+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | TFG clusters COPII-coated transport carriers and promotes early secretory pathway organization. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | EMBO J, Vol. 34, Issue 6, Page 811-827, Year 2015 |
| 掲載日 | 2015年3月12日 |
 著者 著者 | Adam Johnson / Nilakshee Bhattacharya / Michael Hanna / Janice G Pennington / Amber L Schuh / Lei Wang / Marisa S Otegui / Scott M Stagg / Anjon Audhya /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | In mammalian cells, cargo-laden secretory vesicles leave the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) en route to ER-Golgi intermediate compartments (ERGIC) in a manner dependent on the COPII coat complex. We ...In mammalian cells, cargo-laden secretory vesicles leave the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) en route to ER-Golgi intermediate compartments (ERGIC) in a manner dependent on the COPII coat complex. We report here that COPII-coated transport carriers traverse a submicron, TFG (Trk-fused gene)-enriched zone at the ER/ERGIC interface. The architecture of TFG complexes as determined by three-dimensional electron microscopy reveals the formation of flexible, octameric cup-like structures, which are able to self-associate to generate larger polymers in vitro. In cells, loss of TFG function dramatically slows protein export from the ER and results in the accumulation of COPII-coated carriers throughout the cytoplasm. Additionally, the tight association between ER and ERGIC membranes is lost in the absence of TFG. We propose that TFG functions at the ER/ERGIC interface to locally concentrate COPII-coated transport carriers and link exit sites on the ER to ERGIC membranes. Our findings provide a new mechanism by which COPII-coated carriers are retained near their site of formation to facilitate rapid fusion with neighboring ERGIC membranes upon uncoating, thereby promoting interorganellar cargo transport. |
 リンク リンク |  EMBO J / EMBO J /  PubMed:25586378 / PubMed:25586378 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 30.0 Å |
| 構造データ |  EMDB-6075: 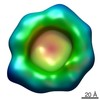 EMDB-6076: |
| 由来 |
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について




 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)