+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Emerging enterococcus pore-forming toxins with MHC/HLA-I as receptors. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Cell, Vol. 185, Issue 7, Page 1157-1171.e22, Year 2022 |
| 掲載日 | 2022年3月31日 |
 著者 著者 | Xiaozhe Xiong / Songhai Tian / Pan Yang / Francois Lebreton / Huan Bao / Kuanwei Sheng / Linxiang Yin / Pengsheng Chen / Jie Zhang / Wanshu Qi / Jianbin Ruan / Hao Wu / Hong Chen / David T Breault / Hao Wu / Ashlee M Earl / Michael S Gilmore / Jonathan Abraham / Min Dong /  |
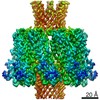
| PubMed 要旨 | Enterococci are a part of human microbiota and a leading cause of multidrug resistant infections. Here, we identify a family of Enterococcus pore-forming toxins (Epxs) in E. faecalis, E. faecium, ...Enterococci are a part of human microbiota and a leading cause of multidrug resistant infections. Here, we identify a family of Enterococcus pore-forming toxins (Epxs) in E. faecalis, E. faecium, and E. hirae strains isolated across the globe. Structural studies reveal that Epxs form a branch of β-barrel pore-forming toxins with a β-barrel protrusion (designated the top domain) sitting atop the cap domain. Through a genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screen, we identify human leukocyte antigen class I (HLA-I) complex as a receptor for two members (Epx2 and Epx3), which preferentially recognize human HLA-I and homologous MHC-I of equine, bovine, and porcine, but not murine, origin. Interferon exposure, which stimulates MHC-I expression, sensitizes human cells and intestinal organoids to Epx2 and Epx3 toxicity. Co-culture with Epx2-harboring E. faecium damages human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and intestinal organoids, and this toxicity is neutralized by an Epx2 antibody, demonstrating the toxin-mediated virulence of Epx-carrying Enterococcus. |
 リンク リンク |  Cell / Cell /  PubMed:35259335 / PubMed:35259335 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) / X線回折 |
| 解像度 | 2.87 - 3 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-25673, PDB-7t4e:  PDB-7t4d: |
| 化合物 | 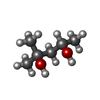 ChemComp-MPD: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | TOXIN / pore-forming toxin |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について