+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Activation of STING by targeting a pocket in the transmembrane domain. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 604, Issue 7906, Page 557-562, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Apr 6, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Defen Lu / Guijun Shang / Jie Li / Yong Lu / Xiao-Chen Bai / Xuewu Zhang /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) is an adaptor protein in innate immunity against DNA viruses or bacteria. STING-mediated immunity could be exploited in the development of vaccines or cancer ...Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) is an adaptor protein in innate immunity against DNA viruses or bacteria. STING-mediated immunity could be exploited in the development of vaccines or cancer immunotherapies. STING is a transmembrane dimeric protein that is located in the endoplasmic reticulum or in the Golgi apparatus. STING is activated by the binding of its cytoplasmic ligand-binding domain to cyclic dinucleotides that are produced by the DNA sensor cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthase or by invading bacteria. Cyclic dinucleotides induce a conformational change in the STING ligand-binding domain, which leads to a high-order oligomerization of STING that is essential for triggering the downstream signalling pathways. However, the cGAMP-induced STING oligomers tend to dissociate in solution and have not been resolved to high resolution, which limits our understanding of the activation mechanism. Here we show that a small-molecule agonist, compound 53 (C53), promotes the oligomerization and activation of human STING through a mechanism orthogonal to that of cGAMP. We determined a cryo-electron microscopy structure of STING bound to both C53 and cGAMP, revealing a stable oligomer that is formed by side-by-side packing and has a curled overall shape. Notably, C53 binds to a cryptic pocket in the STING transmembrane domain, between the two subunits of the STING dimer. This binding triggers outward shifts of transmembrane helices in the dimer, and induces inter-dimer interactions between these helices to mediate the formation of the high-order oligomer. Our functional analyses show that cGAMP and C53 together induce stronger activation of STING than either ligand alone. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:35388221 / PubMed:35388221 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.45 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-25142, PDB-7sii: |
| Chemicals | 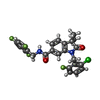 ChemComp-9IM: 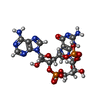 ChemComp-1SY: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / Sting / agonist / activate conformation / oligomer |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)