+Search query
-Structure paper
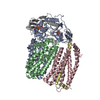
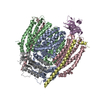
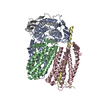
| Title | Architecture of the Heme-translocating CcmABCD/E complex required for Cytochrome c maturation. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 14, Issue 1, Page 5190, Year 2023 |
| Publish date | Aug 25, 2023 |
 Authors Authors | Lorena Ilcu / Lukas Denkhaus / Anton Brausemann / Lin Zhang / Oliver Einsle /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Mono- and multiheme cytochromes c are post-translationally matured by the covalent attachment of heme. For this, Escherichia coli employs the most complex type of maturation machineries, the Ccm- ...Mono- and multiheme cytochromes c are post-translationally matured by the covalent attachment of heme. For this, Escherichia coli employs the most complex type of maturation machineries, the Ccm-system (for cytochrome c maturation). It consists of two membrane protein complexes, one of which shuttles heme across the membrane to a mobile chaperone that then delivers the cofactor to the second complex, an apoprotein:heme lyase, for covalent attachment. Here we report cryo-electron microscopic structures of the heme translocation complex CcmABCD from E. coli, alone and bound to the heme chaperone CcmE. CcmABCD forms a heterooctameric complex centered around the ABC transporter CcmAB that does not by itself transport heme. Our data suggest that the complex flops a heme group from the inner to the outer leaflet at its CcmBC interfaces, driven by ATP hydrolysis at CcmA. A conserved heme-handling motif (WxWD) at the periplasmic side of CcmC rotates the heme by 90° for covalent attachment to the heme chaperone CcmE that we find interacting exclusively with the CcmB subunit. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:37626034 / PubMed:37626034 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.47 - 3.94 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-16597, PDB-8ce1: EMDB-16599, PDB-8ce5: EMDB-16601, PDB-8ce8: EMDB-16602, PDB-8cea: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ATP: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Cytochrome c maturation |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers