS-CoV S-2P-I53-50 in complex with MERS S-2P  EMDB-47585: Negative stain EM map of polyclonal serum from mouse immunized with MERS-CoV S-2P-I53-50 in complex with MERS S-2P  EMDB-47586: Negative stain EM map of polyclonal serum from mouse immunized with MERS-CoV S-2P-T33_dn10 in complex with MERS S-2P  EMDB-47587: Negative stain EM map of polyclonal serum from mouse immunized with MERS-CoV S-2P-T33_dn10 in complex with MERS S-2P 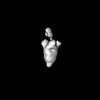 EMDB-47588: Negative stain EM map of polyclonal serum from mouse immunized with MERS-CoV RBD-I53-50 in complex with MERS S-2P  EMDB-47589: Negative stain EM map of polyclonal serum from mouse immunized with MERS-CoV RBD-I53-50 in complex with MERS S-2P  EMDB-47592: Negative stain EM map of polyclonal serum from mouse immunized with MERS-CoV RBD-I53-50 in complex with MERS S-2P |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




