+Search query
-Structure paper
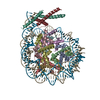
| Title | Basic helix-loop-helix pioneer factors interact with the histone octamer to invade nucleosomes and generate nucleosome-depleted regions. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Mol Cell, Vol. 83, Issue 8, Page 1251-11263.e6, Year 2023 |
| Publish date | Apr 20, 2023 |
 Authors Authors | Benjamin T Donovan / Hengye Chen / Priit Eek / Zhiyuan Meng / Caroline Jipa / Song Tan / Lu Bai / Michael G Poirier /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Nucleosomes drastically limit transcription factor (TF) occupancy, while pioneer transcription factors (PFs) somehow circumvent this nucleosome barrier. In this study, we compare nucleosome binding ...Nucleosomes drastically limit transcription factor (TF) occupancy, while pioneer transcription factors (PFs) somehow circumvent this nucleosome barrier. In this study, we compare nucleosome binding of two conserved S. cerevisiae basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) TFs, Cbf1 and Pho4. A cryo-EM structure of Cbf1 in complex with the nucleosome reveals that the Cbf1 HLH region can electrostatically interact with exposed histone residues within a partially unwrapped nucleosome. Single-molecule fluorescence studies show that the Cbf1 HLH region facilitates efficient nucleosome invasion by slowing its dissociation rate relative to DNA through interactions with histones, whereas the Pho4 HLH region does not. In vivo studies show that this enhanced binding provided by the Cbf1 HLH region enables nucleosome invasion and ensuing repositioning. These structural, single-molecule, and in vivo studies reveal the mechanistic basis of dissociation rate compensation by PFs and how this translates to facilitating chromatin opening inside cells. |
 External links External links |  Mol Cell / Mol Cell /  PubMed:36996811 / PubMed:36996811 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.2 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-25406, PDB-7ssa: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION / Transcription factor / basic helix-loop-helix / complex |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers