+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | An antibody from single human V-rearranging mouse neutralizes all SARS-CoV-2 variants through BA.5 by inhibiting membrane fusion. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Sci Immunol, Vol. 7, Issue 76, Page eadd5446, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Oct 28, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Sai Luo / Jun Zhang / Alex J B Kreutzberger / Amanda Eaton / Robert J Edwards / Changbin Jing / Hai-Qiang Dai / Gregory D Sempowski / Kenneth Cronin / Robert Parks / Adam Yongxin Ye / Katayoun Mansouri / Maggie Barr / Novalia Pishesha / Aimee Chapdelaine Williams / Lucas Vieira Francisco / Anand Saminathan / Hanqin Peng / Himanshu Batra / Lorenza Bellusci / Surender Khurana / S Munir Alam / David C Montefiori / Kevin O Saunders / Ming Tian / Hidde Ploegh / Tom Kirchhausen / Bing Chen / Barton F Haynes / Frederick W Alt /  |
| PubMed Abstract | SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants have generated a worldwide health crisis due to resistance to most approved SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies and evasion of vaccination-induced antibodies. To manage ...SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants have generated a worldwide health crisis due to resistance to most approved SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies and evasion of vaccination-induced antibodies. To manage Omicron subvariants and prepare for new ones, additional means of isolating broad and potent humanized SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies are desirable. Here, we describe a mouse model in which the primary B cell receptor (BCR) repertoire is generated solely through V(D)J recombination of a human V1-2 heavy chain (HC) and, substantially, a human Vκ1-33 light chain (LC). Thus, primary humanized BCR repertoire diversity in these mice derives from immensely diverse HC and LC antigen-contact CDR3 sequences generated by nontemplated junctional modifications during V(D)J recombination. Immunizing this mouse model with SARS-CoV-2 (Wuhan-Hu-1) spike protein immunogens elicited several V1-2/Vκ1-33-based neutralizing antibodies that bound RBD in a different mode from each other and from those of many prior patient-derived V1-2-based neutralizing antibodies. Of these, SP1-77 potently and broadly neutralized all SARS-CoV-2 variants through BA.5. Cryo-EM studies revealed that SP1-77 bound RBD away from the receptor-binding motif via a CDR3-dominated recognition mode. Lattice light-sheet microscopy-based studies showed that SP1-77 did not block ACE2-mediated viral attachment or endocytosis but rather blocked viral-host membrane fusion. The broad and potent SP1-77 neutralization activity and nontraditional mechanism of action suggest that it might have therapeutic potential. Likewise, the SP1-77 binding epitope may inform vaccine strategies. Last, the type of humanized mouse models that we have described may contribute to identifying therapeutic antibodies against future SARS-CoV-2 variants and other pathogens. |
 External links External links |  Sci Immunol / Sci Immunol /  PubMed:35951767 / PubMed:35951767 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.7 - 15.0 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-26676, PDB-7upw: EMDB-26677, PDB-7upx: EMDB-26678, PDB-7upy:  EMDB-27043: Negative stain electron microscopy single particle reconstruction of monoclonal antibody SP1-77 Fab in complex with SARS-CoV2 2P spike  EMDB-27044: Negative stain electron microscopy single particle reconstruction of monoclonal antibody VHH7-7-53 Fab in complex with SARS-CoV2 2P spike 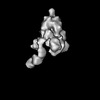 EMDB-27046: Negative stain electron microscopy single particle reconstruction of monoclonal antibody VHH7-5-82 Fab in complex with SARS-CoV2 2P spike |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-NAG: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers








 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)
