+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structural insights into double-stranded RNA recognition and transport by SID-1. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nat Struct Mol Biol, Vol. 31, Issue 7, Page 1095-1104, Year 2024 |
| 掲載日 | 2024年4月25日 |
 著者 著者 | Jiangtao Zhang / Chunhua Zhan / Junping Fan / Dian Wu / Ruixue Zhang / Di Wu / Xinyao Chen / Ying Lu / Ming Li / Min Lin / Jianke Gong / Daohua Jiang /  |
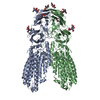
| PubMed 要旨 | RNA uptake by cells is critical for RNA-mediated gene interference (RNAi) and RNA-based therapeutics. In Caenorhabditis elegans, RNAi is systemic as a result of SID-1-mediated double-stranded RNA ...RNA uptake by cells is critical for RNA-mediated gene interference (RNAi) and RNA-based therapeutics. In Caenorhabditis elegans, RNAi is systemic as a result of SID-1-mediated double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) across cells. Despite the functional importance, the underlying mechanisms of dsRNA internalization by SID-1 remain elusive. Here we describe cryogenic electron microscopy structures of SID-1, SID-1-dsRNA complex and human SID-1 homologs SIDT1 and SIDT2, elucidating the structural basis of dsRNA recognition and import by SID-1. The homodimeric SID-1 homologs share conserved architecture, but only SID-1 possesses the molecular determinants within its extracellular domains for distinguishing dsRNA from single-stranded RNA and DNA. We show that the removal of the long intracellular loop between transmembrane helix 1 and 2 attenuates dsRNA uptake and systemic RNAi in vivo, suggesting a possible endocytic mechanism of SID-1-mediated dsRNA internalization. Our study provides mechanistic insights into dsRNA internalization by SID-1, which may facilitate the development of dsRNA applications based on SID-1. |
 リンク リンク |  Nat Struct Mol Biol / Nat Struct Mol Biol /  PubMed:38664565 PubMed:38664565 |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 2.77 - 3.71 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-34825, PDB-8hip: EMDB-34850, PDB-8hke: EMDB-36008, PDB-8j6m: EMDB-36009, PDB-8j6o: |
| 化合物 | 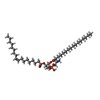 ChemComp-6OU:  ChemComp-ZN:  ChemComp-CLR:  ChemComp-NA: 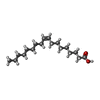 ChemComp-OLA:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-NAG: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | RNA BINDING PROTEIN / dsRNA transporter / TRANSCRIPTION / transport T1 / TRANSPORT PROTEIN / transport T2 |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について









 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト)
