+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Gene- and Species-Specific Hox mRNA Translation by Ribosome Expansion Segments. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Mol Cell, Vol. 80, Issue 6, Page 980-995.e13, Year 2020 |
| Publish date | Dec 17, 2020 |
 Authors Authors | Kathrin Leppek / Kotaro Fujii / Nick Quade / Teodorus Theo Susanto / Daniel Boehringer / Tea Lenarčič / Shifeng Xue / Naomi R Genuth / Nenad Ban / Maria Barna /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Ribosomes have been suggested to directly control gene regulation, but regulatory roles for ribosomal RNA (rRNA) remain largely unexplored. Expansion segments (ESs) consist of multitudes of tentacle- ...Ribosomes have been suggested to directly control gene regulation, but regulatory roles for ribosomal RNA (rRNA) remain largely unexplored. Expansion segments (ESs) consist of multitudes of tentacle-like rRNA structures extending from the core ribosome in eukaryotes. ESs are remarkably variable in sequence and size across eukaryotic evolution with largely unknown functions. In characterizing ribosome binding to a regulatory element within a Homeobox (Hox) 5' UTR, we identify a modular stem-loop within this element that binds to a single ES, ES9S. Engineering chimeric, "humanized" yeast ribosomes for ES9S reveals that an evolutionary change in the sequence of ES9S endows species-specific binding of Hoxa9 mRNA to the ribosome. Genome editing to site-specifically disrupt the Hoxa9-ES9S interaction demonstrates the functional importance for such selective mRNA-rRNA binding in translation control. Together, these studies unravel unexpected gene regulation directly mediated by rRNA and how ribosome evolution drives translation of critical developmental regulators. |
 External links External links |  Mol Cell / Mol Cell /  PubMed:33202249 / PubMed:33202249 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.1 - 4.4 Å |
| Structure data | 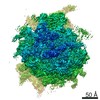 EMDB-11562: 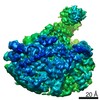 EMDB-11563:  EMDB-11564: 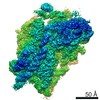 EMDB-11565: 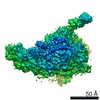 EMDB-11566:  EMDB-11567:  EMDB-11568: |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



 Homo sapiens (human)
Homo sapiens (human)