+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Intermediates in SARS-CoV-2 spike-mediated cell entry. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Sci Adv, Vol. 8, Issue 33, Page eabo3153, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Aug 19, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Tara C Marcink / Thomas Kicmal / Emily Armbruster / Zhening Zhang / Gillian Zipursky / Kate L Golub / Mohab Idris / Jonathan Khao / Jennifer Drew-Bear / Gael McGill / Tom Gallagher / Matteo Porotto / Amédée des Georges / Anne Moscona /   |
| PubMed Abstract | SARS-CoV-2 cell entry is completed after viral spike (S) protein-mediated membrane fusion between viral and host cell membranes. Stable prefusion and postfusion S structures have been resolved by ...SARS-CoV-2 cell entry is completed after viral spike (S) protein-mediated membrane fusion between viral and host cell membranes. Stable prefusion and postfusion S structures have been resolved by cryo-electron microscopy and cryo-electron tomography, but the refolding intermediates on the fusion pathway are transient and have not been examined. We used an antiviral lipopeptide entry inhibitor to arrest S protein refolding and thereby capture intermediates as S proteins interact with hACE2 and fusion-activating proteases on cell-derived target membranes. Cryo-electron tomography imaged both extended and partially folded intermediate states of S2, as well as a novel late-stage conformation on the pathway to membrane fusion. The intermediates now identified in this dynamic S protein-directed fusion provide mechanistic insights that may guide the design of CoV entry inhibitors. |
 External links External links |  Sci Adv / Sci Adv /  PubMed:35984891 / PubMed:35984891 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (tomography) / EM (subtomogram averaging) |
| Resolution | 19.0 Å |
| Structure data | 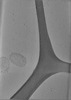 EMDB-24599: Tomogram of SARS-CoV-2 spike-bearing virus-like particles (VLPs) interacting with hACE2-bearing extracellular vesicles (tEVs), showing various intermediate states of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (Fig. 2M,N, Fig 3J, and Supp. Movie 1 of the manuscript Marcink et al., 2021). 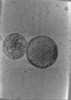 EMDB-24600: Tomogram of SARS-CoV-2 spike-bearing virus-like particles (VLPs) interacting with hACE2-bearing extracellular vesicles (tEVs), showing various intermediate states of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (Fig. 2K,L, and Supp. Movie 2 of the manuscript Marcink et. al 2021,).  EMDB-24601: Tomogram of SARS-CoV-2 spike-bearing virus-like particles (VLPs) interacting with hACE2-bearing extracellular vesicles (tEVs), showing various intermediate states of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (Fig. 4B-E and Supp. Movie 3 of manuscript Marcink et al., 2021). 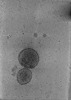 EMDB-24602: Tomogram of SARS-CoV-2 spike-bearing virus-like particles (VLPs) interacting with hACE2-bearing extracellular vesicles (tEVs), showing various intermediate states of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (Fig 2E-G of the manuscript Marcink et al., 2021).  EMDB-24603: Tomogram of SARS-CoV-2 spike-bearing virus-like particles (VLPs) interacting with hACE2-bearing extracellular vesicles (tEVs), showing various intermediate states of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (Fig. 3D,E of the manuscript Marcink et al., 2021). 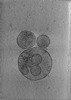 EMDB-24604: Tomogram of SARS-CoV-2 spike-bearing virus-like particles (VLPs) interacting with hACE2-bearing extracellular vesicles (tEVs), showing various intermediate states of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (Fig. 4H-J of the manuscript Marcink et al., 2021)  EMDB-26679: Subtomogram averaged map of hACE2 dimers on the surface of extracellular vesicles |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




 Homo sapiens HEK293-T (human)
Homo sapiens HEK293-T (human)