+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Ca inactivation of the mammalian ryanodine receptor type 1 in a lipidic environment revealed by cryo-EM. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Elife, Vol. 11, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Mar 8, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Ashok R Nayak / Montserrat Samsó /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Activation of the intracellular Ca channel ryanodine receptor (RyR) triggers a cytosolic Ca surge, while elevated cytosolic Ca inhibits the channel in a negative feedback mechanism. Cryogenic ...Activation of the intracellular Ca channel ryanodine receptor (RyR) triggers a cytosolic Ca surge, while elevated cytosolic Ca inhibits the channel in a negative feedback mechanism. Cryogenic electron microscopy of rabbit RyR1 embedded in nanodiscs under partially inactivating Ca conditions revealed an open and a closed-inactivated conformation. Ca binding to the high-affinity site engages the central and C-terminal domains into a block, which pries the S6 four-helix bundle open. Further rotation of this block pushes S6 toward the central axis, closing (inactivating) the channel. Main characteristics of the Ca-inactivated conformation are downward conformation of the cytoplasmic assembly and tightly knit subunit interface contributed by a fully occupied Ca activation site, two inter-subunit resolved lipids, and two salt bridges between the EF hand domain and the S2-S3 loop validated by disease-causing mutations. The structural insight illustrates the prior Ca activation prerequisite for Ca inactivation and provides for a seamless transition from inactivated to closed conformations. |
 External links External links |  Elife / Elife /  PubMed:35257661 / PubMed:35257661 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.3 - 4.3 Å |
| Structure data | 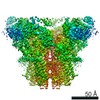 EMDB-22597: EMDB-22616, PDB-7k0t: EMDB-25828, PDB-7tdg: EMDB-25829, PDB-7tdh: EMDB-25830, PDB-7tdi: EMDB-25831, PDB-7tdj: EMDB-25832, PDB-7tdk:  EMDB-25833: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ACP:  ChemComp-ZN:  ChemComp-CA:  ChemComp-POV:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / Ryanodine Receptor / RyR1 / Intracellular Calcium channel / Excitation-Contraction coupling / ATP / Ca2+ / Inactivation |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers