+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Cryo-electron microscopy of Na ,K -ATPase reveals how the extracellular gate locks in the E2·2K state. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | FEBS Lett, Vol. 596, Issue 19, Page 2513-2524, Year 2022 |
| 掲載日 | 2022年7月6日 |
 著者 著者 | Ryuta Kanai / Flemming Cornelius / Bente Vilsen / Chikashi Toyoshima /   |
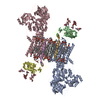
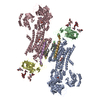
| PubMed 要旨 | Na ,K -ATPase (NKA) is one of the most important members of the P-type ion-translocating ATPases and plays a pivotal role in establishing electrochemical gradients for Na and K across the cell ...Na ,K -ATPase (NKA) is one of the most important members of the P-type ion-translocating ATPases and plays a pivotal role in establishing electrochemical gradients for Na and K across the cell membrane. Presented here is a 3.3 Å resolution structure of NKA in the E2·2K state solved by cryo-electron microscopy. It is a stable state with two occluded K after transferring three Na into the extracellular medium and releasing inorganic phosphate bound to the cytoplasmic P domain. We describe how the extracellular ion pathway wide open in the E2P state becomes closed and locked in E2·2K , linked to events at the phosphorylation site more than 50 Å away. We also show, although at low resolution, how ATP binding to NKA in E2·2K relaxes the gating machinery and thereby accelerates the transition into the next step, that is, the release of K into the cytoplasm, more than 100 times. |
 リンク リンク |  FEBS Lett / FEBS Lett /  PubMed:35747985 PubMed:35747985 |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.3 - 7.2 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-33601, PDB-7y45: EMDB-33602, PDB-7y46: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-K:  ChemComp-CLR:  ChemComp-PCW:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-ATP: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Na+ / K+-ATPase / ion transport / TRANSPORT PROTEIN |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について





 squalus acanthias (アブラツノザメ)
squalus acanthias (アブラツノザメ)