+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structure of ribosome-bound azole-modified peptide phazolicin rationalizes its species-specific mode of bacterial translation inhibition. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nat Commun, Vol. 10, Issue 1, Page 4563, Year 2019 |
| 掲載日 | 2019年10月8日 |
 著者 著者 | Dmitrii Y Travin / Zoe L Watson / Mikhail Metelev / Fred R Ward / Ilya A Osterman / Irina M Khven / Nelli F Khabibullina / Marina Serebryakova / Peter Mergaert / Yury S Polikanov / Jamie H D Cate / Konstantin Severinov /     |
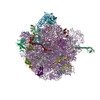
| PubMed 要旨 | Ribosome-synthesized post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs) represent a rapidly expanding class of natural products with various biological activities. Linear azol(in)e-containing peptides ...Ribosome-synthesized post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs) represent a rapidly expanding class of natural products with various biological activities. Linear azol(in)e-containing peptides (LAPs) comprise a subclass of RiPPs that display outstanding diversity of mechanisms of action while sharing common structural features. Here, we report the discovery of a new LAP biosynthetic gene cluster in the genome of Rhizobium Pop5, which encodes the precursor peptide and modification machinery of phazolicin (PHZ) - an extensively modified peptide exhibiting narrow-spectrum antibacterial activity against some symbiotic bacteria of leguminous plants. The cryo-EM structure of the Escherichia coli 70S-PHZ complex reveals that the drug interacts with the 23S rRNA and uL4/uL22 proteins and obstructs ribosomal exit tunnel in a way that is distinct from other compounds. We show that the uL4 loop sequence determines the species-specificity of antibiotic action. PHZ expands the known diversity of LAPs and may be used in the future as biocontrol agent for agricultural needs. |
 リンク リンク |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:31594941 / PubMed:31594941 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 2.87 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-20638, PDB-6u48: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | RIBOSOME/INHIBITOR / ribosome / phazolicin / antimicrobial protein / RIBOSOME-INHIBITOR complex |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について