+Search query
-Structure paper
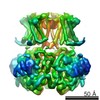
| Title | Cryo-electron microscopy structure of the Slo2.2 Na(+)-activated K(+) channel. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 527, Issue 7577, Page 198-203, Year 2015 |
| Publish date | Nov 12, 2015 |
 Authors Authors | Richard K Hite / Peng Yuan / Zongli Li / Yichun Hsuing / Thomas Walz / Roderick MacKinnon /  |
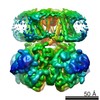
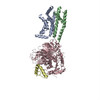
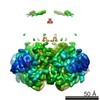
| PubMed Abstract | Na(+)-activated K(+) channels are members of the Slo family of large conductance K(+) channels that are widely expressed in the brain, where their opening regulates neuronal excitability. These ...Na(+)-activated K(+) channels are members of the Slo family of large conductance K(+) channels that are widely expressed in the brain, where their opening regulates neuronal excitability. These channels fulfil a number of biological roles and have intriguing biophysical properties, including conductance levels that are ten times those of most other K(+) channels and gating sensitivity to intracellular Na(+). Here we present the structure of a complete Na(+)-activated K(+) channel, chicken Slo2.2, in the Na(+)-free state, determined by cryo-electron microscopy at a nominal resolution of 4.5 ångströms. The channel is composed of a large cytoplasmic gating ring, in which resides the Na(+)-binding site and a transmembrane domain that closely resembles voltage-gated K(+) channels. In the structure, the cytoplasmic domain adopts a closed conformation and the ion conduction pore is also closed. The structure reveals features that can explain the unusually high conductance of Slo channels and how contraction of the cytoplasmic gating ring closes the pore. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:26436452 / PubMed:26436452 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 4.2 - 5.2 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-3062: Cryo-EM structure of the Slo2.2 Na+-activated K+ channel |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT / ION CHANNEL / POTASSIUM CHANNEL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers