+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural transitions in influenza haemagglutinin at membrane fusion pH. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 583, Issue 7814, Page 150-153, Year 2020 |
| Publish date | May 27, 2020 |
 Authors Authors | Donald J Benton / Steven J Gamblin / Peter B Rosenthal / John J Skehel /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Infection by enveloped viruses involves fusion of their lipid envelopes with cellular membranes to release the viral genome into cells. For HIV, Ebola, influenza and numerous other viruses, envelope ...Infection by enveloped viruses involves fusion of their lipid envelopes with cellular membranes to release the viral genome into cells. For HIV, Ebola, influenza and numerous other viruses, envelope glycoproteins bind the infecting virion to cell-surface receptors and mediate membrane fusion. In the case of influenza, the receptor-binding glycoprotein is the haemagglutinin (HA), and following receptor-mediated uptake of the bound virus by endocytosis, it is the HA that mediates fusion of the virus envelope with the membrane of the endosome. Each subunit of the trimeric HA consists of two disulfide-linked polypeptides, HA1 and HA2. The larger, virus-membrane-distal, HA1 mediates receptor binding; the smaller, membrane-proximal, HA2 anchors HA in the envelope and contains the fusion peptide, a region that is directly involved in membrane interaction. The low pH of endosomes activates fusion by facilitating irreversible conformational changes in the glycoprotein. The structures of the initial HA at neutral pH and the final HA at fusion pH have been investigated by electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography. Here, to further study the process of fusion, we incubate HA for different times at pH 5.0 and directly image structural changes using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. We describe three distinct, previously undescribed forms of HA, most notably a 150 Å-long triple-helical coil of HA2, which may bridge between the viral and endosomal membranes. Comparison of these structures reveals concerted conformational rearrangements through which the HA mediates membrane fusion. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:32461688 / PubMed:32461688 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.0 - 9.9 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-10696, PDB-6y5g: EMDB-10697, PDB-6y5h: EMDB-10698, PDB-6y5i: EMDB-10699, PDB-6y5j: EMDB-10700, PDB-6y5k: EMDB-10701, PDB-6y5l: 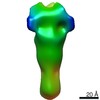 EMDB-10702: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-NAG: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / Haemagglutinin / Hemagglutinin / Fusion protein |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



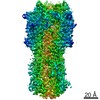
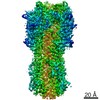



 unidentified influenza virus
unidentified influenza virus