+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Diverse roles of the metal binding domains and transport mechanism of copper transporting P-type ATPases. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 15, Issue 1, Page 2690, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Mar 27, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Zongxin Guo / Fredrik Orädd / Viktoria Bågenholm / Christina Grønberg / Jian Feng Ma / Peter Ott / Yong Wang / Magnus Andersson / Per Amstrup Pedersen / Kaituo Wang / Pontus Gourdon /     |
| PubMed Abstract | Copper transporting P-type (P-) ATPases are essential for cellular homeostasis. Nonetheless, the E1-E1P-E2P-E2 states mechanism of P-ATPases remains poorly understood. In particular, the role of the ...Copper transporting P-type (P-) ATPases are essential for cellular homeostasis. Nonetheless, the E1-E1P-E2P-E2 states mechanism of P-ATPases remains poorly understood. In particular, the role of the intrinsic metal binding domains (MBDs) is enigmatic. Here, four cryo-EM structures and molecular dynamics simulations of a P-ATPase are combined to reveal that in many eukaryotes the MBD immediately prior to the ATPase core, MBD, serves a structural role, remodeling the ion-uptake region. In contrast, the MBD prior to MBD, MBD, likely assists in copper delivery to the ATPase core. Invariant Tyr, Asn and Ser residues in the transmembrane domain assist in positioning sulfur-providing copper-binding amino acids, allowing for copper uptake, binding and release. As such, our findings unify previously conflicting data on the transport and regulation of P-ATPases. The results are critical for a fundamental understanding of cellular copper homeostasis and for comprehension of the molecular bases of P-disorders and ongoing clinical trials. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:38538615 / PubMed:38538615 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.2 - 3.68 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-18202, PDB-8q73: EMDB-18203, PDB-8q74: EMDB-18204, PDB-8q75: EMDB-18205, PDB-8q76: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-CU: 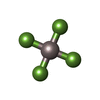 ChemComp-ALF:  ChemComp-MG: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / P-ATPase |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers