+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Visualizing maturation factor extraction from the nascent ribosome by the AAA-ATPase Drg1. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nat Struct Mol Biol, Vol. 29, Issue 9, Page 942-953, Year 2022 |
| 掲載日 | 2022年9月12日 |
 著者 著者 | Michael Prattes / Irina Grishkovskaya / Victor-Valentin Hodirnau / Christina Hetzmannseder / Gertrude Zisser / Carolin Sailer / Vasileios Kargas / Mathias Loibl / Magdalena Gerhalter / Lisa Kofler / Alan J Warren / Florian Stengel / David Haselbach / Helmut Bergler /    |
| PubMed 要旨 | The AAA-ATPase Drg1 is a key factor in eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis that initiates cytoplasmic maturation of the large ribosomal subunit. Drg1 releases the shuttling maturation factor Rlp24 from ...The AAA-ATPase Drg1 is a key factor in eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis that initiates cytoplasmic maturation of the large ribosomal subunit. Drg1 releases the shuttling maturation factor Rlp24 from pre-60S particles shortly after nuclear export, a strict requirement for downstream maturation. The molecular mechanism of release remained elusive. Here, we report a series of cryo-EM structures that captured the extraction of Rlp24 from pre-60S particles by Saccharomyces cerevisiae Drg1. These structures reveal that Arx1 and the eukaryote-specific rRNA expansion segment ES27 form a joint docking platform that positions Drg1 for efficient extraction of Rlp24 from the pre-ribosome. The tips of the Drg1 N domains thereby guide the Rlp24 C terminus into the central pore of the Drg1 hexamer, enabling extraction by a hand-over-hand translocation mechanism. Our results uncover substrate recognition and processing by Drg1 step by step and provide a comprehensive mechanistic picture of the conserved modus operandi of AAA-ATPases. |
 リンク リンク |  Nat Struct Mol Biol / Nat Struct Mol Biol /  PubMed:36097293 / PubMed:36097293 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.2 - 3.8 Å |
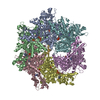
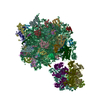
| 構造データ | EMDB-14437, PDB-7z11: EMDB-14471: Structure of pre-60S particle bound to DRG1(AFG2) |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-AGS:  ChemComp-MG: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | CHAPERONE / Ribosome biogenesis / AAA-ATPases / substrate recognition / single particle cryo-EM / RIBOSOME / large ribosomal subunit / substrate translocation mechanism |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について