+Search query
-Structure paper
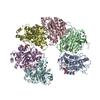
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of transcription termination factor Rho from Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals bicyclomycin resistance mechanism. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Commun Biol, Vol. 5, Issue 1, Page 120, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Feb 9, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Emmanuel Saridakis / Rishi Vishwakarma / Josephine Lai-Kee-Him / Kevin Martin / Isabelle Simon / Martin Cohen-Gonsaud / Franck Coste / Patrick Bron / Emmanuel Margeat / Marc Boudvillain /    |
| PubMed Abstract | The bacterial Rho factor is a ring-shaped motor triggering genome-wide transcription termination and R-loop dissociation. Rho is essential in many species, including in Mycobacterium tuberculosis ...The bacterial Rho factor is a ring-shaped motor triggering genome-wide transcription termination and R-loop dissociation. Rho is essential in many species, including in Mycobacterium tuberculosis where rho gene inactivation leads to rapid death. Yet, the M. tuberculosis Rho [Rho] factor displays poor NTPase and helicase activities, and resistance to the natural Rho inhibitor bicyclomycin [BCM] that remain unexplained. To address these issues, we solved the cryo-EM structure of Rho at 3.3 Å resolution. The Rho hexamer is poised into a pre-catalytic, open-ring state wherein specific contacts stabilize ATP in intersubunit ATPase pockets, thereby explaining the cofactor preference of Rho. We reveal a leucine-to-methionine substitution that creates a steric bulk in BCM binding cavities near the positions of ATP γ-phosphates, and confers resistance to BCM at the expense of motor efficiency. Our work contributes to explain the unusual features of Rho and provides a framework for future antibiotic development. |
 External links External links |  Commun Biol / Commun Biol /  PubMed:35140348 / PubMed:35140348 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.32 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-12701: CryoEM structure of the transcription termination factor Rho from Mycrobacterium Tuberculosis |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ATP:  ChemComp-MG: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / transcription termination factor / RNA helicase / ATP-dependent / molecular motor |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers