+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Origin and arrangement of actin filaments for gliding motility in apicomplexan parasites revealed by cryo-electron tomography. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 14, Issue 1, Page 4800, Year 2023 |
| Publish date | Aug 9, 2023 |
 Authors Authors | Matthew Martinez / Shrawan Kumar Mageswaran / Amandine Guérin / William David Chen / Cameron Parker Thompson / Sabine Chavin / Dominique Soldati-Favre / Boris Striepen / Yi-Wei Chang /   |
| PubMed Abstract | The phylum Apicomplexa comprises important eukaryotic parasites that invade host tissues and cells using a unique mechanism of gliding motility. Gliding is powered by actomyosin motors that ...The phylum Apicomplexa comprises important eukaryotic parasites that invade host tissues and cells using a unique mechanism of gliding motility. Gliding is powered by actomyosin motors that translocate host-attached surface adhesins along the parasite cell body. Actin filaments (F-actin) generated by Formin1 play a central role in this critical parasitic activity. However, their subcellular origin, path and ultrastructural arrangement are poorly understood. Here we used cryo-electron tomography to image motile Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites and reveal the cellular architecture of F-actin at nanometer-scale resolution. We demonstrate that F-actin nucleates at the apically positioned preconoidal rings and is channeled into the pellicular space between the parasite plasma membrane and the inner membrane complex in a conoid extrusion-dependent manner. Within the pellicular space, filaments on the inner membrane complex surface appear to guide the apico-basal flux of F-actin. F-actin concordantly accumulates at the basal end of the parasite. Finally, analyzing a Formin1-depleted Toxoplasma gondii mutant pinpoints the upper preconoidal ring as the conserved nucleation hub for F-actin in Cryptosporidium and Toxoplasma. Together, we provide an ultrastructural model for the life cycle of F-actin for apicomplexan gliding motility. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:37558667 / PubMed:37558667 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (tomography) / EM (subtomogram averaging) |
| Resolution | 30.0 - 65.0 Å |
| Structure data |  EMDB-29753: Tomogram of an apical end of a Toxoplasma Gondii tachyzoite displaying an extruded conoid 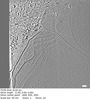 EMDB-29754: Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoite apical end  EMDB-29755: Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoite basal end  EMDB-29784: Subtomogram average of the preconoidal rings from Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites  EMDB-29791: Refined subtomogram average of the top preconoidal ring from Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites  EMDB-29801: Refined subtomogram average of the bottom preconoidal ring from Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites  EMDB-29808: Subtomogram average of the IMC surface filaments, top view, from Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites  EMDB-29809: IMC surface filament, sawtooth conformation, from Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites  EMDB-29810: IMC surface filament, side view, from Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites  EMDB-29826: Upper preconoidal ring from Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites  EMDB-29827: Lower preconoidal ring of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites  EMDB-29832: Preconoidal rings of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites  EMDB-29835: Basal IMC pore of Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites  EMDB-29838: Preconoidal rings of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites with Formin1 conditionally depleted  EMDB-29839: Upper preconoidal ring of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites with Formin1 conditionally depleted  EMDB-29840: Lower preconoidal ring from Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites with Formin1 conditionally depleted |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




