+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | In situ cryo-electron tomography reveals the asymmetric architecture of mammalian sperm axonemes. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Struct Mol Biol, Vol. 30, Issue 3, Page 360-369, Year 2023 |
| Publish date | Jan 2, 2023 |
 Authors Authors | Zhen Chen / Garrett A Greenan / Momoko Shiozaki / Yanxin Liu / Will M Skinner / Xiaowei Zhao / Shumei Zhao / Rui Yan / Zhiheng Yu / Polina V Lishko / David A Agard / Ronald D Vale /  |
| PubMed Abstract | The flagella of mammalian sperm display non-planar, asymmetric beating, in contrast to the planar, symmetric beating of flagella from sea urchin sperm and unicellular organisms. The molecular basis ...The flagella of mammalian sperm display non-planar, asymmetric beating, in contrast to the planar, symmetric beating of flagella from sea urchin sperm and unicellular organisms. The molecular basis of this difference is unclear. Here, we perform in situ cryo-electron tomography of mouse and human sperm, providing the highest-resolution structural information to date. Our subtomogram averages reveal mammalian sperm-specific protein complexes within the microtubules, the radial spokes and nexin-dynein regulatory complexes. The locations and structures of these complexes suggest potential roles in enhancing the mechanical strength of mammalian sperm axonemes and regulating dynein-based axonemal bending. Intriguingly, we find that each of the nine outer microtubule doublets is decorated with a distinct combination of sperm-specific complexes. We propose that this asymmetric distribution of proteins differentially regulates the sliding of each microtubule doublet and may underlie the asymmetric beating of mammalian sperm. |
 External links External links |  Nat Struct Mol Biol / Nat Struct Mol Biol /  PubMed:36593309 / PubMed:36593309 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (subtomogram averaging) |
| Resolution | 18.0 - 35.0 Å |
| Structure data |  EMDB-27444: 96-nm repeat unit of microtubule doublet from mouse sperm 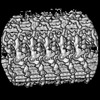 EMDB-27445: 32-nm repeating structure of central pair complex from mouse sperm  EMDB-27446: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 1 from mouse sperm  EMDB-27447: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 2 from mouse sperm  EMDB-27448: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 3 from mouse sperm  EMDB-27449: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 4 from mouse sperm  EMDB-27450: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 5 from mouse sperm  EMDB-27451: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 6 from mouse sperm  EMDB-27452: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 7 from mouse sperm  EMDB-27453: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 8 from mouse sperm  EMDB-27454: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 9 from mouse sperm  EMDB-27455: 48-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet from mouse sperm  EMDB-27456: 5-6 bridge from mouse sperm  EMDB-27457: 32-nm repeating structure of central pair complex from human sperm 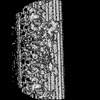 EMDB-27462: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet from human sperm  EMDB-27463: 32-nm repeating structure of central pair complex from human sperm 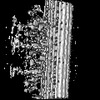 EMDB-27464: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 1 from human sperm 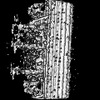 EMDB-27465: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 2 from human sperm  EMDB-27466: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 3 from human sperm  EMDB-27467: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 4 from human sperm  EMDB-27468: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 5 from human sperm  EMDB-27469: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 6 from human sperm  EMDB-27470: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 7 from human sperm  EMDB-27471: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 8 from human sperm  EMDB-27473: 96-nm repeating structure of microtubule doublet 9 from human sperm |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




 Homo sapiens (human)
Homo sapiens (human)